Abstract
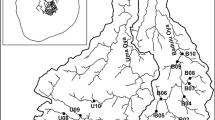
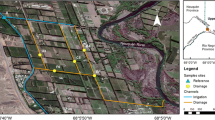
The River Madre de Dios (RMD) and its lagoon is a biodiversity rich watershed formed by a system of streams, rivers, channels, and a coastal lagoon communicating with the Caribbean Sea. This basin sustains a large area of agricultural activity (mostly banana, rice, and pineapple) with intensive use of pesticides, continually detected in water samples. We investigated in situ the toxicological effects caused by pesticide runoff from agriculture and the relation of pesticide concentrations with different biological organization levels: early responses in fish biomarkers (sub-organismal), acute toxicity to Daphnia magna (organismal), and aquatic macroinvertebrate community structure. The evaluation was carried out between October 2011 and November 2012 at five sites along the RMD influenced by agricultural discharges and a reference site in a stream outside the RMD that receives less pesticides. Acute toxicity to D. magna was observed only once in a sample from the RMD (Caño Azul); the index of biomarker responses in fish exposed in situ was higher than controls at the same site and at the RMD-Freeman. However, only macroinvertebrates were statistically related to the presence of pesticides, combined with both physical-chemical parameters and habitat degradation. All three groups of variables determined the distribution of macroinvertebrate taxa through the study sites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmayer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic, London, pp. 671–684
Ålander A (2006) Toxic effects of pesticide run-off from banana plantations on the Northern Atlantic Coast of Costa Rica. Minor field study, master thesis project. University of Stockholm, Sweden
APHA (American Public Health Association). 2005. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st Edition
Arias-Andrés MJ, Rämö R, Mena Torres F, Ugalde R, Grandas L, Ruepert C, Castillo LE, Van den Brink P, Gunnarsson JS (2016) TIER I toxicity assessment of agriculture pesticides detected on the Río Madre de Dios watershed, Costa Rica. (Environ Sci Pollut R)
Barata C, Damasio J, López MA, Kuster M, López de Alda M, Barceló D, Riva M, Raldúa D (2007) Combined use of biomarkers and in situ bioassays in Daphnia magna to monitor environmental hazards of pesticides in the field. Environ Toxicol Chem 26(2):370–379
Beketov MA, Liess M (2008) Potential of 11 pesticides to initiate downstream drift of stream macroinvertebrates. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55:247–253
Bereswill R, Streloke M, Schulz R (2013) Current-use pesticides in stream water and suspended particles following runoff: exposure, effects, and mitigation requirements. Environ Toxicol Chem 32(6):1254–1263
Bocquene G, Galgani F (1998) Biological effects of contaminants: cholinesterase inhibition by organophosphate and carbamate compounds. ICES Techniques in Marine Environmental Sciences 22
Bonada N, Prat N, Resh VH, Statzner B (2006) Developments in aquatic insect biomonitoring: a comparative analysis of recent approaches. Annu Rev Entomol 51:495–523
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dyebinding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bravo V, de la Cruz E, Herrera G, Ramírez F (2013) Agriculture pesticides use as tool for monitoring health hazards. Uniciencia 27(1):351–376
Capper N (2006) The effects of suspended sediment on the aquatic organisms Daphnia magna and Pimephales promela. Clemson University Theses. Master of Science, Environmental Toxicology, 52 p
Castillo LE, Martínez E, Ruepert C, Savage C, Gilek M, Pinnock M, Solis E (2006) Water quality and macroinvertebrate community response following pesticide applications in a banana plantation, Limon, Costa Rica. Sci Total Environ 367:418–432
Castillo LE, Ruepert C, Mena F, Echeverría-Sáenz S, Arias-Andrés M, Ramírez F, Moraga G, Vargas S, Ballestero D, Brenes C, Benavides R, Protti M, Bravo V, Gunnarsson JS (2016) The Laguna Madre de Dios, a Costa Rican tropical coastal lagoon ecosystem at risk. (Environ Sci Pollut R) (in this issue)
Castillo LE, Ruepert C, Solis E (2000) Pesticide residues in the aquatic environment of banana plantation areas in the North Atlantic Zone of Costa Rica. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:1942–1950
CGR (2013) (General Accounting Office of the Republic): Report on the effectiveness of the State to ensure the quality of water in its different uses. Operational and Evaluative Control Division. Area of Environmental and Energy Services. Report No. DEFOE-AE-IF-01, San José, Costa Rica.
Chapman D (1996) Water quality assessments: a guide to the use of biota, sediments and water in environmental monitoring. Second edition, E&FN Spon, London, UK, 626p
Colin N, Porte C, Fernandes D, Barata C, Padrós F, Carrassón M, Monroy M, Cano-Rocabayera O, de Sostoa A, Piña B, Maceda-Veiga A (2016) Ecological relevance of biomarkers in monitoring studies of macro-invertebrates and fish in Mediterranean rivers. Sci Total Environ 540:307–323
Correl DL (1998) The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: a review. J Environ Qual 27:261–266
Crane M, Burton GA, Culp JM, Greenberg MS, Munkittrick KR, Ribeiro R, Salazar MH, St-Jean SD (2007) Review of aquatic in situ approaches for stressor and effect diagnosis. Integr Environ Assess Manag 3(2):234–245
Daam MA, Satapornvanit K, Van den Brink PJ, Nogueira AJA (2009) Sensitivity of macroinvertebrates to carbendazim under semi-field conditions in Thailand: implications for the use of temperate toxicity data in a tropical risk assessment of fungicides. Chemosphere 74:1187–1194
De Zwart D (2002) Observed regularities in species sensitivity distributions for aquatic species. In: Posthuma L, Suter II GW, Traas TP (eds) Species sensitivity distributions in ecotoxicology. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp. 133–154
Devin S, Burgeot T, Giambérini L, Minguez L, Pain-Devin S (2014) The integrated biomarker response revisited: optimization to avoid misuse. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:2448–2454
Diepens NNJ, Pfennig S, Van den Brink PJ, Gunnarsson JS, Ruepert C, Castillo LE (2014) Effect of pesticides used in banana and pineapple plantations on aquatic ecosystems in Costa Rica. J Environ Biol 35:73–84
Dutka BJ (1989) Methods for toxicological analysis of waters, wastewaters and sediments. National Water Research Institute (NWRI), Environmental, Canada, Burlington Ontario
Echeverría-Sáenz S, Mena F, Pinnock M, Ruepert C, Solano C, de la Cruz E, Campos B, Sánchez-Avila J, Lacorte S, Barata C (2012) Environmental hazards of pesticides from pineapple crop production in the Río Jiménez watershed (Caribbean Coast, Costa Rica). Sci Total Environ 440:106–114
Ellman G, Courtney D, Andres V Jr, Featherstone R (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochemistry and Pharmacology 7:88–95
European Commission (2000) Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 December 2000 establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Off J Eur Union L 327
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hamed RR, Farid MN (2003) Glutathione related enzyme levels of freshwater fish as bioindicators of pollution. Environmentalist 23:313–322
Hernández-Romero AH, Tovilla-Hernández D, Malo EA, Bello-Mendoza R (2004) Water quality and presence of pesticides in a tropical coastal wetland in southern Mexico. Mar Pollut Bull 48:1130–1141
ICT (Costa Rican Institute of Tourism) (2016) Annual Statistical Inform (in Spanish). Available at: http://www.ict.go.cr/es/documentos-institucionales/estad%C3%ADsticas/informes-estad%C3%ADsticos/anuarios/2005-2015/685-anuario-de-turismo-2014/file.html (accessed March 2016)
Ippolito A, Kattwinkel M, Rasmussen JJ, Schäfer RB, Fornaroli R, Liess M (2015) Modeling global distribution of agricultural insecticides in surface waters. Environ Pollut 198:54–60
Jáimez-Cuéllar P, Vivas S, Bonada N, Robles S, Mellado A, Álvarez M, Alba-Tercedor J, Avilés J, Casas J, Ortega M, Pardo I, Prat N, Rieradevall M, Sáinz-Cantero C, Sánchez-Ortega A, Suárez ML, Toro M, Vidal-Abarca MR, Zamora-Muñóz C (2002) Protocolo Guadalmed (PRECE). Limnetica 21(3–4):187–204
Jarrad HE, Delaney KR, Kennedy CJ (2004) Impacts of carbamate pesticides on olfactory neurophysiology and cholinesterase activity in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquat Toxicol 69(2):133–148
Kirk KL, Gilbert JJ (1990) Suspended clay and the population dynamics of planktonic rotifers and cladocerans. Ecology 71(5):1741–1755
Kubrak OI, Atamaniuk TM, Husaka VV, Drohomyretska IZ, Storey JM, Storey KB, Lushchak VI (2012) Oxidative stress responses in blood and gills of Carassius auratus exposed to the mancozeb-containing carbamate fungicide Tattoo. Ecotox Environ Safe 85(1):37–43
Kuk-Dzul JG, Gold-Bouchot G, Ardisson P-L (2012) Benthic infauna variability in relation to environmental factors and organic pollutants in tropical coastal lagoons from the northern Yucatan Peninsula. Mar Pollut Bull 64:2725–2733
Levin LA, Ekau W, Gooday AJ, Jorissen F, Middelburg JJ, Naqvi SVA, Neira C, Rabalais NN, Zhang J (2009) Effects of natural and human-induced hypoxia on coastal benthos. Biogeosciences 6:2063–2098
Levine SN, Zehrer RF, Burns CW (2005) Impact of resuspended sediment on zooplankton feeding in Lake Waihola, New Zealand. Freshw Biol 50:1515–1536
Liess M, Beketov M (2011) Traits and stress: keys to identify community effects of low levels of toxicants in test systems. Ecotoxicology 20:1328–1340
Liess M, Von der Ohe PC (2005) Analyzing effects of pesticides on invertebrate communities in streams. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(4):954–965
Liess M, Schäfer RB, Schriever CA (2008) The footprint of pesticide stress in communities—species traits reveal community effects of toxicants. Sci Total Environ 406:484–490
Lorion CM, Kennedy BP (2009) Relationships between deforestation, riparian forest buffers and benthic macroinvertebrates in Neotropic headwater streams. Freshwat Biol 54:165–180
Maltby L, Brock TCM, Van Den Brink PJ (2009) Fungicide risk assessment for aquatic ecosystems: importance of interspecific variation, toxic mode of action and exposure regime. Environ Sci Technol 43:7556–7563
Martinez-Haro M, Beiras R, Bellas J, Capela R, Coelho JP, Lopes I, Moreira-Santos M, Reis-Henriques AM, Ribeiro R, Santos M, Marques JC (2015) A review on the ecological quality status assessment in aquatic systems using community based indicators and ecotoxicological tools: what might be the added value of their combination? Ecol Indic 48:8–16
McCabe GD, O’Brien WJ (1983) The effects of suspended silt on feeding and reproduction of Daphnia pulex. Am Midl Nat 110(2):324–337
Mena F, Azzopardi M, Pffenig S, Ruepert C, Tedengren M, Castillo LE, Gunnarsson JS (2014a) Use of cholinesterase activity as a biomarker of pesticide exposure used on Costa Rican banana plantations in the native tropical fish (Günther, 1860) Astyanax aeneus. J Environ Biol 35:35–42
Mena F, Fernández San Juan M, Campos B, Sánchez-Ávila J, Faria M, Pinnock M, de la Cruz E, Lacorte S, Soares AMVM, Barata C (2014b) Pesticide residue analyses and biomarker responses of native Costa Rican fish of the Poeciliidae and Cichlidae families to assess environmental impacts of pesticides in Palo Verde National Park. J Environ Biol 35:19–27
Merritt RW, Cummins KW, Berg MB (eds) (2008) An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America. 4th edition. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Co. 1158 p
MINAE-S (2007) Decree N° 33903 Reglamento para la Evaluación y Clasificación de la Calidad de Cuerpos de Agua Superficiales. La Gaceta N° 178, San José, Costa Rica
Mount DR, Mount DI (1992) A simple method of pH control for static and static-renewal aquatic toxicity tests. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:609–614
Newton A, Icely J, Cristina S, Brito A, Cardoso AC, Colijn F, Dalla-Rivera S, Gertz F, Hansen JW, Holmer M, Ivanova K, Leppäkoski E, Melaku-Canu D, Mocenni C, Mudge S, Murray N, Pejrup M, Razinkovas A, Reizopoulou S, Pérez-Ruzafa A, Schernewski G, Schubert H, Carr L, Solidoro C, Viaroli P (2013) An overview of ecological status, vulnerability and future perspectives of European large shallow, semi-enclosed coastal systems, lagoons and transitional waters. Estuar Coast Shelf S 140:95–122
Oakes FD, Van Der Kraak VD (2003) Utility of TBARS assay in detecting oxidative stress in white sucker (Catostomus commersoni) populations exposed to pulp mill effluent. Aquat Toxicol 63:447–463
OECD (2004) Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. acute immobilisation test, OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, Section 2, OECD
PAN (Pesticide Action Network) (2015b) PAN international list of highly hazardous pesticides (PAN List of HHPs) June 2015. http://www.pan-germany.org/download/PAN_HHP_List_150602_F.pdf). Accessed 15 January 2016
PAN (Pesticide Action Network): Pesticides Database (2015a). http://www.pesticideinfo.org/Search_Chemicals.jsp. Accessed 8 December 2015
Pennak RW (1978) Fresh-water invertebrates of the United States, 2nd edn. Wiley-InterScience, New York, p. 803
Pérez-Ruzafa A, Marcos C (2012) Fisheries in coastal lagoons: an assumed but poorly researched aspect of the ecology and functioning of coastal lagoons. Estuar Coast Shelf S 110:15–31
Peschke K, Geburzi J, Heinz-R K, Wurm K, Triebskorn R (2014) Invertebrates as indicators for chemical stress in sewage-influenced stream systems: toxic and endocrine effects in gammarids and reactions at the community level in two tributaries of Lake Constance, Schussen and Argen. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:115–125
Polidoro B, Morra MJ (2016) An ecological risk assessment of pesticides and fish kills in the Sixaola watershed, Costa Rica. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:5983–5991
Rämö RA, van den Brink PJ, Ruepert C, Castillo LE, Gunnarsson JS (2016) Toxicity risk assessment of pesticides from banana plantations in the River Madre de Dios, Costa Rica using PERPEST. SSD and msPAF models Environ Sci Pollut R DOI. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-7375-9
Rasmussen JJ, Monberg RJ, Baattrup-Pedersen A, Cedergreen N, Wiberg-Larsen P, Strobel B, Kronvang B (2012) Effects of a triazole fungicide and a pyrethroid insecticide on the decomposition of leaves in the presence or absence of macroinvertebrate shredders. Aquat Toxicol 118–119:54–61
Rico A, Van den Brink PJ (2015) Evaluating aquatic invertebrate vulnerability to insecticides based on intrinsic sensitivity, biological traits, and toxic mode of action. Environ Toxicol Chem 34(8):1907–1917
Sanchez W, Porcher JM (2009) Fish biomarkers for environmental monitoring within the Water Framework Directive of the European Union. TrAC 28(2):150–158
Sayeed I, Parvez S, Pandey S, Bin-Hafeez B, Haque R, Raisuddin S (2003) Oxidative stress biomarkers of exposure to deltamethrin in freshwater fish, Channa punctatus Bloch. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 56:295–301
Springer M, Ramírez A, Hanson P (2010) Macroinvertebrados de agua dulce de Costa Rica I. International Journal of Tropical biology and Conservation 58(4)
Ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2012): Canoco reference manual and user’s guide: software for ordination, version 5.0. Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, USA, 496 pp
US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (1982) Handbook for sampling and sample preservation of water and wastewater. EPA-600/4-82-029
US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (1989) Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater organisms. EPA-821-R-02-013
US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (2015). ECOTOX database. http://www.epa.gov/ecotox. Accessed 8 December 2015
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64(2):178–189
Van den Brink PJ, Hattink J, Bransen F, Van Donk E, Brock TCM (2000) Impact of the fungicide carbendazim in freshwater microcosms. II. Zooplankton, primary producers and final conclusions. Aquat Toxicol 48:251–264
Van den Brink PJ, Van den Brink NW, Ter Braak CJF (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecotoxicological data using ordination: demonstrations of utility on the basis of various examples. Aust J Ecotoxicol 9:141–156
van Wendel de Joode B, Mora AM, Córdoba L, Cano JC, Quesada R, Faniband M, Wesseling C, Ruepert C, Öberg M, Eskenazi B, Mergler D, Lindh CH (2014) Aerial application of mancozeb and urinary ethylene thiourea (ETU) concentrations among pregnant women in Costa Rica: the Infants’ Environmental Health Study (ISA). Environ Health Perspect 122(12):1321–1328
Vannote RL, Misnshall GW, Cummins KW, Senadell JR, Cushing CE (1980) The river continuum concept. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37:130–137
Vasseur P, Cossu-Leguille C (2003) Biomarkers and community indices as complementary tools for environmental safety. Environ Int 28:711–717
Wisconsin Department of Environmental Resources, WDNR (1991) Guidance manual for the certification and registration of laboratories conducting effluent toxicity test. WI DNR PUBL-TS-006 91
Yang W, Gan J, Hunter W, Spurlock F (2006) Effect of suspended solids on bioavailability of pyrethroid insecticides. Environ Toxicol Chem 25(6):1585–1591
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Julio Knight and his family for their valuable help during the sampling campaigns. We are grateful to the EARTH University for allowing us to take the water and biota samples inside of their campus. Also, we thank Geannina Moraga for the elaboration of Fig. 1. Jennifer Crowe and David Lean kindly revised the correct use of language. This study was funded by the Universidad Nacional de Costa Rica and the Swedish Research Council Formas, grant 205-473-3035-21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Echeverría-Sáenz, S., Mena, F., Arias-Andrés, M. et al. In situ toxicity and ecological risk assessment of agro-pesticide runoff in the Madre de Dios River in Costa Rica. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 13270–13282 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7817-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7817-4