Abstract
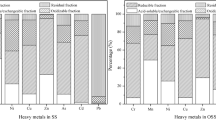
In this paper, transformation of chemical forms of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Ni, Pb, Cr, Cd, Mn, and Mg) in sewage sludge (SS) during ozonation was investigated. Meanwhile, the risk of heavy metals to environment in ozonated sludge (OS) and SS was estimated according to risk assessment code (RAC). The residual rates of heavy metals were over 72.8 %, which demonstrated that the heavy metals in SS were mainly existed in the OS after ozonation. The results indicated that the ozonation had an effect on the redistribution of heavy metals. The comparisons of the RAC between OS and SS indicated that the environmental risk of heavy metals in OS was aggravated compared to SS, except for Mg. Consequently, it was suggested that the OS should be pretreated before application.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braguglia C, Gianico A, Mininni G (2012) Comparison between ozone and ultrasound disintegration on sludge anaerobic digestion. J Environ Manag 95:139–143
Cai M, Liu J, Wei Y (2004) Enhanced biohydrogen production from sewage sludge with alkaline pretreatment. Environ Sci Technol 38:3195–3202
Chen C, Lua Y, Hong J, Ye M, Wang Y, Lu H (2010) Metal and metalloid contaminant availability in Yundang Lagoon sediments, Xiamen Bay, China, after 20 years continuous rehabilitation. J Hazard Mater 175:1048–1055
Chou J, Wey M, Chang S (2009) Evaluation of the distribution patterns of Pb, Cu and Cd from MSWI fly ash during thermal treatment by sequential extraction procedure. J Hazard Mater 162:1000–1006
Chu L, Wang J, Wang B, Xing X, Yan S, Sun X, Jurcik B (2009) Changes in biomass activity and characteristics of activated sludge exposed to low ozone dose. Chemosphere 77:269–272
Dong B, Liu X, Dai L, Dai X (2013) Changes of heavy metal speciation during high-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 131:152–158
Egemen E, Corpening J, Nirmalakhanda N (2001) Evaluation of an ozonation system for reduced waste sludge generation. Water Sci Technol 44:445–452
Fuentes A, Lloréns M, Sáez J, Aguilar MI, Ortuño JF, Meseguer VF (2008) Comparative study of six different sludges by sequential speciation of heavy metals. Bioresour Technol 99:517–525
Guo W, Ding J, Cao G, Ren N, Cui F (2011) Treatability study of using low frequency ultrasonic pretreatment to augment continuous biohydrogen production. Int J Hydrog Energy 36:14180–14185
He S, Xue G, Wang B (2006) Activated sludge ozonation to reduce sludge production in membrane bioreactor (MBR). J Hazard Mater 135:406–411
He M, Li W, Liang X, Wu D, Tian G (2009) Effect of composting process on phytotoxicity and speciation of copper, zinc and lead in sewage sludge and swine manure. Waste Manag 29:590–597
Huang H, Yuan X, Zeng G, Zhu H, Li H, Liu Z, Jiang H, Leng L, Bi W (2011) Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals’ pollution hazards in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:10346–10351
Jain C, Ran D (2004) Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of river Yamuna, India. Water Res 38:569–578
Jin C, Zheng S, He Y, Zhou G, Zhou Z (2005) Lead contamination in tea garden soils and factors affecting its bioavailability. Chemosphere 59:1151–1159
Jin H, Arazo R, Gao J, Capareda S, Chang Z (2014) Leaching of heavy metals from fast pyrolysis residues produced from different particle sizes of sewage sludge. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 109:168–175
Kampasa P, Parsonsa SA, Pearceb P, Ledouxb S, Valec P, Churchleyc J, Cartmella E (2007) Mechanical sludge disintegration for the production of carbon source for biological nutrient removal. Water Res 41:1734–1742
Lasheen M, Ammar N (2009) Assessment of metals speciation in sewage sludge and stabilized sludge from different wastewater treatment plants, Greater Cairo, Egypt. J Hazard Mater 164:740–749
Liu X, Liu H, Chen J, Dua G, Chen J (2008) Enhancement of solubilization and acidification of waste activated sludge by pretreatment. Waste Manag 28:2614–2622
Lu Y, Gong Z, Zhang G, Burghardt W (2003) Concentrations and chemical speciations of Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cr of urban soils in Nanjing, China. Geoderma 115:101–111
Magdalena A, Kathleen L, Hansruedi S, Jan A (2007) Ozonation reduces sludge production and improves denitrification. Water Res 41:543–550
Nemati K, Bakar N, Abas M, Sobhanzadeh E (2011) Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J Hazard Mater 192:402–410
Ngiam L, Lim P (2001) Speciation patterns of heavy metals in tropical estuarine anoxic and oxidized sediments by different sequential extraction schemes. Sci Total Environ 275:53–61
Park W, Ahn J, Hwang S, Lee C (2009) Effect of output power, target temperature, and solid concentration on the solubilization of waste activated sludge using microwave irradiation. Bioresour Technol 101(1):S13–S16
Peiman K, Wayne P, Peter S (2010) An evaluation of protocols for characterization of ozone impacts on WAS properties and digestibility. Bioresour Technol 101:8565–8572
Perin G, Craboledda L, Lucchese M, Cirillo R, Dotta L, Zanette M, Orio A (1985) Heavy metal speciation in the sediments Northern Adriatic sea—a new approach for environmental toxicity determination. Heavy Met Environ 2:454–456
Sliveira M, Alleoni L, O’Connor G, Chang A (2006) Heavy metal sequential extraction methods-a modification for tropical soils. Chemosphere 64:1929–1938
Sprynskyy M, Kosobucki P, Kowalkowski T, Buszewski B (2007) Influence of clinoptilolite rock on chemical speciation of selected heavy metals in sewage sludge. J Hazard Mater 149:310–316
Stals M, Thijssen E, Vangronsveld J, Carleer R, Schreurs S, Yperman J (2010) Flash pyrolysis of heavy metal contaminated biomass from phytoremediation: influence of temperature, entrained flow and wood/leaves blended pyrolysis on the behaviour of heavy metals. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 87:1–7
Tandy S, Healey J, Nason M, Williamson J, Jones D (2009) Heavy metal fractionation during the co-composting of biosolids, deinking paper fibre and green waste. Bioresour Technol 100:4220–4226
Walter I, Martínez F, Cala V (2006) Heavy metal speciation and phytotoxic effects of three representative sewage sludges for agricultural uses. Environ Pollut 139:507–514
Wang X, Chen L, Xia S, Zhao J (2008) Changes of Cu, Zn, and Ni chemical speciation in sewage sludge co-composted with sodium sulfide and lime. J Environ Sci 20:156–160
Wei Y, Houten R, Borger A, Eikelboom D, Fan Y (2003) Minimization of excess sludge production for biological wastewater treatment. Water Res 37:4453–4467
Wilson C, Novak J (2009) Hydrolysis of macromolecular components of primary and secondary wastewater sludge by thermal hydrolytic pretreatment. Water Res 43(18):4489–4498
Wong J, Li K, Fang M, Su D (2001) Toxicity evaluation of sewage sludges in Hong Kong. Environ Int 27:373–380
Wu J, Huang X (2010) Use of ozonation to mitigate fouling in a long-term membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 101:6019–6027
Xiao Z, Yuan X, Li H, Jiang L, Leng L, Chen X, Zeng G, Li F, Cao L (2015) Chemical speciation, mobility and phyto-accessibility of heavy metals in fly ash and slag from combustion of pelletized municipal sewage sludge. Sci Total Environ 536:774–783
Yang J, Lee J, Baek K, Kwon T, Choi J (2009) Extraction behavior of As, Pb, and Zn from mine tailings with acid and base solutions. J Hazard Mater 171:443–451
Yuan X, Huang H, Zeng G, Li H, Wang J, Zhou C, Zhu H, Pei X, Liu Z, Liu Z (2011) Total concentrations and chemical speciation of heavy metals in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:4104–4110
Zhang G, Yang J, Liu H, Zhang J (2009) Sludge ozonation: disintegration, supernatant changes and mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 100:1505–1509
Zhang X, Tian Y, Wang Q, Chen L, Wang X (2012) Heavy metal distribution and speciation during sludge reduction using aquatic worms. Bioresour Technol 126:41–47
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Management (No. 2013ZX07201007, 2014ZX07201012), the State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology (No. 2014DX03), and the Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Heilongjiang Province (JC201303). The authors also appreciate the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology (QA201609-02), and the Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Science Foundation (LBH-Z14093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Tian, Y., Zhang, J. et al. Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sewage sludge after ozonation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 5118–5125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6313-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6313-1