Abstract
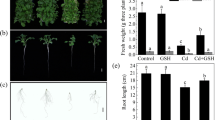
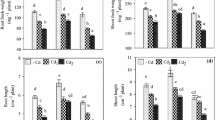
Cadmium (Cd) pollution is present in the world over especially in the industrialized parts of the world. To reduce Cd accumulation in various crops especially food crops, alleviating agents such as reduced glutathione (GSH) can be applied, which are capable either to exclude or to sequester Cd contamination. This study investigated the leaf-based spatial distribution of physiological, metabolic, and microstructural changes in two cotton cultivars (Coker 312 and TM-1) under GSH-mediated Cd stress using single levels of Cd (50 μM) and GSH (50 μM) both separately and in mix along with control. Results showed that GSH revived the morphology and physiology of both cotton cultivars alone or in mix with Cd. Cd uptake was enhanced in all segments of leaf and whole leaf upon the addition of GSH. GSH alleviated Cd-induced reduction in the photosynthetic pigment compositions and chlorophyll a fluorescence parameters. Mean data of biomarkers (2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium (TTC), total soluble protein (TSP), malondialdehyde (MDA), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)) revealed the adverse effects of Cd stress on leaf segments of both cultivars, which were revived by GSH. The oxidative metabolism induced by Cd stress was profoundly influenced by exogenous GSH application. The microstructural alterations were mainly confined to chloroplastic regions of leaves under Cd-stressed conditions, which were greatly revived upon the GSH addition. As a whole, Cd stress greatly affected TM-1 as compared to Coker 312. These results suggest a positive role of GSH in alleviating Cd-mediated changes in different leaf sections of cotton cultivars.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahammed GJ, Choudhary SP, Chen S, Xia X, Shi K, Zhou Y, Yu Y (2012) Role of brassinosteroids in alleviation of phenanthrene–cadmium co-contamination-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in tomato. J Exp Bot 63:695–709
Ahsan N, Renault J, Komatsu S (2009) Recent developments in the application of proteomics to the analysis of plant responses to heavy metals. Proteom 9:2602–2621
Anwaar SA, Ali S, Ishaque W, Farid M, Farooq MA, Najeeb U, Abbas F, Sharif M (2014) Silicon (Si) alleviates cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) from zinc (Zn) toxicity stress by limiting Zn uptake and oxidative damage. Environ Sci Pollu Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3938-9
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2005) Cadmium–zinc interactions in a hydroponic system using Ceratophyllum demersum L.: adaptive ecophysiology, biochemistry and molecular toxicology, Braz. J. Plant Physiol 17:3–20
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34
Bernstein N, Shoresh M, Xu Y, Huang B (2010) Involvement of the plant antioxidative response in the differential growth sensitivity to salinity of leaves vs roots during cell development. Free Radical Biol Med 49:1161–1171
Bradford NM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cai Y, Cao F, Wei K, Zhang GP, Wu FB (2011) Genotypic dependent effect of exogenous glutathione on Cd-induced changes in proteins, ultrastructure and antioxidant defense enzymes in rice seedlings. J Hazard Mater 192:1056–1066
Chaffei C, Pageau K, Suzuki A, Gouia H, Ghorbel HM, Mascalaux-Daubresse C (2004) Cadmium toxicity induced changes in nitrogen management in Lycopersicon esculentum leading to a metabolic safeguard through an amino acid storage strategy. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1681–1693
Chen F, Wang F, Wu F, Mao W, Zhang G, Zhou M (2010) Modulation of exogenous glutathione in antioxidant defense system against Cd stress in the two barley genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:663–672
Cherkasov AS, Taylor C, Sokolova IM (2010) Seasonal variation in mitochondrial responses to cadmium and temperature in eastern oysters Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin) from different latitudes. Aquat Toxicol 97:68–78
Clemens S (2006) Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochim 88:1707–1719
Cosio C, DeSantis L, Frey B, Diallo S, Keller C (2005) Cadmium distribution in leaves of Thlaspi caerulescens. J Exp Bot 56:765–775
Cosio C, Vollenweider P, Keller C (2006) Localization and effects of cadmium in leaves of a cadmium-tolerant willow (Salix viminalis L.): I. Macrolocalization and phytotoxic effects of cadmium. Environ Exp Bot 58:64–74
Daud MK, Sun YQ, Dawood M, Hayat Y, Variath MT, Wu YX, Raziuddin M, Salahuddin U, Najeeb U, Zhu SJ (2009a) Cadmium-induced functional and ultrastructural alterations in roots of two transgenic cotton cultivars. J Hazard Mater 161:463–473
Daud MK, Variath MT, Ali S, Najeeb U, Jamil M, Hayat Y, Dawood M, Khan MI, Zaffar M, Cheema SA, Tong XH, Zhu SJ (2009b) Cadmium-induced ultramorphological and physiological changes in leaves of two transgenic cotton cultivars and their wild relative. J Hazard Mater 168:614–625
Daud MK, Mei L, Ali B, Chen Y, Cheng X, Zhu SJ (2013) Cadmium-induced upregulation of lipid peroxidation and reactive oxygen species caused physiological, biochemical and ultra-structural changes in cotton seedlings. Biomed Res Interna. doi:10.1155/2013/374063
Daud MK, Quiling H, Lie M, Ali B, Zhu SJ (2015) Ultrastructural, metabolic and proteomic changes in leaves of upland cotton in response to cadmium stress. Chemosphere 120:309–320
Dawood M, Cao F, Jahangir MM, Zhang G, Wu F (2012) Alleviation of aluminum toxicity by hydrogen sulfide is related to elevated ATPase, and suppressed aluminum uptake and oxidative stress in barley. J Hazard Mater 209–210:121–128
Dazy M, Masfaraud JF, Ferard JF (2009) Induction of oxidative stress biomarkers associated with heavy metal stress in Fontinalis antipyretica Hedw. Chemosphere 75:297–302
Ernst S, Lau I, Ahner B, Kochian L (2002) Phytochelatins synthesis is not responsible for Cd tolerance in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant 214:635–640
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unraveling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Gong JM, Lee DA, Schroeder JI (2003) Long-distance root- to-shoot transport of phytochelatins and cadmium in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10118–10123
Hasan SA, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2011) Brassinosteroids protect photosynthetic machinery against the cadmium induced oxidative stress in two tomato cultivars. Chemosphere 84:1446–1451
Hegedüs A, Erdei S, Horváth G (2001) Comparative studies of H2O2 detoxifying enzymes in green and greening barley seedlings under cadmium stress. Plant Sci 160:1085–1093
Howden R, Goldsbrough PB, Andersen CR, Cobbett CS (1995) Cadmium sensitive, cad1 mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana are phytochelatin deficient. Plant Physiol 107:1059–1066
Jiang M, Zhang J (2002) Water stress-induced abscisic acid accumulation triggers the increased generation of reactive oxygen species and upregulates the activities of antioxidant enzymes in maize leaves. J Exp Bot 53:2401–2410
Jin X, Yang X, Islam E, Liu D, Mahmood Q (2008) Effects of cadmium on ultrastructure and antioxidative defense system in hyperaccumulator and non-hyperaccumulator ecotypes of Sedum alfredii Hance. J Hazard Mater 156(1–3):387–397
Joshi MK, Mohanty P (2004) Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a probe of heavy metal ion toxicity in plants in chlorophyll a fluorescence. Adv Photosyn Res 19:637–661
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food stuffs irrigated with wastewater in Beijing China. Environ Pollut 152:686–692
Khan S, Reid BJ, Li G, Zhu YG (2014) Application of biochar to soil reduces cancer risk via rice consumption: a case study in Miaoqian village, Longyan, China. Environ Int 68:154–161
Khan A, Khan S, Khan MA, Qamar Z, Waqas M (2015a) The uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by food plants, their effects on plants nutrients, and associated health risk: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:13772–13799
Khan S, Waqas M, Ding F, Shamshad I, Peter H, Arp H, Li G (2015b) The influence of various biochars on the bioaccessibility and bioaccumulation of PAHs and potentially toxic elements to turnips (Brassica rapa L.). J Hazard Mater 300:243–253
Kumar A, Prasad MNV, Achary MMVV, Panda BB (2013) Elucidation of lead-induced oxidative stress in Talinum triangulare roots by analysis of antioxidant responses and DNA damage at cellular level. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:4551–4561
Küpper H, Lombi E, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (2000) Cellular compartmentation of cadmium and zinc in relation to other elements in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. Plant 212:75–84
Lage-Pinto F, Oliveira JG, Cunha MD, Souza CMM, Rezende CE, Azevedo RA, Vitória AP (2008) Chlorophyll a fluorescence and ultrastructural changes in chloroplast of water hyacinth as indicators of environmental stress. Environ Exp Bot 64:307–331
Lannig G, Cherkasov AS, Sokolova IM (2006) Temperature-dependent effects of cadmium on mitochondrial and whole-organism bioenergetics of oysters (Crassostrea virginica). Mar Environ Res 62:79–82
Liu D, Kottke I (2004) Subcellular localization of cadmium in the root cells of Allium cepa by electron energy loss spectroscopy and cytochemistry. J Biosci 29:329–335
Liu XM, Kim KE, Kim KC, Nguyen XC, Han HJ, Jung MS, Kim HS, Kim SH, Park HGC, Yun DJ, Chung WS (2010) Cadmium activates Arabidopsis MPK3 and MPK6 via accumulation of reactive oxygen species. Phytochem 71:614–618
Maksymiec W, Wianowska D, Dawidowicz AL, Radkiewicz S, Mardarowicz M, Krupa Z (2005) The level of jasmonic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana and Phaseolus coccineus plants under heavy metal stress. J Plant Physiol 162:1338–1346
Masood A, Iqbal N, Khan NA (2012) Role of ethylene in alleviation of cadmium-induced photosynthetic capacity inhibition by sulphur in mustard. Plant, Cell Environ 35:524–533
Mendoza-Cózatl D, Loza-Tavera H, Hernández-Navarro A, Moreno-Sánchez R (2005) Sulfur assimilation and glutathione metabolism under cadmium stress in yeast, photosynthetic protists and plants. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:653–671
Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Govindarajan R, Kuriakose SV, Prasad MNV (2006) Phytochelatin synthesis and response of antioxidants during cadmium stress in Bacopa monnieri L. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:25–37
Najeeb U, Jilani G, Ali S, Sarwar M, Xu L, Zhou W (2011) Insights into cadmium induced physiological and ultrastructural disorders in Juncus effusus L. and its remediation through exogenous citric acid. J Hazard Mater 186:565–574
Nakamura S, Suzui N, Nagasaka T, Komatsu F, Ishioka NS, Ito-Tanabata S, Kawachi N, Rai H, Hattori H, Chino M, Fujimaki S (2013) Application of glutathione to roots selectively inhibits cadmium transport from roots to shoots in oilseed rape. J Exp Bot 64:1073–1081. doi:10.1093/jxb/ers388
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Noctor G, Queval G, Mhamdi A, Chaouch S, Foyer CH (2011) Glutathione. Arabidopsis Book 9:1–42
Noctor G, Lelarge-Trouverie C, Mhamdi A (2014) The metabolomics of oxidative stress. Phytochem. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.09.002
Pandey N, Sharma CP (2002) Effect of heavy metals Co2+, Ni2+ and Cd2+ on growth and metabolism of cabbage. Plant Sci 163:753–758
Rouhier N, Lemoire SD, Jacquot JP (2008) The role of glutathione in photosynthetic organisms: emerging functions for glutaredoxins and glutathionylation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:143–166. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092811
Salt DE, Rauser WE (1995) Mg ATP-dependent transport of phytochelatins across the tonoplast of oat roots. Plant Physiol 107:1293–1301
Sarry JE, Kuhn L, Ducruix C, Lafaye A, Junot C, Hugouvieux V, Jourdain A, Bastien O, Fievet JB, Vailhen D, Amekraz B, Moulin C, Ezan E, Garin J, Bourguignon J (2006) The early responses of Arabidopsis thaliana cells to cadmium exposure explored by protein and metabolite profiling analyses. Proteom 6:2180–2198
Schützendübel A, Schwanz P, Teichmann T, Gross K, Langenfeld-Heyser R, Godbold DL, Polle A (2001) Cadmium induced changes in antioxidative systems, hydrogen peroxide content, and differentiation in Scots pine roots. Plant Physiol 127:887–898
Sun HY, Wang XY, Dai HX, Zhang GP, Wu FB (2013) Effect of exogenous glutathione and selenium on cadmium-induced changes in cadmium and mineral concentrations and antioxidative metabolism in maize seedlings. Asia J Chem 25:2970–2976
Tian SK, Lu LL, Yang XE, Huang HG, Wang K, Brown PH (2012) Root adaptations to cadmium-induced oxidative stress contribute to Cd tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. Biol Plant 56:344–350
Vadas TM, Ahner BA (2009) Cysteine- and glutathione-mediated uptake of lead and cadmium into Zea mays and Brassica napus roots. Environ Pollut 157:2558–2563. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.02.036
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants. Plant Sci 151:59–66
Vitória AP, Rodriguez APM, Cunha M, Lea PJ, Azevedo RA (2004) Structural changes in radish seedlings (Raphanus sativus) exposed to cadmium. Biol Plant 47:561–568
Wang F, Chen F, Cai Y, Zhang G, Wu FB (2011) Modulation of exogenous glutathione in ultrastructure and photosynthetic performance against Cd stress in the two barley genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:1275–1288
Wu FB, Zhang GP, Dominy P (2003) Four barley genotypes respond differently to cadmium, lipid peroxidation and activities of antioxidant capacity. Environ Exp Bot 50:67–78
Wu FB, Chen F, Wei K, Zhang GP (2004) Effect of cadmium on free amino acid, glutathione and ascorbic acid concentrations in two barley genotypes (Hordeum vulgare L.) differing in cadmium tolerance. Chemosphere 57:447–454
Yousuf, P.Y., Hakeem, K.D.U.R., Chandna, R., Ahmad, P., 2012. Role of glutathione reductase in plant abiotic stress. P. Ahmad and M.N.V. Prasad (eds.), Abiotic stress responses in plants: metabolism, productivity and sustainability, DOI 10.1007/978-1-4614-0634-1_8.
Zapata JM, Salinas C, Calderón AA, Muñoz R, Ros Barceló A (1991) Reduction of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride by the KCN-insensitive salicylhydroxamic acid-sensitive alternative pathway of mitochondria from cultured grapevine cells. Plant Cell Rep 10:579–582
Zeng FR, Qui BY, Wu XJ, Niu SZ, Wu FB, Zhang GP (2012) Glutathione-mediated alleviation of chromium toxicity in rice plants. Biol Trace Elem Res 148:256–263
Zhang ZF, Zhang F, Raziuddin R, Gong HJ, Yang ZM, Lu L, Ye QF, Zhou WJ (2008) Effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid on oilseed rape seedling growth under herbicide toxicity stress. J Plant Growth Regul 27:159–169
Zhao FJ, Jiang RF, Dunham SJ, McGrath SP (2006) Cadmium uptake, translocation and tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. New Phytol 172:646–654
Zhou WJ, Leul M (1998) Uniconazole-induced alleviation of freezing injury in relation to changes in hormonal balance, enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in winter rape. J Plant Growth Regul 26:41–47
Acknowledgments
The project was financially supported by 973 Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China. Submitted paper is a part of first author postdoctoral research titled “Metabolomic, proteomic and transcriptomic changes in upland cotton under heavy metal stresses.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daud, M.K., Mei, L., Azizullah, A. et al. Leaf-based physiological, metabolic, and ultrastructural changes in cultivated cotton cultivars under cadmium stress mediated by glutathione. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 15551–15564 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6739-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6739-5