Abstract
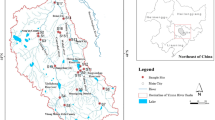
The Songhua River represents one of the seven major river systems in China. It flows through Harbin city with 66 km long, locating in the northern China with a longer winter time. This paper aimed to study concentration distributions, stability, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals including chromium (Cr), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), arsenic (As), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), and nickel (Ni) in 11 selected sections of the Songhua River Harbin region. Results showed that Cr, Cd, Pb, Hg, and As exceeded their respective geochemical background values in sediments of most monitoring sections. Compared with other important rivers and lakes in China, Cr, Hg, Cd, and As pollutions in surface sediments were above medium level. Further analysis of chemical speciation indicated that Cr and As in surface sediments were relatively stable while Pb and Cd were easily bioavailable. Correlation analysis revealed sources of these metals except As might be identical. Pollution levels and ecological risks of heavy metals in surface sediments presented higher in the mainstream region (45° 47.0′ N ~ 45° 53.3′ N, 126° 37.0′ E ~ 126° 42.1′ E). Source apportionment found Hejiagou and Ashi River were the main contributors to metal pollution of this region. Thus, anthropogenic activities along the Hejiagou and Ashi River should be restricted in order to protect the Songhua River Harbin region from metal contamination.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 20th edn. Washington, DC
Bartoli G, Papa S, Sagnella E, Fioretto A (2012) Heavy metal content in sediments along the Calore river: relationships with physical–chemical characteristics. J Environ Manag 95:9–14
Chabukdhara M, Nema AK (2012) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in Hindon River sediments: a chemometric and geochemical approach. Chemosphere 87:945–953
Chae JS, Choi MS, Song YH, Um IK, Kim JG (2014) Source identification of heavy metal contamination using metal association and Pb isotopes in Ulsan Bay sediments, East Sea, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 88:373–382
Cheng H, Li M, Zhao C, Yang K, Li K, Peng M, Yin G (2015a) Concentrations of toxic metals and ecological risk assessment for sediments of major freshwater lakes in China. J Geochem Explor 157:15–26
Cheng Q, Wang R, Huang W, Wang W, Li X (2015b) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments from the Yellow River Wetland National Nature Reserve (the Sanmenxia section), China. Environ Sci Pollut R:1–8
Dong ZH (2015) Research on characteristics of sediment based on analysis of the upstream raw water quality of Songhua River in Harbin region. Dissertation, Harbin Institute of Technology
Fu J, Zhao C, Luo Y, Liu C, Kyzas GZ, Luo Y, Zhu H (2014) Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: their relations to environmental factors. J Hazard Mater 270:102–109
Gao X, Chen CTA (2012) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res 46:1901–1911
Gao YN, Li WG, Zhang DY, Wang GZ (2010) Bio-enhanced activated carbon filter with immobilized microorganisms for removing organic pollutants in the Songhua River. Water Sci Technol 62:2819–2828
Guo SH, Wang XL, Li Y, Chen JJ, Yang JC (2006) Investigation on Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Pb and Cd fractions in the natural surface coating samples and suflicial sediments in the Songhua River, China. J Environ Sci 18:1193–1198
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hamdoun H, Van-Veen E, Basset B, Lemoine CJ, Leleyter L, Baraud F (2015) Characterization of harbor sediments from the English Channel: assessment of heavy metal enrichment, biological effect and mobility. Mar Pollut Bull 90:273–280
Jung HS, Lim D, Xu Z, Kang JH (2014) Quantitative compensation of grain-size effects in elemental concentration: a Korean coastal sediments case study. Eatuar Coast Shelf S 151:69–77
Liang LN, He B, Jiang GB, Chen DY, Yao ZW (2004) Evaluation of mollusks as biomonitors to investigate heavy metal contaminations along the Chinese Bohai Sea. Sci Total Environ 324:105–113
Li J (2014) Risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Yanghe River, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11:12441–12453
Lin YC, Chang-Chien GP, Chiang PC, Chen WH, Lin YC (2013) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contaminations in seawater and sediments from a heavily industrialized harbor in Southern Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 76:266–275
Li Y, Xu LY, Li S (2009) Water quality analysis of the Songhua River Basin using multivariate techniques. J Water Resour Protect 2:110–121
Maanan M, Saddik M, Maanan M, Chaibi M, Assobhei O, Zourarah B (2015) Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon. Morocco. Ecol Indic 48:616–626
Miao CY, Yang L, Liu BY, Gao Y, Li S (2011) Streamflow changes and its influencing factors in the mainstream of the Songhua River basin, Northeast China over the past 50 years. Environ Earth Sci 63:489–499
Resongles E, Casiot C, Freydier R, Dezileau L, Viers J, Elbaz-Poulichet F (2014) Persisting impact of historical mining activity to metal (Pb, Zn, Cd, Tl, Hg) and metalloid (As, Sb) enrichment in sediments of the Gardon River, Southern France. Sci Total Environ 481:509–521
Singh AK, Srivastava SC, Verma P, Ansari A, Verma A (2014) Hazard assessment of metals in invasive fish species of the Yamuna River, India in relation to bioaccumulation factor and exposure concentration for human health implications. Environ Monit Assess 186:3823–3836
Song Y, Choi MS, Lee JY, Jang DJ (2014) Regional background concentrations of heavy metals (Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Pb) in coastal sediments of the South Sea of Korea. Sci Total Environ 482:80–91
Song Y, Ji J, Yang Z, Yuan X, Mao C, Frost RL, Ayoko GA (2011) Geochemical behavior assessment and apportionment of heavy metal contaminants in the bottom sediments of lower reach of Changjiang River. Catena 85:73–81
Sundaray SK, Nayak BB, Lin S, Bhatta D (2011) Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—a case study: Mahanadi basin, India. J Hazard Mater 186:1837–1846
Sun YY (2012) Study on survey of water quality and sediment adsorption and release of Songhua River in Harbin section. Dissertation, Harbin Institute of Technology
Tang W, Zhao Y, Wang C, Shan B, Cui J (2013) Heavy metal contamination of overlying waters and bed sediments of Haihe Basin in China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:317–323
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresun 33:566–575
Ure AM, Quevauviller P, Muntau H, Griepink B (1993) Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. Int J Environ An Ch 51:135–151
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang J, Liu G, Lu L, Zhang J, Liu H (2015) Geochemical normalization and assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, and Ni) in sediments from the Huaihe River, Anhui, China. Catena 129:30–38
Wang J, Liu R, Zhang P, Yu W, Shen Z, Feng C (2014a) Spatial variation, environmental assessment and source identification of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 87:364–373
Wang Y, Wang P, Bai YJ, Tian ZX, Li JW, Shao X, Mustavich LF, Li BL (2013) Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Songhua River Harbin region. China J Hydro-Environ Res 7:30–40
Wang ZM, Chen LD, Zhang HP, Sun RH (2014b) Multivariate statistical analysis and risk assessment of heavy metals monitored in surface sediment of the Luan River and its tributaries, China. Human Ecol Risk Assess: Int J 20:1521–1537
Xiao H, Zang S, Guan Y, Liu S, Gao Y, Sun Q, Pei X (2014) Assessment of potential risks associated with heavy metal contamination in sediment in Aobaopao Lake, China, determined from sediment cores. Ecotoxicology 23:527–537
Xiao R, Bai J, Huang L, Zhang H, Cui B, Liu X (2013) Distribution and pollution, toxicity and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from urban and rural rivers of the Pearl River delta in southern China. Ecotoxicology 22:1564–1575
Xu Y, Sun Q, Yi L, Yin X, Wang A, Li Y, Chen J (2014) The source of natural and anthropogenic heavy metals in the sediments of the Minjiang River Estuary (SE China): implications for historical pollution. Sci Total Environ 493:729–736
Yang XX (2014) Research on temporal and spatial variation of water environmental quality in Harbin section of the Songhua River. Dissertation, Harbin Institute of Technology
Yang Y, Liu Z, Chen F, Wu S, Zhang L, Kang M, Li J (2014) Assessment of trace element contamination in sediment cores from the Pearl River and estuary, South China: geochemical and multivariate analysis approaches. Environ Monit Assess 186:8089–8107
Yao S, Xue B (2014) Heavy metal records in the sediments of Nanyihu Lake, China: influencing factors and source identification. J Paleolimnol 51:15–27
You H, Ding J, Zhao XS, Li YF, Liu LY, Ma WL, Qi H, Shen JM (2011) Spatial and seasonal variation of polychlorinated biphenyls in Songhua River, China. Environ. Geochem Health 33:291–299
Zhang W, Liu X, Cheng H, Zeng EY, Hu Y (2012) Heavy metal pollution in sediments of a typical mariculture zone in South China. Mar Pollut Bull 64:712–720
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Management (No. 2013ZX07201007, 2014ZX07201012), the State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology (No. 2014DX03) and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20112302110060). The authors also appreciate the Funds for Creative Research Groups of China (No. 51121062).
The authors also appreciate the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology (QA201609-02), the Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Science Foundation (LBH-Z14093), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. HIT.NSRIF. 2015096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Céline Guéguen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Tian, Y., Zhang, J. et al. Heavy metal contamination status and source apportionment in sediments of Songhua River Harbin region, Northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 3214–3225 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7132-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7132-0