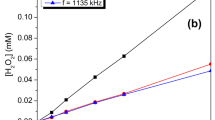
Abstract
Ultrasound is known to degrade organic compounds by pyrolysis and by the reaction of free radicals. In this work, sonolytic degradation of an identified water pollutant, coomassie brilliant blue (CBB), has been carried out in pure water as well as in river water. In the case of pure water, 90 % degradation was obtained after 30 min of sonication (350 kHz frequency, 60 W power), whereas in river water, the same efficiency was achieved only after 90 min. The degradation was also performed in the presence of varying concentration of (10–100 mg L−1) inorganic ions such as chloride, sulfate, nitrate, bicarbonate, and carbonate ions which were detected in the river water sample. Higher concentration of chloride enhanced the degradation due to the salting out mechanism. The enhancement of degradation in the presence of nitrate is mainly due to the change in the surface potential at the interface of the cavitating bubble. Bicarbonate ion and carbonate ion enhanced the degradation due to the involvement of carbonate radicals. A possible degradation mechanism is proposed based on the product profile determined by LC-Q-ToF-MS. The low efficiency of degradation in river water compared to that in pure water is likely due to the increased rate of bubble dissolution or escape of bubbles (degassing effect), and the scavenging of •OH by the organic content (high chemical oxygen demand (COD)).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashokkumar M (2011) The characterization of acoustic cavitation bubbles—an overview. Ultrason Sonochem 18:864–872. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.11.016
Autin O, Hart J, Jarvis P, MacAdam J, Parsons SA, Jefferson B (2013) The impact of background organic matter and alkalinity on the degradation of the pesticide metaldehyde by two advanced oxidation processes: UV/H2O2 and UV/TiO2. Water Res 47:2041–2049. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.01.022
Bukallah SB, Rauf MA, Ashraf SS (2007) Photocatalytic decoloration of Coomassie Brilliant Blue with titanium oxide. Dyes Pigments 72:353–356. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.09.016
Buxton GV, Greenstock CL, Helman WP, Ross AB (1988) Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals OH/⋅O− in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem Ref Data 17:513–886. doi:10.1063/1.555805
Chen S-N, Hoffman MZ, Parsons GH (1975) Reactivity of the carbonate radical toward aromatic compounds in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem 79:1911–1912. doi:10.1021/j100585a004
Cheng J, Vecitis CD, Park H, Mader BT, Hoffmann MR (2008) Sonochemical degradation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in landfill groundwater: environmental matrix effects. Environ Sci Technol 42:8057–8063. doi:10.1021/es8013858
Cheng J, Vecitis CD, Park H, Mader BT, Hoffmann MR (2009) Sonochemical degradation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in groundwater: kinetic effects of matrix inorganics. Environ Sci Technol 44:445–450. doi:10.1021/es902651g
Chowdhury P, Viraraghavan T (2009) Sonochemical degradation of chlorinated organic compounds, phenolic compounds and organic dyes—a review. Sci Total Environ 407:2474–2492. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.12.031
Colón I, Richoll SM (2005) Determination of methyl and ethyl esters of methanesulfonic, benzenesulfonic and p-toluenesulfonic acids in active pharmaceutical ingredients by solid-phase microextraction (SPME) coupled to GC/SIM-MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal 39:477–485. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2005.04.037
Colonna GM, Caronna T, Marcandalli B (1999) Oxidative degradation of dyes by ultraviolet radiation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Dyes Pigments 41:211–220. doi:10.1016/S0143-7208(98)00085-0
Ding F et al (2012) Potential toxicity and affinity of triphenylmethane dye malachite green to lysozyme. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:41–49. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.11.006
Grčić I, Papić S, Mesec D, Koprivanac N, Vujević D (2014) The kinetics and efficiency of UV assisted advanced oxidation of various types of commercial organic dyes in water. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 273:49–58. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2013.09.009
Guin JP, Bhardwaj YK, Naik DB, Varshney L (2014) Evaluation of efficiencies of radiolysis, photocatalysis and ozonolysis of modified simulated textile dye waste-water. RSC Adv 4:53921–53926. doi:10.1039/c4ra10304a
Jarvis NL, Scheiman MA (1968) Surface potentials of aqueous electrolyte solutions. J Phys Chem 72:74–78. doi:10.1021/j100847a014
Jiang Y, Pétrier C, Waite TD (2002) Effect of pH on the ultrasonic degradation of ionic aromatic compounds in aqueous solution. Ultrason Sonochem 9:163–168. doi:10.1016/S1350-4177(01)00114-6
Khan R, Bhawana P, Fulekar MH (2013) Microbial decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 12:75–97. doi:10.1007/s11157-012-9287-6
Kumar VV, Sathyaselvabala V, Premkumar MP, Vidyadevi T, Sivanesan S (2012) Biochemical characterization of three phase partitioned laccase and its application in decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes. J Mol Catal B Enzym 74:63–72. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2011.08.015
Makino K, Mossoba MM, Riesz P (1982) Chemical effects of ultrasound on aqueous solutions. Evidence for hydroxyl and hydrogen free radicals (.cntdot.OH and.cntdot.H) by spin trapping. J Am Chem Soc 104:3537–3539. doi:10.1021/ja00376a064
Merouani S, Hamdaoui O, Saoudi F, Chiha M, Pétrier C (2010) Influence of bicarbonate and carbonate ions on sonochemical degradation of Rhodamine B in aqueous phase. J Hazard Mater 175:593–599. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.046
Nakatani N, Hashimoto N, Shindo H, Yamamoto M, Kikkawa M, Sakugawa H (2007) Determination of photoformation rates and scavenging rate constants of hydroxyl radicals in natural waters using an automatic light irradiation and injection system. Anal Chim Acta 581:260–267. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2006.08.021
Nanzai B, Okitsu K, Takenaka N, Bandow H, Maeda Y (2008) Sonochemical degradation of various monocyclic aromatic compounds: relation between hydrophobicities of organic compounds and the decomposition rates. Ultrason Sonochem 15:478–483. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2007.06.010
Navarro NM, Chave T, Pochon P, Bisel I, Nikitenko SI (2011) Effect of ultrasonic frequency on the mechanism of formic acid sonolysis. J Phys Chem B 115:2024–2029. doi:10.1021/jp109444h
Nejumal KK, Manoj PR, Aravind U, Aravindakumar CT (2014) Sonochemical degradation of a pharmaceutical waste, atenolol, in aqueous medium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:4297–4308. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-2301-x
Nigam P, Banat IM, Singh D, Marchant R (1996) Microbial process for the decolorization of textile effluent containing azo, diazo and reactive dyes. Process Biochem 31:435–442. doi:10.1016/0032-9592(95)00085-2
O’Neill C, Hawkes FR, Hawkes DL, Lourenço ND, Pinheiro HM, Delée W (1999) Colour in textile effluents—sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74:1009–1018. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-4660(199911)74:11<1009::aid-jctb153>3.0.co;2-n
Pearce CI, Guthrie JT, Lloyd JR (2008) Reduction of pigment dispersions by Shewanella strain J18 143. Dyes Pigments 76:696–705. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.01.008
Pétrier C, Torres-Palma R, Combet E, Sarantakos G, Baup S, Pulgarin C (2010) Enhanced sonochemical degradation of bisphenol-A by bicarbonate ions. Ultrason Sonochem 17:111–115. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.05.010
Ramachandran H, Amirul AA (2013) Evaluation of unrefined glycerine pitch as an efficient renewable carbon resource for the biosynthesis of novel yellow-pigmented P(3HB-co-4HB) copolymer towards green technology. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 18:1250–1257. doi:10.1007/s12257-013-0452-8
Rauf MA, Ashraf S, Alhadrami SN (2005) Photolytic oxidation of Coomassie brilliant blue with H2O2. Dyes Pigments 66:197–200. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.09.006
Rayaroth MP, Aravind UK, Aravindakumar CT (2015a) Sonochemical degradation of Coomassie brilliant blue: effect of frequency, power density, pH and various additives. Chemosphere 119:848–855. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.037
Rayaroth MP, Khalid NK, Sasi S, Aravind UK, Aravindakumar CT (2015b) Identification of chlorophene in a backwater stream in Kerala (India) and its sonochemical degradation studies. Clean: Soil Air Water 43:1338–1343. doi:10.1002/clen.201400508
Šafařı́k I, Šafařı́ková M (2002) Detection of low concentrations of malachite green and crystal violet in water. Water Res 36:196–200. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00243-3
Sasi S, Rayaroth MP, Devadasan D, Aravind UK, Aravindakumar CT (2015) Influence of inorganic ions and selected emerging contaminants on the degradation of Methylparaben: a sonochemical approach. J Hazard Mater 300:202–209. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.072
Schwitzguebel JP, Aubert S, Grosse W, Laturnus F (2002) Sulphonated aromatic pollutants—limits of microbial degradability and potential of phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 9:62–72. doi:10.1007/bf02987317
Seymour JD, Gupta RB (1997) Oxidation of aqueous pollutants using ultrasound: salt-induced enhancement. Ind Eng Chem Res 36:3453–3457. doi:10.1021/ie970069o
Singh K, Arora S (2011) Removal of synthetic textile dyes from wastewaters: a critical review on present treatment technologies. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:807–878. doi:10.1080/10643380903218376
Sirés I, Guivarch E, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2008) Efficient removal of triphenylmethane dyes from aqueous medium by in situ electrogenerated Fenton’s reagent at carbon-felt cathode. Chemosphere 72:592–600. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.03.010
Sirés I, Brillas E, Oturan M, Rodrigo M, Panizza M (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow. A review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8336–8367. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-2783-1
Stopper H, Lutz WK (2002) Induction of micronuclei in human cell lines and primary cells by combination treatment with γ-radiation and ethyl methanesulfonate. Mutagenesis 17:177–181. doi:10.1093/mutage/17.2.177
Sunartio D, Ashokkumar M, Grieser F (2007) Study of the coalescence of acoustic bubbles as a function of frequency, power, and water-soluble additives. J Am Chem Soc 129:6031–6036. doi:10.1021/ja068980w
Torres RA, Abdelmalek F, Combet E, Pétrier C, Pulgarin C (2007) A comparative study of ultrasonic cavitation and Fenton’s reagent for bisphenol A degradation in deionised and natural waters. J Hazard Mater 146:546–551. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.056
Ziylan A, Koltypin Y, Gedanken A, Ince NH (2013) More on sonolytic and sonocatalytic decomposition of Diclofenac using zero-valent iron. Ultrason Sonochem 20:580–586. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2012.05.005
Acknowledgments
Financial support from Kerala State Council for Science Technology and Environment (KSCSTE) is gratefully acknowledged. CTA is thankful to DST, New Delhi (purse and FIST programmes), for partial financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Santiago V. Luis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rayaroth, M.P., Aravind, U.K. & Aravindakumar, C.T. Ultrasound based AOP for emerging pollutants: from degradation to mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 6261–6269 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6606-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6606-4