Abstract
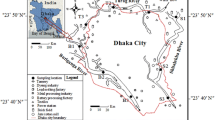
The aim of this study was to investigate the presence of metal contamination in water, sediments and three different fish species. All samples were taken from the Danube River in Belgrade Region, a location upstream from Grocka. Concentrations of Cd, Hg and Pb in water samples were not detected, while concentrations of Zn, Fe, Cu and As were in the range of 0.004–0.41 mg L−1. Iron was the most deposited metal in sediment samples (17,530.00 mg kg−1). For the purpose of heavy metal determination in fish tissue, silver carp, common carp and wels catfish were collected. Concentrations of Pb, Cd and As were determined in muscle, digestive tract and liver by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrophotometry (IPC-OES). The highest concentration of Pb was in the digestive tract of all three fish species, while Cd was mostly deposited in the liver. The highest concentration of Hg was in the muscle tissue of wels catfish, and these values are above the maximum residual levels prescribed by the European Union and the maximum allowed concentrations (MACs) for Serbia. Concentration of As was mostly deposited in the liver, but under the MAC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari S, Ghosh L, Rai S, Ayyappan S (2009) Metal concentrations in water, sediment, and fish from sewage-fed aquaculture ponds of Kolkata, India. Environ Monit Assess 159:217–230
Agarwal R, Kumar R, Behari J (2007) Mercury and lead content in fish species from the River Gomti, Lucknow, India, as biomarkers of contamination. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78:118–122
Ajeagah C, Maria P, Mirela O, Constantin M, Palela G, Bahrim G (2013) An ecological assessment of the pollution status of the Danube River basin in the Galati Region—Romania. J Water Resour Prot 5:876–886
Alimentarius Codex Commissione: (2012) Joint FAO/WHO food standards programme Codex committee on contaminants in food, sixth session, Maastricht, The Netherlands
Alloway B. (2013) Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability. Environ. Pollut doi:10.1007/978-94-007-4470-7_1
Bervoets L, Blust R (2003) Metal concentrations in water, sediments and gudgeon (Gobio gobio) from a pollution gradient: relationship with fish condition factor. Environ Pollut 126:9–19
Canli M, Guluzar A (2003) The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ Pollut 121:129–136
Dural M, Goksu MZL, Ozak AA (2007) Investigation of heavy metal levels in economically important fish species captured from the Tuzla Lagoon. Food Chem 102:415–421
Gammons C, Slotton D, Gerbrandt B, Weight W, Young C, McNearny R (2006) Mercury concentration of fish, river water, and sediment in the Río Ramis-Lake Titicaca watershed, Peru. Sci Total Environ 368:637–648
Gu YG, Wang XN, Lin Q, Du FY, Ning JJ, Wang LG, Li YF (2016a) Fuzzy comprehensive assessment of heavy metals and Pb isotopic signature in surface sediments from a bay under serious anthropogenic influences: Daya Bay, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:38–44
Gu YG, Gao YP, Lin Q (2016b) Contamination, bioaccessibility and human health risk of heavy metals in exposed-lawn soils from 28 urban parks in southern China’s largest city, Guangzhou. Appl Geochem 67:52–58
Gundacker C (2000) Comparison of heavy metal bioaccumulation in freshwater molluscs of urban river habitats in Vienna. Environ Pollut 110(1):61–71
Has-Schön E, Bogut I, Strelec I (2006) Heavy metal profile in five fish species included in human diet, domiciled in the end flow of River Neretva (Croatia). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:545–551
Janjić J, Ivanović J, Marković R, Starčević M, Bošković M, Đorđević V, Baltić ŽM (2015) Metal concentration in muscle tissue of carp and pike from different fish ponds in Belgrade area. J Agric Sci Technol 5:429–436
Jarić S, Cvijanović G, Hegediš A, Lenhardt M (2012) Assessing the range of newly established invasive species in rivers using probabilistic methods. Hydrobiologia 680:171–178
Jorgensen S E (Ed.) (2011) Handbook of ecological models used in ecosystem and environmental management. CRC press 3
Lenhardt M, Markovic G, Hegedis A, Maletin S, Cirkovic M, Markovic Z (2011) Non-native and translocated fish species in Serbia and their impact on the native ichthyofauna. Rev Fish Biol Fish 21(3):407–421
MacDonald D, Ingersoll C, Berger T (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Maceda-Veiga A, Monroy M, Navarro E, Viscor E, Sostoa A (2013) Metal concentrations and pathological responses of wild native fish exposed to sewage discharge in a Mediterranean river. Sci Total Environ 449:9–19
Mendil D, Unal F, Tuzen M, Soylak M (2010) Determination of trace metals in different fish species and sediments from the River Yesilırmak in Tokat, Turkey. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1383–1392
Milanov R, Krstić M, Marković R, Jovanović D, Baltić B, Ivanović J, Jovetić M, Baltić ŽM (2016) Analysis of heavy metals concentration in tissues of three different fish species included in human diet from Danube River, in the Belgrade Region, Serbia. Acta Vet (Beograd) 66(1):89–102
Milenkovic N, Damjanovic M, Ristic M (2005) Study of heavy metal pollution in sediments from the Iron Gate (Danube River), Serbia and Montenegro. Pol J Environ Stud 14(6):781–787
Miller PA, Munkittrick KR, Dixon DG (1992) Relationship between concentrations of copper and zinc in water, sediment, benthic invertebrates, and tissues of white sucker (Catostomus commersoni). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49(5):978–984
Monroy M, Maceda-Veiga A, Sostoa A (2014) Metal concentration in water, sediment and four fish species from Lake Titicaca reveals a large-scale environmental concern. Sci Total Environ 487:233–244
Noël L, Chekri R, Millour S, Merlo M, Leblanc J, Guérin T (2013) Distribution and relationships of As, Cd, Pb and Hg in freshwater fish from five French fishing areas. Chemosphere 90:1900–1910
Official Gazette of Republic of Serbia (2011) No. 28/2011 Regulation on quantity of pesticides, metals, metalloids, and other toxic substances, chemotherapeutics, anabolics, and other substances which can be found in food
Official Journal of the European Communities (2001) Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 466/2001
Pajević S, Borišev M, Rončević S, Vukov D, Igić R (2008) Heavy metal accumulation of Danube river aquatic plants—indication of chemical contamination. Open Life Sci 3(3):285–294
Pantelica A, Ene A, Georgescu II (2012) Instrumental neutron activation analysis of some fish species from Danube River in Romania. Microchem J 103:142–147
Poleksić V, Lenhardt M, Jarić I, Djordjević D, Gačić Z, Cvijanović M, Rašković B (2010) Liver, gills and skin histopathology and heavy metals content of the Danube sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus Linnaeus, 1758). Environ Toxicol Chem 29(3):515–521
Regulation Commision (2006) No 1881/2006 of 19 December. Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs
Regulation Council (2001) No 2375/2001 of 29 November 2001 amending Commission Regulation (EC) No 466/2001 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Communities, L, 321(1): 6–12
Squadrone S, Prearo M, Brizio P, Gavinelli S, Pellegrino M, Scanzio T, Guarise S, Benedetto A, Abete M (2013) Heavy metals distribution in muscle, liver, kidney and gill of European catfish (Silurus glanis) from Italian rivers. Chemosphere 90:358–365
Subotić S, Jeftić ŽV, Spasić S, Hegediš A, Krpo-Ćetković J, Lenhardt M (2013) Distribution and accumulation of elements (As, Cu, Fe, Hg, Mn, and Zn) in tissues of fish species from different trophic levels in the Danube River at the confluence with the Sava River (Serbia). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(8):5309–5317
Verep B, Multu C, Apaydin G, Cevik U (2012) The trace element analysis in freshwater fish species, water and sediments in Iyidere Stream (Rize-Turkey). Pak J Biol Sci 15(14):658–665
Vuković Ž, Vuković D, Radenković M, Stanković S (2012) A new approach to the analysis of the accumulation and enrichment of heavy metals in the Danube River sediment along the Iron Gate reservoir in Serbia. J Serb Chem Soc 77(3):381–392
Vuković D, Vuković Ž, Stanković S (2014) The impact of the Danube Iron Gate Dam on heavy metal storage and sediment flux within the reservoir. Catena 113:18–23
Wei Y, Zhang J, Zhang D, Tu T, Luo L (2014) Metal concentrations in various fish organs of different fish species from Poyang Lake, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:182–188
Zrnčić S, Oraić D, Ćaleta M, Mihaljević Ž, Zanella D, Bilandžić N (2013) Biomonitoring of heavy metals in fish from the Danube River. Environ Monit Assess 185:1189–1198
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development, Republic of Serbia, via the project “Selected biological hazards to the safety/quality of food of animal origin and control measures from farm to consumer” (31034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Céline Guéguen
Highlights
• Cd, Hg and Pb concentrations in water were not detected.
• Danube sediments had high levels of Fe, Zn and Pb.
• High levels of Hg were found in the muscle tissue of wels catfish from the Danube River.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanović, J., Janjić, J., Baltić, M. et al. Metal concentrations in water, sediment and three fish species from the Danube River, Serbia: a cause for environmental concern. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 17105–17112 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6875-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6875-y