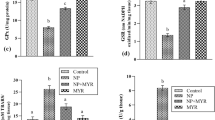
Abstract
Benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) is an environmental toxicant and endocrine disruptor. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the toxicity of B[a]P in testis of rats and also to study the role of silymarin and thymoquinone (TQ) as natural antioxidants in the alleviation of such toxicity. Data of the present study showed that levels of testosterone, estrogen and progesterone were significantly decreased after treatment of rats with B[a]P. In addition, B[a]P caused downregulation of the expressions of steroidogenic enzymes including CYP17A1 and CP19A1, and decreased the activity of 17-β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (17β-HSD). Moreover, B[a]P decreased the activities of antioxidant enzymes including catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), and significantly increased free radicals levels in testis of male rats. However, pretreatment of rats with silymarin prior to administration of B[a]P was found to restore the level of free radicals, antioxidant status, and activities of steroidogenic enzymes to their normal levels in testicular tissues. Moreover, histopathological finding showed that silymarin recovered the abnormalities occurred in tubules caused by B[a] P in testis of rats. On the other hand, TQ showed pro-oxidant effects and did not ameliorate the toxic effects of B[a] P on the testicular tissue since it decreased antioxidant enzymes activities and inhibited the protein expression of CYP11A1 and CYP21A2 compared to control rats. Moreover, TQ decreased the levels of testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone either in the presence or absence of B[a]P. It is concluded that B[a]P decreased testosterone levels, inhibited antioxidant enzymes activities, caused downregulation of CYP isozymes involved in steroidogenesis, and increased free radical levels in testis. Moreover, silymarin was more effective than TQ in restoring organism health and alleviating the deleterious effects caused by B[a]P in the testis of rats. Due to its negative impact, it is highly recommended to limit the use of TQ as a dietary supplement since millions of people in the Middle East are using it to improve their health.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken RJ, Roman SD (2008) Antioxidant systems and oxidative stress in the testes. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 1(1):15–24
Beers RF Jr, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195(1):133–140
Bogovich K, Payne AH (1980) Purification of rat testicular microsomal 17-ketosteroid reductase. Evidence that 17-ketosteroid reductase and 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase are distinct enzymes. J Biol Chem 255(12):5552–5559
Bolton JL, Trush MA, Penning TM et al (2000) Role of quinones in toxicology. Chem Res Toxicol 13(3):135–160
Bonde JP (1996) Environmental factors. In: Comhaire FH (ed) Male infertility, clinical investigation, cause evaluation and treatment. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 267–284
Bostrom CE, Gerde P, Hanberg A et al (2002) Cancer risk assessment, indicators, and guidelines for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the ambient air. Environ Health Perspect 110(Suppl 3):451–488
Carleton HM, Drury RAB, Wallington EA (1967) Carleton’s histological technique. Oxford University Press, Toronto
Chandrashekar N, Selvamani A, Subramanian R, Pandi A, Thiruvengadam D (2012) Baicalein inhibits pulmonary carcinogenesis-associated inflammation and interferes with COX-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in-vivo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 261(1):10–21
Chen X, An H, Ao L et al (2011) The combined toxicity of dibutyl phthalate and benzo (a) pyrene on the reproductive system of male Sprague Dawley rats in vivo. J Hazard Mater 186(1):835–841
Chiu DT, Stults FH, Tappel AL (1976) Purification and properties of rat lung soluble glutathione peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta 445(3):558–566
Choudhary R, Chawala VK, Soni ND et al (2010) Oxidative stress and role of antioxidants in male infertility. Pak J Physiol 6(2):54–59
Chung JY, Kim YJ, Kim JY et al (2011) Benzo[a]pyrene reduces testosterone production in rat Leydig cells via a direct disturbance of testicular steroidogenic machinery. Environ Health Perspect 119(11):1569–1574
Duan L, Tang Y, Chen CZ et al (2013) Effects of benzo(a)pyrene exposure on oxidative stress and ATPase in the hippocampus of rats. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 31(7):500–503
El-Shahat AE-R, Gabr A, Meki A-R et al (2009) Altered testicular morphology and oxidative stress induced by cadmium in experimental rats and protective effect of simultaneous green tea extract. Int J Morphol 27(3):757–764
Fatemi N, Sanati MH, Jamali Zavarehei M et al (2013) Effect of tertiary-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP)-induced oxidative stress on mice sperm quality and testis histopathology. Andrologia 45(4):232–239
Frasor J, Weaver AE, Pradhan M et al (2008) Synergistic up-regulation of prostaglandin E synthase expression in breast cancer cells by 17beta-estradiol and proinflammatory cytokines. Endocrinology 149(12):6272–6279
Georgellis A, Parvinen M, Rydström J (1989) Inhibition of stage-specific DNA synthesis in rat spermatogenic cells by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chem Biol Interact 72(1):79–92
Ghosh D, Das UB, Ghosh S et al (2002) Testicular gametogenic and steroidogenic activities in cyclophosphamide treated rat: a correlative study with testicular oxidative stress. Drug Chem Toxicol 25(3):281–292
Gill-Sharma MK, Dsouza S, Padwal V et al (2001) Antifertility effects of estradiol in adult male rats. J Endocrinol Investig 24(8):598–607
Gu A, Ji G, Long Y, Zhou Y, Shi X, Song L, Wang X (2011) Assessment of an association between an aryl hydrocarbon receptor gene (AHR) polymorphism and risk of male infertility. Toxicol Sci 122(2):415–421
Hamada AJ, Montgomery B, Agarwal A (2012) Male infertility: a critical review of pharmacologic management. Expert Opin Pharmacother 13(17):2511–2531
Jeng HA, Chen YL (2014) Orally subchronic exposure to benzo [a] pyrene alters reproductive hormone profile. Polycycl Aromat Compd 34(1):54–68
Ji K, Xing C, Jiang F et al (2013) Benzo [a] pyrene induces oxidative stress and endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction via the activation of the NF-kB pathway. Int J Mol Med 31(4):922–930
Jiang J, Briedé JJ, Jennen DG, Van Summeren A, Saritas-Brauers K, Schaart G, Kleinjans JC, de Kok TM (2015) Increased mitochondrial ROS formation by acetaminophen in human hepatic cells is associated with gene expression changes suggesting disruption of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Toxicol Lett 234(2):139–150
Kaina B (2003) DNA damage-triggered apoptosis: critical role of DNA repair, double-strand breaks, cell proliferation and signaling. Biochem Pharmacol 66(8):1547–1554
Koka PS, Mondal D, Schultz M et al (2010) Studies on molecular mechanisms of growth inhibitory effects of thymoquinone against prostate cancer cells: role of reactive oxygen species. Exp Biol Med 235(6):751–760
Li D, Xu D, Wang T et al (2015) Silymarin attenuates airway inflammation induced by cigarette smoke in mice. Inflammation 38(2):871–878
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL et al (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247(10):3170–3175
Mukhopadhyay D, Nandi P, Varghese AC, Gutgutia R, Banerjee S, Bhattacharyya AK (2010) The in vitro effect of benzo[a]pyrene on human sperm hyperactivation and acrosome reaction. Fertil Steril 94(2):595–598
Neal MS, Zhu J, Foster WG (2008) Quantification of benzo[a]pyrene and other PAHs in the serum and follicular fluid of smokers versus non-smokers. Reprod Toxicol 25(1):100–106
Neuvians TP, Schams D, Berisha B et al (2004) Involvement of pro-inflammatory cytokines, mediators of inflammation, and basic fibroblast growth factor in prostaglandin F2alpha-induced luteolysis in bovine corpus luteum. Biol Reprod 70(2):473–480
Perrin J, Tassistro V, Mandon M, Grillo JM, Botta A, Sari-Minodier I (2011) Tobacco consumption and benzo(a)pyrene-diol-epoxide-DNA adducts in spermatozoa: in smokers, swim-up procedure selects spermatozoa with decreased DNA damage. Fertil Steril 95(6):2013–2017
Rahmani AH, Alzohairy MA, Khan MA et al (2014) Therapeutic implications of black seed and its constituent thymoquinone in the prevention of cancer through inactivation and activation of molecular pathways. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. doi:10.1155/2014/724658
Reddy KP, Girish BP, Reddy PS (2015) Reproductive and paternal mediated developmental toxicity of benzo (a) pyrene in adult male Wistar rats. Toxicol Res 4(2):223–232
Russo A, Troncoso N, Sanchez F, Garbarino JA, Vanella A (2006) Propolis protects human spermatozoa from DNA damage caused by benzo[a]pyrene and exogenous reactive oxygen species. Life Sci 78(13):1401–1406
Sheweita SA (2000) Drug-metabolizing enzymes: mechanisms and functions. Curr Drug Metab 1(2):107–132
Sheweita SA, Sheikh BY (2011) Can dietary antioxidants reduce the incidence of brain tumors? Curr Drug Metab 12(6):587–593
Sheweita SA, Tilmisany AM, Al-Sawaf H (2005) Mechanisms of male infertility: role of antioxidants. Curr Drug Metab 6(5):495–501
Shikita M, Talalay P (1979) Preparation of highly purified 3 alpha- and 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases from Pseudomonas sp. Anal Biochem 95(1):286–292
Shimizu Y, Nakatsuru Y, Ichinose M et al (2000) Benzo[a]pyrene carcinogenicity is lost in mice lacking the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(2):779–782
Shuangmei T, Pan L, Tao Y, Sun X (2015) Environmentally relevant concentrations of benzo [a] pyrene affect steroid levels and affect gonad of male scallop Chlamys farreri. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 114:150–156
Spira A, Multigner L (1998) The effect of industrial and agricultural pollution on human spermatogenesis. Hum Reprod 13(8):2041–2042
Surai PF (2015) Silymarin as a natural antioxidant: an overview of the current evidence and perspectives. Antioxidants (Basel) 4(1):204–247
Tian S, Pan L, Tao Y et al (2015) Environmentally relevant concentrations of benzo[a]pyrene affect steroid levels and affect gonad of male scallop Chlamys farreri. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 114:150–156
Tsuji G, Takahara M, Uchi H et al (2011) An environmental contaminant, benzo (a) pyrene, induces oxidative stress-mediated interleukin-8 production in human keratinocytes via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway. J Dermatol Sci 62(1):42–49
Turner TT, Lysiak JJ (2008) Oxidative stress: a common factor in testicular dysfunction. J Androl 29(5):488–498
Vasdev S, Gill VD, Singal PK (2006) Modulation of oxidative stress-induced changes in hypertension and atherosclerosis by antioxidants. Exp Clin Cardiol 11(3):206–216
Wajid N, Ali F, Tahir M et al (2014) Dual properties of Nigella sativa: anti-oxidant and pro-oxidant. Adv Life Sci 1(2):79–88
Williams G (2012) Aromatase up-regulation, insulin and raised intracellular oestrogens in men, induce adiposity, metabolic syndrome and prostate disease, via aberrant ER-alpha and GPER signalling. Mol Cell Endocrinol 351(2):269–278
Yu SM, Kim SJ (2015) The thymoquinone-induced production of reactive oxygen species promotes dedifferentiation through the ERK pathway and inflammation through the p38 and PI3K pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med 35(2):325–332
Zheng SJ, Tian HJ, Cao J, Gao YQ (2010) Exposure to di(n-butyl)phthalate and benzo(a)pyrene alters IL-1β secretion and subset expression of testicular macrophages, resulting in decreased testosterone production in rats. J Biol Chem 255 no 12 (1980): 5552–5559. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 248(1):28–37
Zubair H, Khan HY, Sohail A et al (2013) Redox cycling of endogenous copper by thymoquinone leads to ROS-mediated DNA breakage and consequent cell death: putative anticancer mechanism of antioxidants. Cell Death Dis. doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Markus Hecker
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheweita, S.A., Al-Shora, S. & Hassan, M. Effects of benzo[a]pyrene as an environmental pollutant and two natural antioxidants on biomarkers of reproductive dysfunction in male rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 17226–17235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6934-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6934-4