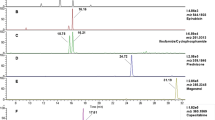
Abstract
This study describes a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analytical method for the analysis of cytostatic cyclophosphamide (CP), ifosfamide (IF) and their selected metabolites/transformation products (TPs): carboxy-cyclophosphamide (carboxy-CP), keto-cyclophosphamide (keto-CP) and 3-dechloroethyl-ifosfamide/N-dechloroethyl-cyclophosphamide (N-decl-CP) in wastewater (WW). Keto-cyclophosphamide, CP and IF were extracted with Oasis HLB and N-decl-CP and carboxy-CP with Isolute ENV+ cartridges. Analyte derivatization was performed by silylation (metabolites/TPs) and acetylation (CP and IF). The recoveries and LOQs of the developed method were 58, 87 and 103 % and 77.7, 43.7 and 6.7 ng L−1 for carboxy-CP, keto-CP and N-decl-CP, respectively. After validation, the analytical method was applied to hospital WW and influent and effluent samples of a receiving WW treatment plant. In hospital WW, levels up to 2690, 47.0, 13,200, 2100 and 178 ng L−1 were detected for CP, IF, carboxy-CP, N-decl-CP and keto-CP, respectively, while in influent and effluent samples concentrations were below LOQs. The formation of TPs during abiotic treatments was also studied. Liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry was used to identify CP and IF TPs in ultrapure water, treated with UV and UV/H2O2. UV treatment produced four CP TPs and four IF TPs, while UV/H2O2 resulted in five CPs and four IF TPs. Besides already known TPs, three novel TPs (CP-TP138a, imino-ifosfamide and IF-TP138) have been tentatively identified. In hospital WW treated by UV/O3/H2O2, none of the target metabolites/TPs resulted above LOQs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besse J-P, Latour J-F, Garric J (2012) Anticancer drugs in surface waters: what can we say about the occurrence and environmental significance of cytotoxic, cytostatic and endocrine therapy drugs? Environ Int 39:73–86
Booker V, Halsall C, Llewellyn N, Johnson A, Williams R (2014) Prioritising anticancer drugs for environmental monitoring and risk assessment purposes. Sci Total Environ 473–474:159–170
Buerge IJ, Buser H-R, Poiger T, Müller MD (2006) Occurrence and fate of the cytostatic drugs cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in wastewater and surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 40:7242–7250
Busetti F, Heitz A, Cuomo M, Badoer S, Traverso P (2006) Determination of sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous and solid samples from an Italian wastewater treatment plant. J Chromatogr A 1102:104–115
Busetti F, Linge KL, Heitz A (2009) Analysis of pharmaceuticals in indirect potable reuse systems using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216:5807–5818
Busetti F, Ruff M, Linge KL (2015) Target screening of chemicals of concern in recycled water. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 1:659–667
Castiglioni S, Bagnati R, Calamari D, Fanelli R, Zuccato E (2005) A multiresidue analytical method using solid-phase extraction and high-pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to measure pharmaceuticals of different therapeutic classes in urban wastewaters. J Chromatogr A 1092:206–215
Česen M, Kosjek T, Laimou-Geraniou M, Kompare B, Širok B, Lambropolou D, Heath E (2015) Occurrence of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in aqueous environment and their removal by biological and abiotic wastewater treatment processes. Sci Total Environ 527–528:465–473
Česen M, Eleršek T, Novak M, Žegura B, Kosjek T, Filipič M, Heath E (2016) Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of cyclophospamide, ifosfamide, their metabolites/transformation products and their mixtures. Environ Pollut 210:192–201
Chen Z, Park G, Herckes P, Westerhoff P (2008) Physicochemical treatment of three chemotherapy drugs: irinotecan, tamoxifen, and cyclophosphamide. J Adv Oxid Technol 11:254–260
Delgado LF, Faucet-Marquis V, Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Dorandeu C, Marion B, Schetrite S, Albasi C (2011) Cytotoxicity micropollutant removal in a crossflow membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 102:4395–4401
Eitel A, Scherrer M, Kümmerer K (2000) Handling cytostatic drugs: a practical guide (monograph). http://www.bms.com/Documents/sustainability/downloads/zyto_e.pdf
Farré M l, Pérez S, Kantiani L, Barceló D (2008) Fate and toxicity of emerging pollutants, their metabolites and transformation products in the aquatic environment. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 27:991–1007
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136:E359–E386
Fernández LA, Hernández C, Bataller M, Véliz E, López A, Ledea O, Padrón S (2010) Cyclophosphamide degradation by advanced oxidation processes. Water Environ J 24:174–180
Ferrando-Climent L, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Barceló D (2013) Development of a UPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of ten anticancer drugs in hospital and urban wastewaters, and its application for the screening of human metabolites assisted by information-dependent acquisition tool (IDA) in sewage samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:5937–5952
Franquet-Griell H, Gómez-Canela C, Ventura F, Lacorte S (2015) Predicting concentrations of cytostatic drugs in sewage effluents and surface waters of Catalonia (NE Spain). Environ Res 138:161–172
Garcia-Ac A, Broséus R, Vincent S, Barbeau B, Prévost M, Sauvé S (2010) Oxidation kinetics of cyclophosphamide and methotrexate by ozone in drinking water. Chemosphere 79:1056–1063
Gilard V, Malet-Martino MC, de Forni M, Niemeyer U, Ader JC, Martino R (1993) Determination of the urinary excretion of ifosfamide and its phosphorated metabolites by phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 31:387–394
Gómez-Canela C, Cortés-Francisco N, Oliva X, Pujol C, Ventura F, Lacorte S, Caixach J (2012) Occurrence of cyclophosphamide and epirubicin in wastewaters by direct injection analysis–liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:3210–3218
Gomez-Canela C, Ventura F, Caixach J, Lacorte S (2014) Occurrence of cytostatic compounds in hospital effluents and wastewaters, determined by liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:3801–3814
Joqueviel C, Martino R, Gilard V, Malet-Martino M, Canal P, Niemeyer U (1998) Urinary Excretion of Cyclophosphamide in Humans, Determined by Phosphorus-31 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Drug Metab Dispos 26:418–428
Kaijser GP, Beijnen J, Bult A, Underberg WJ (1994) Ifosfamide metabolism and pharmacokinetics (review). Anticancer Res 14:517–531
Kalhorn TF, Ren S, Howald WN, Lawrence RF, Slattery JT (1999) Analysis of cyclophosphamide and five metabolites from human plasma using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and gas chromatography–nitrogen–phosphorus detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 732:287–298
Kiffmeyer T, Götze H-J, Jursch M, Lüders U (1998) Trace enrichment, chromatographic separation and biodegradation of cytostatic compounds in surface water. Fresenius J Anal Chem 361:185–191
Kim I, Tanaka H (2009) Photodegradation characteristics of PPCPs in water with UV treatment. Environ Int 35:793–802
Kim I, Yamashita N, Tanaka H (2009) Performance of UV and UV/H2O2 processes for the removal of pharmaceuticals detected in secondary effluent of a sewage treatment plant in Japan. J Hazard Mater 166:1134–1140
Köhler C, Venditti S, Igos E, Klepiszewski K, Benetto E, Cornelissen A (2012) Elimination of pharmaceutical residues in biologically pre-treated hospital wastewater using advanced UV irradiation technology: a comparative assessment. J Hazard Mater 239–240:70–77
Kosjek T, Heath E (2011) Occurrence, fate and determination of cytostatic pharmaceuticals in the environment. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 30:1065–1087
Kosjek T, Heath E, Kompare B (2007) Removal of pharmaceutical residues in a pilot wastewater treatment plant. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1379–1387
Kovalova L, Siegrist H, Singer H, Wittmer A, McArdell CS (2012) Hospital wastewater treatment by membrane bioreactor: performance and efficiency for organic micropollutant elimination. Environ Sci Technol 46:1536–1545
Kümmerer K, Steger-Hartmann T, Meyer M (1997) Biodegradability of the anti-tumour agent ifosfamide and its occurrence in hospital effluents and communal sewage. Water Res 31:2705–2710
Lai WW-P, Lin HH-H, Lin AY-C (2015) TiO2 photocatalytic degradation and transformation of oxazaphosphorine drugs in an aqueous environment. J Hazard Mater 287:133–141
Li F, Patterson AD, Höfer CC, Krausz KW, Gonzalez FJ, Idle JR (2010) Comparative metabolism of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in the mouse using UPLC–ESI-QTOFMS-based metabolomics. Biochem Pharmacol 80:1063–1074
Lin AY-C, Lin Y-C, Lee W-N (2014) Prevalence and sunlight photolysis of controlled and chemotherapeutic drugs in aqueous environments. Environ Pollut 187:170–181
Lin AY, Hsueh JH, Hong PK (2015) Removal of antineoplastic drugs cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and 5-fluorouracil and a vasodilator drug pentoxifylline from wastewaters by ozonation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:508–515
Llewellyn N, Lloyd P, Jürgens MD, Johnson AC (2011) Determination of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in sewage effluent by stable isotope-dilution liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1218:8519–8528
Lutterbeck CA, Machado ÊL, Kümmerer K (2015) Photodegradation of the antineoplastic cyclophosphamide: a comparative study of the efficiencies of UV/H2O2, UV/Fe2+/H2O2 and UV/TiO2 processes. Chemosphere 120:538–546
Martín J, Camacho-Muñoz D, Santos JL, Aparicio I, Alonso E (2011) Simultaneous determination of a selected group of cytostatic drugs in water using high-performance liquid chromatography–triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 34:3166–3177
Moldovan Z (2006) Occurrences of pharmaceutical and personal care products as micropollutants in rivers from Romania. Chemosphere 64:1808–1817
Momerency G, Van Cauwenberghe K, De Bruijn EA, Van Oosterom AT, Highley MS, Harper PG (1994) Determination of iphosphamide and seven metabolites in blood plasma, as stable trifluoroacetyl derivatives, by electron capture chemical ionization GC-MS. J High Resolut Chromatogr 17:655–661
Negreira N, de Alda ML, Barceló D (2014) Cytostatic drugs and metabolites in municipal and hospital wastewaters in Spain: Filtration, occurrence, and environmental risk. Sci Total Environ 497–498:68–77
Nicole I, De Laat J, Dore M, Duguet JP, Bonnel C (1990) Utilisation du rayonnement ultraviolet dans le traitement des eaux: mesure du flux photonique par actinometrie chimique au peroxyde d’hydrogene. Water Res 24:157–168
Steger-Hartmann T, Kümmerer K, Schecker J (1996) Trace analysis of the antineoplastics ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide in sewage water by twostep solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 726:179–184
Steger-Hartmann T, Kümmerer K, Hartmann A (1997) Biological degradation of cyclophosphamide and its occurrence in sewage water. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 36:174–179
Tasso M, Boddy A, Price L, Wyllie R, Pearson AJ, Idle J (1992) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of cyclophosphamide in paediatric patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 30:207–211
Ternes TA (1998) Occurrence of drugs in German sewage treatment plants and rivers. Water Res 32:3245–3260
Thomas KV, Dye C, Schlabach M, Langford KH (2007) Source to sink tracking of selected human pharmaceuticals from two Oslo city hospitals and a wastewater treatment works. J Environ Monit 9:1410–1418
Valcárcel Y, González Alonso S, Rodríguez-Gil JL, Gil A, Catalá M (2011) Detection of pharmaceutically active compounds in the rivers and tap water of the Madrid Region (Spain) and potential ecotoxicological risk. Chemosphere 84:1336–1348
Venta MB, Castro CH, Garcia LA, Marzo AL, Lorenzo EV, Alvarez CA (2005) Effect of O3/H2O2 molar concentration ratio at different pH values on cyclophosphamide degradation. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 54:403–410
Weiss RB (1991) Ifosfamide vs cyclophosphamide in cancer therapy. Oncology (Williston Park) 5(5):67–76
Yin J, Shao B, Zhang J, Li K (2010) A preliminary study on the occurrence of cytostatic drugs in hospital effluents in Beijing, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:39–45
Zhang J, Tian Q, Zhou S-F (2006) Clinical pharmacology of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide. Curr Drug Ther 1:55–84
Zhang J, Chang VWC, Giannis A, Wang J-Y (2013) Removal of cytostatic drugs from aquatic environment: a review. Sci Total Environ 445–446:281–298
Zuccato E, Castiglioni S, Fanelli R (2005) Identification of the pharmaceuticals for human use contaminating the Italian aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 122:205–209
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the EU through the EU FP7 project CytoThreat (fate and effects of cytostatic pharmaceuticals in the environment and the identification of biomarkers for an improved risk assessment on environmental exposure (Grant Agreement No.: 265264), by the Slovenian Research Agency (Program Groups P1-0143, Project L1-5457, Project J1-6744 and Young Researcher Grant to M. Č.) and the Slovene Human Resources Development and Scholarship Fund (Ad futura). The authors would like to thank the staff at the hospital and the WWTP involved in the study for their collaboration and help during sampling campaign.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1053 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Česen, M., Kosjek, T., Busetti, F. et al. Human metabolites and transformation products of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide: analysis, occurrence and formation during abiotic treatments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 11209–11223 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6321-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6321-1