Abstract
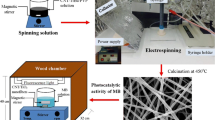
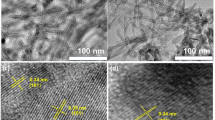
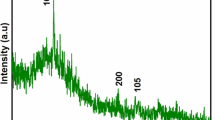
TiO2 nanoparticles and nanofibers have been used to carry out a comparative study of the destruction of H2S gas. Effects of sulphur doping have also been incorporated to assess the maximum destruction potential of the nanomaterials. An analysis has been made in this paper to evaluate and compare the performance of pure and sulphur-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and nanofibers for the destruction of H2S gas using photocatalysis under laboratory conditions. Regression modelling has been performed to ascertain the individual degradation rates of the nanoparticles and nanofibers. In addition, oxidation rates of H2S gas using the nanoparticles and nanofibers have been used to further elucidate our findings. It was observed that the destruction potential of nanofibers was 10 times more as compared to nanoparticles.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrios AG, Pichat P (2005) An overview of the state of the art and perspectives on materials and applications of photocatalysis over TiO2. J Appl Electrochem 35:655–663
Alvarez RJT, Morales PJR (1995) Regression models for the determination of the absorbed dose rate with an extrapolation chamber for flat ophthalmic applicators. Health Phys 68:234–252
Azargohar R (2009) Production of activated carbon and its catalytic application for oxidation of hydrogen sulfide. PhD Dissertation, University of Saskatchewan, Canada
Canela MC, Rosana MA, Jardim WF (1998) Gas-phase destruction of H2S using TiO2/UV-VIS. J Photoch Photobio A 12:73–80
Choi SK, Kim S, Lim SK, Park H (2010) Photocatalytic comparison of TiO2 nanoparticles and electrospun TiO2 nanofibers: effects of mesoporosity and interparticle charge transfer. J Phys Chem C 114:16475–16480
Chong MN, Jin B, Chow CWK, Saint S (2010) Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: a review. Water Res 44:2997–3027
Fujishima A, Rao TN, Tryk DA (2000) Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol C 1:1–21
Hussain ST, Khaiber K, Hussain R (2009) Size control synthesis of sulfur doped titanium dioxide (anatase) nanoparticles, its optical property and its photo catalytic reactivity for CO2 + H2O conversion and phenol degradation. J Nat Gas Chem 18:383–391
Iliuta I, Larachi F (2003) Concept of bifunctional redox iron-chelate process for H2S removal in pulp and paper atmospheric emissions. Chem Eng Sci 58:5305–5314
Lewandowski M, Ollis DF (2004) Photocatalytic oxidation of gas phase aromatic pollutants. In: Ramamurthy V, Schanze KS (eds) Seminoconductor photochemistry and photophysics. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 249–282
Shahzad N (2012) An investigation into the potential of pure and doped TiO2 nanoparticles for the abatement of air pollution. PhD Dissertation, National University of Sciences and Technology, Pakistan
Shahzad N, Qiao C (2013) Evaluation of the photocatalytic potential of TiO2 nanofibers for the destruction of H2S gas. Mater Sci Forum 756:225–229
Shahzad N, Hussain ST, Baig MA (2012a) Air pollution abatement through TiO2 nanoparticles. International Journal of Climate Changes: Impact and Responses 3:95–101
Shahzad N, Hussain ST, Siddiqua A, Baig MA (2012b) A comparison of TiO2 nanoparticles and nanotubes for catalytic gas phase destruction of H2S gas at high temperatures. J Nanosci Nanotechno 12:5061–5065
Strang G (1991) Exponentials and logarithms. In: Calculus. Wellesley-Cambridge Press. pp. 228–282
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahzad, N., Azfar, R.W. Comparison of H2S gas destruction potential using TIO2 nanofibers and nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 1133–1136 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7644-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7644-7