Abstract
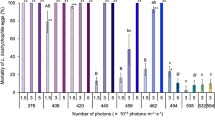
The ultraviolet light (UV-A) range of 320–400 nm is widely used as light trap for insect pests. Present investigation was aimed to determine the effect of UV light-A radiation on development, adult longevity, reproduction, and development of F1 generation of Mythimna separata. Our results revealed that the mortality of the second instar larvae was higher than the third and fourth instar larvae after UV-A radiation. As the time of UV-A irradiation for pupae prolonged, the rate of adult emergence reduced. Along with the extension of radiation time decreased the longevity of adult females and males. However, the radiation exposure of 1 and 4 h/day increased fecundity of female adults, and a significant difference was observed in a 1 h/day group. The oviposition rates of female adults in all the treatments were significantly higher than the control. In addition, UV-A radiation treatments resulted in declined cumulative survival of F1 immature stages (eggs, larvae, and pupae). After exposure time of 4 and 7 h/day, the developmental periods of F1 larvae increased significantly, but no significant effects on F1 pupal period were recorded.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antignus Y (2000) Manipulation of wavelength-dependent behaviour of insects: an IPM tool to impede insects and restrict epidemics of insect-borne viruses. Virus Res 71:213–220
Barlett AC, Hooker PA, Hardee DD (1968) Behaviour of irradiated boll weevils. I. Feeding, attraction, mating and mortality. J Econ Entomol 61:1677–1680
Chen RL, Bao XZ (1987) Research on the migration of oriental armyworm in China and a discussion of management strategy. Insect Sci Appl 8:571–572
Chen RL, Sun YJ, Wang SY, Zhai BP, Bao XZ (1995) Migration of the oriental armyworm Mythimna separata in East Aisa in relation to weather and climate. I. Northeastern China. In: Drake VA, Gatehouse AG (eds) Insect migration: tracking resource in space and time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 93–104
Chun BF (1981) A new artificial diet for army worm. Acta Entomol Sin 24:379–383
De Jong G, Van Noordwijk AJ (1992) Acquisition and allocation of resources: genetic (co) variances, selection, and life histories. Am Nat 139:749–770
Emura K, Tazawa S (2004) The development of the eco-engineering insect control technology-physical control of insect behavior using artificial lights. Eco-engineering 16:237
Faruki SI, Das DR, Khatun S (2005) Effects of UV-radiation on the larvae of the lesser mealworm, Alphitobius diaperinus (Panzer) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) and their progeny. J Biol Sci 5:444–448
Faruki SI, Das DR, Khan AR, Khatu M (2007) Effects of ultraviolet (254nm) irradiation on egg hatching and adult emergence of the flour beetles Tribolium castaneum, T confusum and the almond moth Cadra cautella. J Insect Sci 7:1–6
Gintenreiter S, Ortel J, Nopp HJ (1993) Effects of different dietary levels of cadmium, lead copper, and zinc on the vitality of the forest pest insect Lymantria disparL. (Lymantriidae, Lepid). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 25:62–66
Gunn A (1998) The determination of larval phase coloration in the African armyworm Spodoptera exempta and its consequences for thermoregulation and protection from UV light. Entomol Exp Appl 86:125–133
Guven E, Pandir D, Bas H (2015) UV radiation-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage on Mediterranean flour moth, Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) larvae. Turk J Entomol 39:23–33
Hasan M (1995) Comparative sensitivity of Tribolium spp. To gamma irradiation throughout ontogeny. PhD Thesis, Newcastle Univ, UK, pp-261
Hasan M, Jahan MS, Khan AR (1998) Effect of ultraviolet irradiation on the Uzi-fly, Exorista sorbillans Wiedmann, an endoparasitoid of the silkworm, L. Int J Trop Insect Sci 18:87–91
Holloway GJ, Sibly RM, Povey SR (1990) Evolution in toxin-stressed evironments. Funct Ecol 4:289–294
Kojima Y, Aoyagi K, Yasue T (2005) Effect of lithium ion addition on afterglow time of green-emitting Ce3 + and Pr3 + codoped CaS phosphor by black light irradiation. J Lumin 115:13–18
LaChance LE, Richard RD, Proshold FI (1975) Radiation response in pink boll worm: a comparative study of sperm bundle production, Sperm transfer, and oviposition response elicited by native and laboratory reared males. Environ Entomol 4:321–324
Mackerness SAH, Surplus SL, Blake P, John CF, Buchanan-Wollaston V, Jordan BR, Thomas B (1999) Ultraviolet-B-induced stress and changes in gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana: role of signalling pathways controlled by jasmonic acid, ethylene and reactive oxygen species. Plant Cell Environ 22:1413–1423
Mazza CA, Izaguirre MM, Zavala J, Scopel AL, Ballare CL (2002) Insect perception of ambient ultraviolet-B radiation. Ecol Lett 5:722–726
McMillan TJ, Leatherman E, Ridley A, Shorrocks J, Tobi SE, Whiteside JR (2008) Cellular effects of long wavelength UV light (UVA) in mammalian cells. J Pharm Pharmacol 60:969–976
Meng JY, Zhang CY, Zhu F, Wang XP, Lei CL (2009) Ultraviolet light-induced oxidative stress: effects on antioxidant response of Helicoverpa armigera adults. J Insect Physiol 55:588–592
Meng JY, Zhang CY, Lei CL (2010) A proteomic analysis of Helicoverpa armigera adults after exposure to UV light irradiation. J Insect Physiol 56:405–411
Meyer-Rochow VB (2000) Risks, especially for the eye, emanating from the rise of solar UV-radiation in the Arctic and Antarctic regions. Int J Circ Health 59:38–51
North DT, Holt GG (1968) Inherited sterility in Progeny of irradiated male cabbage loopers. J Econ Entomol 61:928–931
Pandır D, Guven E (2014) Effect of microwave radiation on stored product pest Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) larvae. Turk J Entomol 38(2):135–142
Proverbs MD (1969) Sterilization and insect control. Annu Rev Entomol 14:81–102
Qureshi ZA, Wilbur DA, Mills RB (1970) Irradiation of early instar of the Angoumois moth. J Econ Entomol 63:1241–1247
Roff DA (1992) In: Roff DA (ed) The evolution of life histories: theory and analysis. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 384–385
Schauen M, Hornig-Do HT, Schomberg S, Herrmann G, Wiesner RJ (2007) Mitochondrial electron transport chain activity is not involved in ultraviolet A (UVA)-induced cell death. Free Radic Biol Med 42:499–509
Shayesteh N, Barthakur NN (1996) Mortality and behavior of two stored-product insect species during microwave irradiation. J Stored Prod Res 32:239–246
Steinbauer MJ (2003) Using ultra-violet light traps to monitor autumn gum moth, Mnesampela private (Lepidoptera: Geometridae), in south-east Australia. Aust For 66:279–286
Tilton EW, Brower JH (1983) Radiation effects of on arthropods. In: Josephson ES, Peterson MS, Boca R (eds) Preservation of food by ionizing radiation, vol 11. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, pp 269–316
Tsubaki Y, Bunroongsook S (1990) Sexual competitive ability of mass-reared male sand mate preference in wild females: their effect on eradication of melonflies. Appl Entomol Zool 25:457–466
Van Ooik T, Rantala MJ, Saloniemi I (2007) Dietmediated effects of heavy metal pollution on growth and immune response in the geometrid moth Epirrita autumnata. Environ Pollut 145:348–354
Van Steenyk RA, Henneberry TJ, Ballmer GR, Wolf WW, Sevacherian V (1979) Mating competitiveness of laboratory culture sandsterilized Pink boll worm for use in a sterile moth release programme. J Econ Entomol 72:502–550
Vile GF, Tyrrell RM (1995) UVA radiation-induced oxidative damage to lipids and proteins in vitro and in human skin fibroblasts is dependent on iron and singlet oxygen. Free Radic Biol Med 18:721–730
Watters FL (1976) Microwave radiation for control of Tribolium confusum in wheat and flour. J Stored Prod Res 12:19–25
Wei GS, Zhang QW, Zhou MZ, Wu WG (2000) Studies on the phototaxis of Helicoverpa armigera. Acta Biophys Sin 16:89–95
Williams GC (1966) Natural selection, the costs of reproduction, and a refinement of Lack’s principle. Am Nat 100:687–690
Yang YG, He DY, Zhu SM, Yang PZ, Zho YS (1984) Studies on the generations and migration of armyworm Mythimna separata (Walker) in Yunnan province. Zool Res 1:1–20
Ye PY (2012) Farmers battle armyworms. http://www.globaltimes.cn/content/726757.shtml
Zera AJ, Denno RF (1997) Physiology and ecology of dispersal polymorphism in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 42:207–231
Zera AJ, Harshman LG (2001) The physiology of lifehistory trade-offs in animals. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 32:95–126
Zhang CY, Meng JY, Wang XP, Lei CL (2011) Effects of UV-A exposures on longevity and reproduction in Helicoverpa armigera, and on the development of its F1 generation. Insect Sci 18:697–702
Zhao S, Qiu C, Xiong S, Cheng X (2007) A thermal lethal model of rice weevils subjected to microwave irradiation. J Stored Prod Res 43:430–434
Zheng JL (2011) Effect of UVA radiation on biological fitness and antioxidant system of fruit fly, Drosophila Melanogaster. M.S. thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the National Department Public Benefit (Agriculture) Research Foundation (201403031) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30871639).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, A., Rashid, M.A., Huang, Q.Y. et al. Effect of UV-A radiation as an environmental stress on the development, longevity, and reproduction of the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 17002–17007 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6865-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6865-0