Abstract
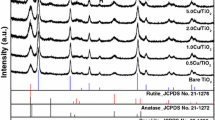
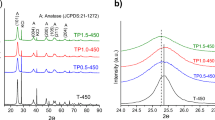
The rate of methylene blue and terephthalic acid degradation assisted with double metal-modified catalyst (0.1 mol% Cu and 1.0 mol% Zr) was enhanced as compared with single metal-modified catalysts (0.1, 0.5 mol% Cu and 1.0 mol% Zr). The wet impregnation method was used for copper and zirconium modification of the surface of Aeroxide P25 TiO2 particles. Simultaneous loading of both metals on the surface of P25 leads to an increased specific surface area of the obtained material despite negative Cu influence. The tendency of stabilization and agglomerate size rising with the time for Cu and Zr-modified catalysts were traced by dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements. The observed optical characteristics suggest that Cu compensated the broadening of band gap caused by Zr loading. Crystal structure of obtained photocatalysts was explored by XRD; morphological data and particle size were obtained by SEM. EDX was used for Zr and Cu content determination. Cu K-edge extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) analytical techniques were used to investigate the local Cu neighbourhood in the samples and to identify copper coordination and valence state of copper species in the synthesized nanocomposites.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bubacz K, Kusiak-Nejman E, Tryba B, Morawski AW (2013) Investigation of OH radicals formation on the surface of TiO2/N photocatalyst at the presence of terephthalic acid solution. Estimation of optimal conditions. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 261:7–11. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2013.04.003
Carp O, Huisman CL, Reller A (2004) Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Prog Solid State Chem 32:33–177. doi:10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2004.08.001
Castagnola NB, Kropf AJ, Marshall CL (2005) Studies of Cu-ZSM-5 by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and its application for the oxidation of benzene to phenol by air. Appl Catal A Gen 290:110–122. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2005.05.022
Černigoj U, Kete M, Štangar UL (2010) Development of a fluorescence-based method for evaluation of self-cleaning properties of photocatalytic layers. Catal Today 151:46–52. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2010.03.043
Chiang K, Amal R, Tran T (2002) Photocatalytic degradation of cyanide using titanium dioxide modified with copper oxide. Adv Environ Res 6:471–485. doi:10.1016/S1093-0191(01)00074-0
Choi W, Termin A, Hoffmann MR (1994) The role of metal ion dopants in quantum-sized TiO2: correlation between photoreactivity and charge carrier recombination dynamics. J Phys Chem 98:13669–13679. doi:10.1021/j100102a038
Choudhury B, Dey M, Choudhury A (2013) Defect generation, d-d transition, and band gap reduction in Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Int Nano Lett 3:25. doi:10.1186/2228-5326-3-25
Dahl M, Liu Y, Yin Y (2014) Composite titanium dioxide nanomaterials. Chem Rev 114:9853–9889. doi:10.1021/cr400634p
Di Paola A, Marcì G, Palmisano L et al (2002) Preparation of polycrystalline TiO2 photocatalysts impregnated with various transition metal ions: characterization and photocatalytic activity for the degradation of 4-nitrophenol. J Phys Chem B 106:637–645. doi:10.1021/jp013074l
Domingos RF, Baalousha MA, Ju-Nam Y et al (2009) Characterizing manufactured nanoparticles in the environment: multimethod determination of particle sizes. Environ Sci Technol 43:7277–7284. doi:10.1021/es900249m
Dong H, Zeng G, Tang L et al (2015) An overview on limitations of TiO2-based particles for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants and the corresponding countermeasures. Water Res 79:128–146. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.038
Frenkel AI, Korshin G V., Ankudinov AL (2000) XANES study of Cu -binding sites in aquatic humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 34:2138–2142. doi:10.1021/es990561u
Fu X, Clark LA, Yang Q, Anderson MA (1996) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of titania-based binary metal oxides: TiO2/SiO2 and TiO2/ZrO2. Environ Sci Technol 30:647–653. doi:10.1021/es950391v
Fujishima A, Rao TN, Tryk DA (2000) Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol C Photochem Rev 1:1–21. doi:10.1016/S1389-5567(00)00002-2
Goldstein J, Newbury DE, Joy DC, et al (2003) Scanning electron microscopy and X-ray microanalysis
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saleh TA et al (2012) Chemical treatment technologies for waste-water recycling—an overview. RSC Adv 2:6380. doi:10.1039/c2ra20340e
Hernández-Alonso MD, Tejedor-Tejedor I, Coronado JM et al (2006) Sol–gel preparation of TiO2–ZrO2 thin films supported on glass rings: influence of phase composition on photocatalytic activity. Thin Solid Films 502:125–131. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2005.07.256
Hoffmann MR, Martin ST, Choi W, Bahnemannt DW (1995) Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem Rev 95:69–96. doi:10.1021/cr00033a004
Ilkhechi NN, Ahmadi A, Kaleji BK (2015a) Optical and structural properties of nanocrystalline anatase powders doped by Zr, Si and Cu at high temperature. Opt Quant Electron 47:2423–2434. doi:10.1007/s11082-015-0120-7
Ilkhechi NN, Kaleji BK, Salahi E, Hosseinabadi N (2015b) Comparison of optical and structural properties of Cu doped and Cu/Zr co-doped TiO2 nanopowders calcined at various temperatures. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 765–773. doi: 10.1007/s10971–015–3661-0
Khan AI, O’Hare D (2002) Intercalation chemistry of layered double hydroxides: recent developments and applications. J Mater Chem 12:3191–3198. doi:10.1039/b204076j
Klosek S, Raftery D (2002) Visible light driven V-doped TiO2 photocatalyst and its photooxidation of ethanol. J Phys Chem B 105:2815–2819. doi:10.1021/jp004295e
Kubacka A, Fernández-García M, Colón G (2012) Advanced nanoarchitectures for solar photocatalytic applications. Chem Rev 112:1555–1614. doi:10.1021/cr100454n
Li G, Dimitrijevic NM, Chen L et al (2008) Role of surface/interfacial Cu 2+ sites in the photocatalytic activity of coupled CuO–TiO2 nanocomposites. J Phys Chem C 112:19040–19044. doi:10.1021/jp8068392
Lin W, Frei H (2005) Photochemical CO2 splitting by metal-to-metal charge-transfer excitation in mesoporous ZrCu(I)-MCM-41 silicate sieve. J Am Chem Soc 127:1610–1611. doi:10.1021/ja040162l
Lytle FW, Greegor RB, Panson AJ (1988) Discussion of x-ray-absorption near-edge structure: Application to Cu in the high-T superconductors La Sr CuO and YBa Cu O . Phys Rev B 37:1550–1562. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.37.1550
Manceau A, Matynia A (2010) The nature of Cu bonding to natural organic matter. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:2556–2580. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2010.01.027
Morozov IV, Znamenkov KO, Korenev YM, Shlyakhtin OA (2003) Thermal decomposition of Cu(NO3)2x3H2O at reduced pressures. Thermochim Acta 403:173–179. doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00057-1
Nagaveni K, Hegde MS, Madras G (2004) Structure and photocatalytic activity of Ti1-xMxO2±δ (M = W, V, Ce, Zr, Fe, and Cu) synthesized by solution combustion method. J Phys Chem B 108:20204–20212. doi:10.1021/jp047917v
Paulauskas IE, Modeshia DR, Ali TT et al (2013) Photocatalytic activity of doped and undoped titanium dioxide nanoparticles synthesised by flame spray pyrolysis. Platin Met Rev 57:32–43. doi:10.1595/147106713X659109
Phenrat T, Saleh N, Sirk K et al (2008) Stabilization of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions by anionic polyelectrolytes: adsorbed anionic polyelectrolyte layer properties and their effect on aggregation and sedimentation. J Nanopart Res 10:795–814. doi:10.1007/s11051-007-9315-6
Pliekhov O, Arčon I, Tušar NN, Štangar UL (2016) Photocatalytic activity of zirconium- and manganese-codoped titania in aqueous media: the role of the metal dopant and its incorporation site. ChemCatChem. doi:10.1002/cctc.201600206
Ravel B, Newville M (2005) ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J Synchrotron Radiat 12:537–41. doi:10.1107/S0909049505012719
Rehr JJ, Albers RC, Zabinsky SI (1992) High-order multiple-scattering calculations of x-rayabsorption fine structure. Phys Rev Lett 69:3397–3400. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.3397
Sahu M, Biswas P (2011) Single-step processing of copper-doped titania nanomaterials in a flame aerosol reactor. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:441. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-6-441
Schneider J, Matsuoka M, Takeuchi M et al (2014) Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis : mechanisms and materials. Chem Rev 114:9919–9986. doi:10.1021/cr5001892
Slamet, Nasution HW, Purnama E et al (2005) Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on copper-doped titania catalysts prepared by improved-impregnation method. Catal Commun 6:313–319. doi:10.1016/j.catcom.2005.01.011
Su K, Ai Z, Zhang L (2012) Efficient visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of pentachlorophenol with Bi2O3/TiO2–xBx. J Phys Chem C 116:17118–17123. doi:10.1021/jp305432g
Taurozzi JS, Hackley VA, Wiesner MR (2012) Preparation of a nanoscale TiO2 aqueous dispersion for toxicological or environmental testing. NIST Spec Publ 1200:3. doi:10.6028/NIST.SP.1200
Thiruvenkatachari R, Kwon TO, Jun JC et al (2007) Application of several advanced oxidation processes for the destruction of terephthalic acid (TPA. J Hazard Mater 142:308–314. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.023
Wang Y, Shi R, Lin J, Zhu Y (2010) Significant photocatalytic enhancement in methylene blue degradation of TiO2 photocatalysts via graphene-like carbon in situ hybridization. Appl Catal B Environ 100:179–183. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.07.028
Wendlandt WW (1956) The thermolysis of the rare earth and other metal nitrates. Anal Chim Acta 15:435–439. doi:10.1016/0003-2670(56)80082-2
WHO/UNICEF (2016) Reports of world helth organization.| Progress on sanitation and drinking water. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/monitoring/jmp-2015-update/en/
Zorn ME, Tompkins DT, Zeltner WA, Anderson MA (1999) Photocatalytic oxidation of acetone vapor on TiO2/ZrO2 thin films. Appl Catal B Environ 23:1–8. doi:10.1016/S0926-3373(99)00067-3
Zorn ME, Tompkins DT, Zeltner WA, Anderson MA (2000) Catalytic and photocatalytic oxidation of ethylene on titania-based thin-films. Environ Sci Technol 34:5206–5210. doi:10.1021/es991250m
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by INFINITY project in the framework of the EU Erasmus Mundus Action 2. Financial support from Belgian-Slovenian (FWO-ARRS) project “Development of advanced TiO2-based photocatalyst for the degradation of organic pollutants from wastewater” and from the Ministry of Education, Science and Sport of Slovenia, the Slovenian Research Agency is acknowledged (research programs P2-0377, P1-0112 and P1-0021). Access to synchrotron radiation facilities of ELETTRA, Trieste, Italy, beamline XAFS, in the frame of project 20140041, is also acknowledged. We thank Giuliana Aquilanti and Luca Olivi, from XAFS beamline at synchrotron ELETTRA, for the support and expert advice on beamline operation. We also thank Dr. Mattia Fanetti from Materials Research Laboratory, University of Nova Gorica, and Helena Spreizer from National Institute of Chemistry for performing SEM-EDX and UV–Vis DRS measurements, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 120 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pliekhova, O., Arčon, I., Pliekhov, O. et al. Cu and Zr surface sites in the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 12571–12581 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7685-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7685-y