Abstract
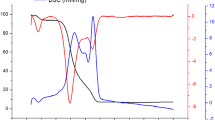
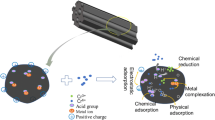
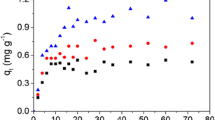
The adsorption characteristics of Arundo donax L.(AD) biochars for ammonium(NH4 +-N) were investigated. Absorbents were characterized through scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analyses. AD-500 and AD-800 were produced from raw AD and pyrolyzed from room temperature to 500 and 800 °C, respectively. PD-500 was prepared by impregnating AD with a mild alkali solution and pyrolyzing from room temperature to 500 °C. The feasibility of the use of AD-500, AD-800, and PD-500 removing NH4 +-N from an aqueous solution was examined. The adsorption system followed the pseudo-first-order model. Results showed that the adsorption capacities of AD-biochars for NH4 +-N were enhanced after the final pyrolysis; temperature was increased or the mild alkali pretreatment was administered. When the initial NH4 +-N concentration was changed from 4 to 8 mM, the NH4 +-N sorption capacity of the biochar increased from 23 to 51%, with the final pyrolysis temperature increasing from 500 to 800 °C. The improved ratios were 12 to 33% when the biochar was prepared at 500 °C after the mild alkali pretreatment, and NH4 +-N sorption was enhanced due to ion exchange in the PD biochar.

Biochars derived from giant reed (Arundo donax L.) with different treatment :characterization and ammonium adsorption potential.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Arundo donax L.
- AD-RT:
-
raw Arundo donax L. straw
- AD-biochars:
-
AD-500, AD-800, and PD-500
- PD-RT:
-
Pretreated Arundo donax L. straw
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- SA:
-
Surface area
References
Amin NK (2008) Removal of reactive dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbons prepared from sugarcane bagasse pith. Desalination 223:152–161
Cao X, Ma L, Gao B, Harris W (2009) Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environ Sci Technol 43:3285–3291
Chen B, Chen Z (2009) Uptake of naphthalene and 1-naphthol by biochars of orange peels with different pyrolytic temperatures. Chemosphere 76:127–133
Chen B, Zhou D, Zhu L (2008) Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environ Sci Technol 42:5137–5143
Chen H, Chen D, Hong L (2015) Influences of activation agent impregnated sewage sludge pyrolysis on emission characteristics of volatile combustion and De-NOx performance of activated char. Appl Energy 156:767–775
Erdoğan BC, Ülkü S (2011) Ammonium uptake by Gördes clinoptilolite rich mineral specimen. Appl Clay Sci 54:217–225
Evans M, Halliop E, MacDonald J (1999) The production of chemically-activated carbon. Carbon 37:269–274
Girgis BS, Yunis SS, Soliman AM (2002) Characteristics of activated carbon from peanut hulls in relation to conditions of preparation. Materials Letters 57:164–172
Huang L, Gao X, Liu M, Du G, Guo J, Ntakirutimana T (2012) Correlation among soil microorganisms, soil enzyme activities, and removal rates of pollutants in three constructed wetlands purifying micro-polluted river water. Ecological Eng 46:98–106
Huang L, Lu Y, Gao X, Du G, Ma X, Liu M, Guo J, Chen Y (2013) Ammonium-induced oxidative stress on plant growth and antioxidative response of duckweed (Lemna minor L.) Ecological Eng 58:355–362
Huang L, Chen YC, Liu G, Li SN, Liu Y, Xu G (2015) Non-isothermal pyrolysis characteristics of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy 87:31–40
Illán-Gómez M, Garcia-Garcia A, Salinas-Martinez de Lecea C, Linares-Solano A (1996) Activated carbons from Spanish coals. 2. Chemical activation. Energy Fuels 10:1108–1114
Kalavathy MH, Karthikeyan T, Rajgopal S, Miranda LR (2005) Kinetic and isotherm studies of Cu (II) adsorption onto H3 PO4-activated rubber wood sawdust. J Colloid Interface Sci 292:354–362
Kasozi GN, Zimmerman AR, Nkedi-Kizza P, Gao B (2010) Catechol and humic acid uptake onto a range of laboratory-produced black carbons (biochars). Environ Sci Technol 44:6189–6195
Lehmann J, Gaunt J, Rondon M (2006) Bio-char sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems–a review. Mitigation Adaptation Strategies Global Change 11:395–419
Lim W, Srinivasakannan C, Balasubramanian N (2010) Activation of palm shells by phosphoric acid impregnation for high yielding activated carbon. J Analytical App Pyrolysis 88:181–186
Ma H, Liu WW, Chen X, Wu YJ, Yu ZL (2009) Enhanced enzymatic saccharification of rice straw by microwave pretreatment. Bioresource Technol 100:1279–1284
Marris E (2006) Putting the carbon back: Black is the new green. Nature 442:624–626
Mochizuki T, Kubota M, Matsuda H, Camacho LFE (2016) Adsorption behaviors of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide on activated carbon prepared from petroleum coke by KOH chemical activation. Fuel Processing Technol 144:164–169
Özer A, Akkaya G, Turabik M (2006) The removal of acid red 274 from wastewater: Combined biosorption and biocoagulation with< i> Spirogyra rhizopus</i>. Dyes and pigments 71, 83–89
Patnukao P, Pavasant P (2008) Activated carbon from Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehn bark using phosphoric acid activation. Bioresource Technol 99:8540–8543
Peng P, Lang Y-H, Wang X-M (2016) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of pentachlorophenol on reed biochars: pH effect, pyrolysis temperature, hydrochloric acid treatment and isotherms. Ecological Eng 90:225–233
Pezoti O, Cazetta AL, Bedin KC, Souza LS, Martins AC, Silva TL, Júnior OOS, Visentainer JV, Almeida VC (2016) NaOH-activated carbon of high surface area produced from guava seeds as a high-efficiency adsorbent for amoxicillin removal: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 288:778–788
Pezoti O, Cazetta AL, Souza IP, Bedin KC, Martins AC, Silva TL, Almeida VC (2014) Adsorption studies of methylene blue onto ZnCl 2-activated carbon produced from buriti shells (Mauritia flexuosa L.) J Industrial Eng Chem 20:4401–4407
Roberts KG, Gloy BA, Joseph S, Scott NR, Lehmann J (2009) Life cycle assessment of biochar systems: estimating the energetic, economic, and climate change potential. Environ Sci Technol 44:827–833
Uchimiya M, Lima IM, Klasson KT, Wartelle LH (2010a) Contaminant immobilization and nutrient release by biochar soil amendment: roles of natural organic matter. Chemosphere 80:935–940
Uchimiya M, Lima IM, Thomas Klasson K, Chang S, Wartelle LH, Rodgers JE (2010b) Immobilization of heavy metal ions (CuII, CdII, NiII, and PbII) by broiler litter-derived biochars in water and soil. J Agricultural Food Chemistry 58:5538–5544
Yang R, Liu G, Xu X, Li M, Zhang J, Hao X (2011) Surface texture, chemistry and adsorption properties of acid blue 9 of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) bast-based activated carbon fibers prepared by phosphoric acid activation. Biomass Bioenergy 35:437–445
Yao Y, Gao B, Inyang M, Zimmerman AR, Cao X, Pullammanappallil P, Yang L (2011) Biochar derived from anaerobically digested sugar beet tailings: characterization and phosphate removal potential. Bioresource Technol 102:6273–6278
Zhu G-z, Deng X-l, Hou M, Sun K, Y-p Z, Li P, Liang F-m (2016) Comparative study on characterization and adsorption properties of activated carbons by phosphoric acid activation from corncob and its acid and alkaline hydrolysis residues. Fuel Processing Technol 144:255–261
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of PR China (NO. 51408493) and Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Southwest University (NO. SWU114013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Highlight
• Biochars were produced from raw and pretreated Arundo donax L.
• An increase in pyrolysis temperature promoted the NH4 +-N removal.
• The mild alkali (H2O2 + NaOH) pretreatment benefited for NH4 +-N removal.
• NH4 +-N sorption enhanced due to ion exchange in the pretreated AD biochar.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Huang, L. & Chen, Y. Biochars derived from giant reed (Arundo donax L.) with different treatment: characterization and ammonium adsorption potential. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 25889–25898 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0110-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0110-3