Abstract
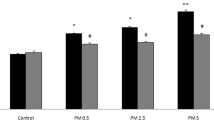
Particulate matter (PM) inhalation is an established trigger of cardiovascular events such as cardiac arrhythmias that occur within hours to days after exposure. Higher daily PM levels are related to acute increases in systemic arterial blood pressure (BP). The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of PM10 on electrocardiogram (ECG) parameters, blood pressure, lipid peroxidation (MDA), xanthine oxidase, and antioxidant enzyme in healthy rats and also to examine the protective effects of vanillic acid (VA) in this respect. Eighty male Wistar rats were divided into eight groups (n = 10), namely control (normal saline, gavage), VAc (10 mg/kg), sham (normal saline, intratracheal instillation), VA (10 mg/kg VA, 10 days gavage +0.1 ml normal saline, intratracheal instillation), PM1 (0.5 mg/kg), PM2 (2.5 mg/kg), PM3 (5 mg/kg), PM3 + VA (5 mg/kg, intratracheal instillation + 10 mg/kg VA, 10 days, gavage) groups. The rats were anesthetized and 0.1 ml of saline as well as a certain concentration of PM10 was instilled into the trachea and it was repeated after 48 h, then 30 min after that, PR interval, QTc, and systolic blood pressure were measured. The activities of antioxidant enzymes, xanthine oxidase (XOX), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were measured in plasma by special Kits. A significant increase in blood pressure (BP), PR interval, QTc, MDA, and XOX and a significant decrease in antioxidant enzyme (CAT, SOD, and GPx) occurred in PM10 groups. Vanillic acid ameliorated blood pressure, QTc, PR interval, XOX, MDA, and increased antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, and GPx) significantly. In the present study, it was shown that PM10 had devastating effects on the heart and blood pressure, probably due to the increased oxidative stress in healthy rats. Vanillic acid could improve the symptoms of PM10 exposure and can be used as an antioxidant agent against the harmful effects of PM10.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PM:
-
particulate matter
- PM10 :
-
particles with aerodynamic diameter < 10 μm
- VA:
-
vanillic acid
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- CAT:
-
catalase
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- XOX:
-
xanthine oxidase
- BP:
-
blood pressure
- CVD:
-
cardiovascular disease
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- ECG:
-
electrocardiogram
References
Akhondali Z, Dianat M, Radan M (2015) Negative Chronotropic and antidysrhythmic effects of hydroalcoholic extract of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.) on CaCl2-induced arrhythmias in rats. Electron Phys 7(1):971–976. doi:10.14661/2015.971-976
Barros L, Duenas M, Ferreira IC, Baptista P, Santos-Buelga C (2009) Phenolic acids determination by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS in sixteen different Portuguese wild mushrooms species. Food Chem Toxicol 47:1076–1079. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.01.039
Bascom R (1996) Health effects of outdoor air pollution. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 3:3–50
Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Pope CA III, Brook JR, Bhatnagar A, Diez-Roux AV, Holguin F, Hong Y, Luepker RV, Mittleman MA, Peters A, Siscovick D, Smith SC Jr, Whitsel L, Kaufman JD (2010) Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: an update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 121:2331–2378. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e3181dbece1
Chuang KJ, Chan CC, Shiao GM, Su TC (2005) Associations between submicrometer particles exposures and blood pressure and heart rate in patients with lung function impairments. J Occup Environ Med 47:1093–1098
Delfino RJ, Staimer N, Vaziri ND (2011) Air pollution and circulating biomarkers of oxidative stress. Air Qual Atmos Health 4:37–52. doi:10.1007/s11869-010-0095-2
Dianat M, Hamzavi GH, Badavi M, Samarbafzadeh A (2014a) Effects of losartan and vanillic acid Co-administration on ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in isolated rat heart. Iran Red Crescent Med J 16(7):e16664 . doi:10.5812/ircmj.16664 1-7
Dianat M, Radan M, Badavi M, Sarkaki A (2014b) The evaluation of inotropic properties and antidysrhythmic effect of vanillic acid and exercise on Cacl2-induced arrhythmia in young and aged rats. RJPBCS 5(3):1545
Dianat M, Saadat Fard S, Badavi M, Ahangarpour A (2012) The effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on QT interval in cirrhotic rats. Health MED 6(10):3281–3285
Dianat M, Radmanesh E, Badavi M, Mard SA, Goudarzi G (2016) Disturbance effects of PM10 on iNOS and eNOS mRNA expression levels and antioxidant activity induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart: protective role of vanillic acid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(6):5154–5165. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-5759-x
Dianat M, Veisi A, Ahangarpour A, Fathi Moghaddam H (2015) The effect of hydro-alcoholic celery (Apium graveolens) leaf extract on cardiovascular parameters and lipid profile in animal model of hypertension induced by fructose. AJP 5(3):203–209
Dominici F, Peng RD, Bell ML, Pham L, McDermott A, Zeger SL, Samet JM (2006) Fine particulate air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. JAMA 295:1127–1134. doi:10.1001/jama.295.10.1127
Dvonch JT, Kannan S, Schulz AJ, Keeler GJ, Mentz G, House J, Benjamin A, Max P, Bard RL, Brook RD (2009) Acute effects of ambient particulate matter on blood pressure: differential effects across urban communities. Hypertension 53:853–859. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.123877
Golomb E, Matza D, Cummings CA, Schwalb H, Kodavanti UP, Schneider A, et al. (2012) Myocardial mitochondrial injury induced by pulmonary exposure to particulate matter in rats. Toxicol Pathol 40:779–788. doi:10.1177/0192623312441409
Gong H Jr, Linn WS, Sioutas C, Terrell SL, Clark KW, Anderson KR, Terrell LL (2003) Controlled exposures of healthy and asthmatic volunteers to concentrated ambient fine particles in Los Angeles. Inhal Toxicol 15:305–325. doi:10.1080/08958370304455
Goudie AS (2014) Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ Int 63:101–113. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2013.10.011
Grahame TJ, Schlesinger RB (2010) Cardiovascular health and particulate vehicular emissions: a critical evaluation of the evidence. Air Qual Atmos Health 3:3–27. doi:10.1007/s11869-009-0047-x
Gurgueira SA, Lawrence J, Coull B, Krishna Murthy GG, Gonzalez-Flecha B (2002) Rapid increases in the steady-state concentration of reactive oxygen species in the lungs and heart after particulate air pollution inhalation. Environ Health Perspect 110:749–755
Heidari-Farsani M, Shirmardi M, Goudarzi G, Alavi-Bakhtiariv N, Ahmadi-Ankali K, Zallaghi E, Naeimabadi A, Hashemzadeh B (2014) The evaluation of heavy metals concentration related to PM10 in ambient air of Ahvaz city, Iran. J Adv Environ Health Res 1(2):120–128 http://jaehr.muk.ac.ir
Hoffmann C, Funk R, Wieland R, Li Y, Sommer M (2008) Effects of grazing and topography on dust flux and deposition in the Xilingele grassland, Inner Mongolia. J Arid Environ 72(5):792–807. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2007.09.004
Hoseiny Nejad Kh, Dianat M, Sarkaki A, Gharib Naseri M K, Badavi M, Farbood Y (2015) Ellagic acid improves electrocardiogram waves and blood pressure against global cerebral ischemia rat experimental models. Electron Phys 7(4): 1153–1162. Doi: 10.14661/2015.1153–1162.
Ibald-Mulli A, Stieber J, Wichmann HE, Koenig W, Peters A (2001) Effects of air pollution on blood pressure: a population-based approach. Am J Public Health 91:571–577
King AA, Shaughnessy DT, Mure K, et al. (2007) Antimutagenicity of cinnamaldehyde and vanillin in human cells: global gene expression and possible role of DNA damage and repair. Mutat Res 616:60–69. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.11.022
Kodavanti UP, Schladweiler MC, Gilmour PS, Wallenborn JG, Mandavilli BS, Ledbetter AD, et al. (2008) The role of particulate matter-associated zinc in cardiac injury in rats. Environ Health 116(1):13–20
Kogure K, Goto S, Nishimura M, et al. (2002) Mechanism of potent antiperoxidative effect of capsaicin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1573:84–92
Kurhanewicz N, McIntosh-Kastrinsky R, Tong H, Walsh L, Farraj A, Hazari M (2014) Ozone co-exposure modifies cardiac responses to fine and ultrafine ambient particulate matter in mice: concordance of electrocardiogram and mechanical responses. Particle and fibre toxicology. BioMed Central Ltd, London Uk 11(1):54
Kwon HJ, Cho SH, Chun Y, Lagarde F, Pershagen G (2002) Effects of the Asian dust events on daily mortality in Seoul, Korea. Environ Res Sec A 90:1–5
Madamanchi NR, Vendrov A, Runge MS (2005) Oxidative stress and vascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:29–23. doi:10.1186/1743-8977-9-21
Manzano-Leon N, Quintana R, Sanchez B, Serrano J, Vega E, Vazquez-Lopez I, et al. (2013) Variation in the composition and in vitro pro inflammatory effect of urban particulate matter from different sites. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 27(1):87–97. doi:10.1002/jbt.21471
Mohd TN, Poh SC, Suratman S, Ariffin MM, Shazali NA, Yunus K (2009) Determination of trace metals in airborne particulate matter of Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83(2):199–203. doi:10.1007/s00128-009-9751-3
Peters A, Liu E, Verrier RL, Schwartz J, Gold DR, Mittleman M, Baliff J, Oh JA, Allen G, Monahan K, Dockery DW (2000) Air pollution and incidence of cardiac arrhythmia. Epidemiology 11:11–17
Poljsak B, Šuput D, Milisav I (2013) Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: when to use the synthetic antioxidants. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity Article ID 956792. doi:10.1155/2013/956792
Rich DQ, Kim MH, Turner JR, Mittleman MA, Schwartz J, Catalano PJ, Dockery DW (2006) Association of ventricular arrhythmias detected by implantable cardioverter defibrillator and ambient air pollutants in the St Louis, Missouri metropolitan area. Occup Environ Med 63:591–596. doi:10.1136/oem.2005.023457
Rhoden CR, Gregory A, Wellenius EG, Lawrence J, Gonza B (2005) PM-induced cardiac oxidative stress and dysfunction are mediated by autonomic stimulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1725:305–313. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.05.025
Sarnat SE, Suh HH, Coull BA, Schwartz J, Stone PH, Gold DR (2006) Ambient particulate air pollution and cardiac arrhythmia in a panel of older adults in Steubenville, Ohio. Occup Environ Med 63:700–706. doi:10.1136/oem.2006.027292
Schnabel RB, Sullivan LM, Levy D, Pencina MJ, Massaro JM, D’Agostino RBS, Newton-Cheh C, Yamamoto JF, Magnani JW, Tadros TM, Kannel WB, Wang TJ, Ellinor PT, Wolf PA, Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ (2009) Development of a risk score for atrial fibrillation (Framingham Heart Study): a community-based cohort study. Lancet 373:739–745. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60443-8
Shahsavani A, Naddafi K, Jafarzade Haghighifard N, Mesdaghinia A, Yunesian M, Nabizadeh R, et al. (2012) Theevaluation of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 concentrations during the Middle Eastern dust (MED) events inAhvaz, Iran, from april through september 2010. J Arid Environ 77:72–83. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2011.09.007
Sies H (1991) Oxidative stress: from basic research to clinical application. Am J Med 91:31S–38S
Soleimani Z, Parhizgari N, Dehdari Rad H, Akhoond MR, Kermani M, Bagherian Marzouni M, et al. (2015) Normal and dusty days comparison of culturable indoor airborne bacteria in Ahvaz, Iran. Aerobiologia 31(2):127–141. doi:10.1007/s10453-014-9352-4
Sumanth DP (2006) Environmental pollution: relationship to cardiac dysfunction and heart disease. Sustain 13:12–16
Grahame TJ, Schlesinger RB (2012) Oxidative stress-induced telomeric erosion as a mechanism underlying airborne particulate matter-related cardiovascular disease. Grahame Schlesinger Part Fibre Toxicol 9:21. doi:10.1186/1743-8977-9-21 http://www.particleandfibretoxicology.com/content/9/1/21
Tofler GH, Muller JE (2006) Triggering of acute cardiovascular disease and potential preventive strategies. Circulation 114:1863–1872. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.596189
Zanobetti A, Canner MJ, Stone PH, Schwartz J, Sher D, Eagan-Bengston E, Gates KA, Hartley LH, Suh H, Gold DR (2004) Ambient pollution and blood pressure in cardiac rehabilitation patients. Circulation 110:2184–2189. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000143831.33243.D8
Zhang W, Zhuang G, Guo J, Xu D, Wang W, Baumgardner D, et al. (2010) Sources of aerosol as determined from elemental composition and size distributions in Beijing. Atmos Res 95(2–3):197–209. doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2009.09.017
Acknowledgment
The source of data used in this paper was from the Ph.D. thesis of Mrs. Esmat Radmanesh, a student of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran. Authors gratefully acknowledge the help and financial support of Physiology Research Center of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (No. ajums APRC-9316).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dianat, M., Radmanesh, E., Badavi, M. et al. The effects of PM10 on electrocardiogram parameters, blood pressure and oxidative stress in healthy rats: the protective effects of vanillic acid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 19551–19560 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7168-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7168-1