Abstract
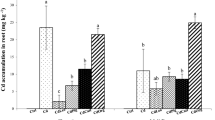
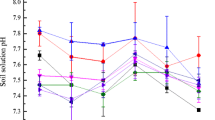
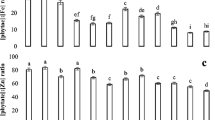
Rice ( Oryza sativa L.) is one of the main staple food crops which is inherently low in micronutrients, especially iron (Fe), and can lead to severe Fe deficiency in populations having higher consumption of rice. Soils polluted with nickel (Ni) can cause toxicity to rice and decreased Fe uptake by rice plants. We investigated the potential role of biochar (BC) and gravel sludge (GS), alone and in combination, for in situ immobilization of Ni in an industrially Ni-contaminated soil at original and sulfur-amended altered soil pH. Our further aim was to increase Fe bioavailability to rice plants by the exogenous application of ferrous sulfate to the Ni-immobilized soil. Application of the mixture of both amendments reduced grain Ni concentration, phytate, Phytate/Fe, Phyt/Zn molar ratios, and soil DTPA-extractable Ni. In addition, the amendment mixture increased 70 % Fe and 229 % ferritin concentrations in rice grains grown in the soil at original pH. The Fe and ferritin concentrations in S-treated soil was increased up to 113 and 383 % relative to control respectively. This enhanced Fe concentration and corresponding ferritin in rice grains can be attributed to Ni/Fe antagonism where Ni has been immobilized by GS and BC mixture. This proposed technique can be used to enhance growth, yield, and Fe biofortification in rice by reducing soil pH while in parallel in situ immobilizing Ni in polluted soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Rehman MZ, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015a) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MK, Irshad MK (2015b) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:186–197
Ahmad M, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Zhang M, Bolan N, Mohan D, Vithanage M, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: a review. Chemosphere 99:19–33
Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Kanwal S, Ali Q, Ibrahim M, Gill RA, Khan MD (2015) Fulvic acid mediates chromium (Cr) tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) through lowering of Cr uptake and improved antioxidant defense system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10601–10609
Allison LE, Moodie CD (1965) Carbonate. In: Black CA (ed) Methods soil analysis part 2: chemical and microbiological properties. Am Soc Agron Madison USA, p 1379–1396
Almaroai YA, Usman ARA, Mahtab A, Deok HM, Ju-Sik C, Young KJ, Choong J, Sang SL, Ok YS (2014) "Effects of biochar, cow bone, and eggshell on Pb availability to maize in contaminated soil irrigated with saline water. Environ Earth Sci 71:1289–1296
AOAC (2003) Official methods of analysis of the association of official’s analytical chemists, 17th edn. Association of official analytical chemists, Arlington, Virginia. Application on mycorrhizal root colonisation, growth and nutrition of wheat. Aust J Soil Res 48:546–554
Barcelo F, Miralles F, Arean CO (1997) Purification and characterization of ferritin from alfalfa seeds. J Inorg Biochem 66:23–27
Bertrand J, Mars A, Boyle C, Bove F, Yeargin-Allsopp M, Decoufle P (2001) Prevalence of autism in a United States population: the Brick Township, New Jersey, investigation. Pediatrics 108:1155–1161
Bingham FT, Pereyea FJ, Jarrell WM (1986) Metal toxicity to agricultural crops. Met Ions Biol Syst 20:119–156
Borrell AK, Hammer GL, Douglas ACL (2000) Does maintaining green leaf area in sorghum improve yield under drought? I. Leaf growth and senescence. Crop Sci J 40:1026–1037
Bouis HE, Welch RM (2010) Biofortification: a sustainable agricultural strategy for reducing micronutrient malnutrition in the global south. Crop Sci 50:20–32
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen total. p. 595–624. In A. L. Page (ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Agron. No. 9, part 2: chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd ed., Am Soc Agron Madison WI USA
Cao XD, Ma LN, Gao B, Harris W (2009) Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environ Sci Technol 43:3285–3291
Cataldo DA, Garland TR, Wildung RE (1978) Nickel in plants. I. Uptake kinetics using intact soybean seedling. Plant Physiol 62:563
Chen Z, Watanabe TT, Shinano T, Exawa J, Washaki K, Kimura T, Osaki M, Xhu Y (2009) Element interconnections in Lotus japonicas: a systematic study of the effects of element additions on different natural variants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 55:91–101
Cook JD, Dassenko SA, Lynch SR (1991) Assessment of the role of nonheme-iron availability in iron balance. Am J Clin Nutr 54:717–722
Friesl W, Friedl J, Platzer K, Horak O, Gerzabek MH (2006) Remediation of contaminated agricultural soils near a former Pb/Zn smelter in Austria: batch, pot and field experiments. Environ Pollut 144:40–50
Friesl-Hanl W, Platzer K, Horak O, Gerzabek MH (2009) Immobilising of Cd, Pb, and Zn contaminated arable soils close to a former Pb/Zn smelter: a field study in Austria over 5 years. Environ Geochem Health 31:581–594
Gajewska E, Sklodowska M, Slaba M, Mazur J (2006) Effect of nickel on antioxidative enzyme activities, proline and chlorophyll content in wheat shoots. Biol Plant 50:653–659
Gajewska E, Wielanek M, Bergier K, Skłodowska M (2009) Nickel-induced depression of nitrogen assimilation in wheat roots. Acta Physiol Plant 31:1291–1300
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods soil anal. Part 1: physical and mineralogical methods. Agron Monogr 9. Soil Sci Soc Am. Madison, USA, p 383–409
Ghasemi R, Ghaderian SM, Kramer U (2009) Interference of nickel with copper and iron homeostasis contributes to metal toxicity symptoms in the nickel hyperaccumulator plant Alyssum inflatum. New Phytol 184:566–580
Gray CW, Dunham SJ, Dennis PG, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (2006) Field evaluation of in situ remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil using lime and red-mud. Environ Pollut 142:530–539
Guo Y, Marschner H (1995) Uptake, distribution, and binding of cadmium and nickel in different plant species. J Plant Nutr 18:2691–2706
Hambidge KM, Miller LV, Westcott JE, Sheng X, Krebs NF (2010) Zinc bioavailability and homeostasis. Am J Clin Nutr 91:1478–1483
Haug W, Lantzsch H (1983) Sensitive method for the rapid determination of phytate in cereals and cereal products. J Sci Food Agric 34:1423–1426
Herath I, Kumarathilaka P, Navaratne A, Rajakaruna N, Vithanage M (2015) Immobilization and phytotoxicity reduction of heavy metals in serpentine soil using biochar. J Soils Sediments 15:126–138
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013a) Mobility, bioavailability and pH-dependent leaching of cadmium, zinc and lead in a contaminated soil amended with biochar. Chemosphere 92:1450–1457
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013b) Beneficial effects of biochar application to contaminated soils on the bioavailability of Cd, Pb and Zn and the biomass production of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Biomass Bioenergy 57:196–204
Hussain S, Maqsood MA, Aziz T, Basra SMA (2013) Zinc bioavailability response curvature in wheat grains under incremental zinc applications. Arch Agron Soil Sci 59:1001–1016
Ippolito JA, Barbarick KA, Elliott HA (2011) Drinking water treatment residuals: a review of recent uses. J Environ Qual 40:1–12
Iqbal M, Puschenreiter M, Oburger E, Santner J, Wenzel WW (2012) Sulfur-aided phytoextraction of Cd and Zn by Salix smithiana combined with in situ metal immobilization by gravel sludge and red mud. Environ Pollut 170:222–231
Jackson ML (1973) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice-hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
Kaplan M, Orman S (1998) Effect of elemental sulfur and sulfur containing waste in a calcareous soil in Turkey. J Plant Nutr 21:1655–1665
Khaliq A, Ali S, Hameed A, Farooq MA, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Mahmood K, Ishaque W, Rizwan M (2016) Silicon alleviates nickel toxicity in cotton seedlings through enhancing growth, photosynthesis and suppressing Ni uptake and oxidative stress. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:633–647
Khanmohammadi Z, Afyuni M, Mosaddeghi MR (2015) Effect of pyrolysis temperature on chemical and physical properties of sewage sludge biochar. Waste Manag Res 33:275–283
Kimetu JM, Lehmann J, Ngoze S, Mugendi DN, Kinyangi JM, Riha S, Verchot L, Recha JW, Pell A (2008) Reversibility of soil productivity decline with organic matter of differing quality along a degradation gradient. Ecosystems 11:726–739
Krebs R, Gupta SK, Furrer G, Schulin R (1999) Gravel sludge as an immobilising agent in soils contaminated by heavy metals: a field study. Water Air Soil Pollut 115:465–479
Laulhere JP, Lescure AM, Briat JF (1988) Purification and characterization of ferritins from maize, pea, and soybean seeds distribution in various pea organs. J Biol Chem 263:10289–10294
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Loneragan JF, Grunes DL, Welch RM, Aduayi EA, Tengah A, Lazar VA, Cary EE (1982) Phosphorus accumulation and toxicity in leaves in relation to zinc supply. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:345–352
Lonnerdal B (2007) The importance and bioavailability of phytoferritin- bound iron in cereals and legume foods. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 77:152–157
Lothenbach B, Krebs R, Furrer G, Gupta SK, Schulin R (1998) Immobilization of cadmium and zinc in soil by Al-montmorillonite and gravel sludge. Eur J Soil Sci 49:141–148
Lott JNA, Greenwood JS, Batten GD (1995) Mechanisms and regulation of mineral nutrient storage during seed development. In: Kigel J, Galili G (eds) Seed development and germination. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 215–235
Lukac RJ, Aluru MA, Reddy MB (2009) Quantification of ferritin from staple food crops. J Agric Food Chem 57:2155–2161
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press Inc., San Diego
Meng F, Wei Y, Yang X (2005) Iron content and bioavailability in rice. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18:333–338
Michael B, Zink E, Lantzsch HJ (1980) Effect of phosphate application on phytin-phosphorus and other phosphate fractions in developing wheat grains. Z Pflanzenernaehr Bodenkd 143:369–376
Modaihsh S, Al-mustafa WA, Metwally AE (1989) Effect of elemental sulfur on chemical changes and nutrient availability in calcareous soils. Plant Soil 116:95–101
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Surfactant-enhanced remediation of contaminated soil: a review. Eng Geol 60:371–380
Namgay T, Singh B, Singh BP (2010) Influence of biochar application to soil on the availability of As, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn to maize (Zea mays L.). Aust J Soil Res 48:638–647
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 2: chemical and microbiological properties. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp. 570–571
Nishida S, Aisu A, Mizuno T (2012) Induction of IRT1 by the nickel-induced iron-deficient response in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 7:13–19
Ogawa M, Tanaka K, Kasai Z (1977) Note on the phytin containing particles isolated from rice scutellum. Cereal Chem 54:1029–1034
Olaniran AO, Balgobind A, Pillay B (2013) Bioavailability of heavy metals in soil: impact on microbial biodegradation of organic compounds and possible improvement strategies. Int J Mol Sci 14:10197–10228
Ouzounidou G, Moustakas M, Symeonidis L, Karataglis S (2006) Response of wheat seedlings to Ni stress: effects of supplemental calcium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:346–352
Panda BB, Sharma S, Mohapatra PK, Das A (2014) Iron nutrition vis-à-vis aconitase activity and ferritin accumulation in tropical indica rice cultivars differing in grain iron concentration. Am J Plant Sci 5:2829–2841
Park JH, Choppala GH, Bolan NS, Chung JW, Chuasavathi T (2011) Biochar reduces the bioavailability and phytotoxicity of heavy metals. Plant Soil 348:439–451
Prom-u-thai C, Glahn PR, Cheng Z, Fukai S, Rerkasem B, Huang L (2009) The bioavailability of iron fortified in whole grain parboiled rice. Food Chem 89:2565–2571
Qureshi S, Richards BK, Steenhuis TS, McBride MB, Baveye P, Dousset S (2004) Microbial acidification and pH effects on trace element release from sewage sludge. Environ Pollut 132:61–71
Raboy V, Dickinson DB (1993) Phytic acid levels in seeds of Glycine max and G. soja as influenced by phosphorus status. Crop Sci 33:1300–1305
Rahman H, Sabreen S, Alam S, Kawai S (2005) Effects of nickel on growth and composition of metal micronutrients in barley plants grown in nutrient solution. J Plant Nutr 28:393–404
Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2008) Effects of inoculation of plant-growth promoting bacteria on Ni uptake by Indian mustard. Bioresour Technol 99:3491–3498
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ghafoor A, Naeem A, Ali S, Sabir M, Qayyum MF (2015) Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soil and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16897–16906
Rengel Z, Graham RD (1995) Wheat genotypes differ in zinc efficiency when grown in the chelate-buffered nutrient solution. II. Nutrient uptake. Plant Soil 176:317–324
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Rehman MZ, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016a) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-6436-4
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ibrahim M, Rehman MZ, Abbas T, Ok YS (2016c) Mechanisms of biochar-mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2230–2248
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Keller C (2016b) Silicon alleviates Cd stress of wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in hydroponics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1414–1427
Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Rehman MZ, Hannan F, Keller C, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS (2016d) Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:43–53
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Hélène M, Keller C (2012) Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J Hazard Mater 209-210:326–334
Roitto M, Rautio P, Julkunen-Tiitto R, Kukkola E, Huttunen S (2005) Changes in the concentrations of phenolics and photosynthates in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) seedlings exposed to nickel and copper. Environ Pollut 137:603–609
Rubio MI, Escrig I, Martínez-Cortina C, López-Benet F, Sanz A (1994) Cadmium and nickel accumulation in rice plants. Effects on mineral nutrition and possible interactions of abscisic and gibberellic acids. Plant Growth Regul 14:151–157
Salt DE, Blaylock M, Kumar NPBA, Dusenkov V, Ensley BD, Chet I, Raskin I (1995) Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology 13:468–474
Solaiman ZM, Blackwell P, Abbott LK, Storer P (2010) Direct and residual effect of biochar application on mycorrhizal root colonisation, growth and nutrition of wheat. Aust J Soil Res 48:546–554
Sruthy OA, Jayalekshmi S (2014) Electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Int J Struct Civil Eng Res 3:103–111
Steel RGD, Torrie JH, Dickey DA (1997) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill Publishing Co., New York
Theil EC, Briat JF (2004) Plant ferritin and non-heme iron nutrition in humans; harvest plus technical monograph 1; International Food Policy Research Institute and International Center for Tropical. Agriculture, Washington DC
Thiel J, Riewe D, Rutten T, Melzer M, Friedel S, Bollenbeck F, Weschke W, Weber H (2012) Differentiation of endosperm transfer cells of barley: a comprehensive analysis at the micro-scale. Plant J 71:639–655
Usman ARA, Alkredaa RS, Al-Wabel MI (2013) Heavy metal contamination in sediments and mangroves from the coast of RedSea: Avicennia marina as potential metal bioaccumulator. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 97:263–270
Velikova V, Tsonev T, Loreto F, Centritto M (2010) Changes in photosynthesis, mesophyll conductance to CO2, and isoprenoid emissions in Populus nigra plants exposed to excess nickel. Environ Pollut 1–9
Wang J, Pan X, Liu Y, Zhang X, Xiong Z (2012) Effects of biochar amendment in two soils on greenhouse gas emissions and crop production. Plant Soil 360:287–298
Wang K, Gao F, Ji YX, Liu Y, Dan ZW, Yang PF, Zhu YG, Li SQ (2013a) ORFH79 impairs mitochondrial function via interaction with a subunit of electron transport chain complex III in Honglian cytoplasmic male sterile rice. New Phytol 198:408–418
Watanabe FS, Olsen SR (1965) Test of an ascorbic acid method for determining phosphorus in water and NaHCO3 extracts. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 29:677–678
Welch RM, Graham RD (2004) Breeding for micronutrients in staple food crops from a human nutrition perspective. J Exp Bot 55:353–364
Wood BW (2013) Iron-induced nickel deficiency in pecan. Hortic Sci 48:1145–1153
Yang X, Baligar VC, Martens DC, Clark PB (1996) Plant tolerance to nickel toxicity. II Nickel effect on influx and transport of mineral nutrients in four plant species. J Plant Nutr 19:265–279
Zhou JR, Erdman JW Jr (1995) Phytic acid in health and disease. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 35:495–508
Zielińska-Dawidziak M (2015) Plant ferritin—a source of iron to prevent its deficiency. Nutrients 7:1184–1201
Acknowledgment
We are highly thankful to the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan, and Government College University, Faisalabad, Pakistan, for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramzani, P.M.A., Khan, WuD., Iqbal, M. et al. Effect of different amendments on rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth, yield, nutrient uptake and grain quality in Ni-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 18585–18595 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7038-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7038-x