Abstract
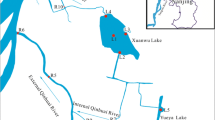
Organic UV filters that have been widely used in sunscreens and other personal care products have drawn much public concern because of their widespread contamination in the environment and their potential ecological risks to ecosystems. We selected three UV filters with high frequency of detection in the environment, namely butyl methoxy dibenzoylmethane (BM-DBM), ethylhexyl dimethyl p-aminobenzoate (OD-PABA), and 4-methylbenzylidene camphor (4-MBC), to investigate the sorption and degradation behaviors of these compounds in lab-scale water-sediment systems set up with natural water and sediment samples collected from different rivers and lakes (i.e., Yangtze River, Qinhuai River, Xuanwu Lake, and Mochou Lake) in Nanjing, East China. The sorption isotherms of these UV filters were well described by the Freundlich equation (C s = K f × C w n). The sorption of three UV filters in four sediments was all linear or close to it, with n values between 0.92 and 1.13. A moderate to strong sorption affinity was observed for these compounds, and the sorption appears to be irreversible. For the combined sorption and degradation studies, sorption was found to be a primary mechanism for the disappearance of these UV filters from the water phase, and biotransformation appears to be the predominant factor for the degradation of the target compounds in the water-sediment systems. All three UV filters were found to be slightly resistant to the microbes in these systems, with DT50total and DT90total values—the disappearance time (DT) describes the time in which the initial total mass of the UV filters in the whole system is reduced by 50 and 90 %—ranging between 18 and 31 days and 68 and 101 days, respectively.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey GW, White JL (1970) Factors influencing the adsorption, desorption, and movement of pesticides in soil. Single pesticide volume: the triazine herbicides. Springer, New York, pp 29–92
Barón E, Gago-Ferrero P, Gorga M, Rudolph I, Mendoza G, Zapata AM, Díaz-Cruz S, Barra R, Ocampo-Duque W, Páez M (2013) Occurrence of hydrophobic organic pollutants (BFRs and UV-filters) in sediments from South America. Chemosphere 92:309–16
Brausch JM, Rand GM (2011) A review of personal care products in the aquatic environment: environmental concentrations and toxicity. Chemosphere 82:1518–32
Buser H-R, Balmer ME, Schmid P, Kohler M (2006) Occurrence of UV filters 4-methylbenzylidene camphor and octocrylene in fish from various Swiss rivers with inputs from wastewater treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 40:1427–31
Calafat AM, Wong L-Y, Ye X, Reidy JA, Needham LL (2008) Concentrations of the sunscreen agent benzophenone-3 in residents of the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2004. Environ Health Persp 116:893–7
Chefetz B, Mualem T, Ben-Ari J (2008) Sorption and mobility of pharmaceutical compounds in soil irrigated with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 73:1335–43
Das B, Lee L, Rao P, Hultgren R (2004) Sorption and degradation of steroid hormones in soils during transport: column studies and model evaluation. Environ Sci Technol 38(5):1460–70
Díaz-Cruz MS, Gago-Ferrero P, Llorca M, Barceló D (2012) Analysis of UV filters in tap water and other clean waters in Spain. Ana Bioanal Chem 402:2325–33
Doll TE, Frimmel FH (2003) Fate of pharmaceuticals––photodegradation by simulated solar UV-light. Chemosphere 52:1757–69
Eriksson E, Auffarth K, Eilersen AM, Henze M, Ledin A (2003) Household chemicals and personal care products as sources for xenobiotic organic compounds in grey wastewater. Water SA 29(2):135–46
Fu G, Kan AT, Tomson M (1994) Adsorption and desorption hysteresis of PAHs in surface sediment. Environ Toxicol Chem 13(10):1559–67
Gago-Ferrero P, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2012) An overview of UV-absorbing compounds (organic UV filters) in aquatic biota. Anal Bioanal Chem 404:2597–610
Gago-Ferrero P, Alonso MB, Bertozzi CP, Marigo J, Lr B, Cremer M, Secchi ER, Azevedo A, Lailson-Brito J Jr, Torres JP (2013) First determination of UV filters in marine mammals. Octocrylene levels in Franciscana dolphins. Environmental Sci Technol 47:5619–25
Inui M, Adachi T, Takenaka S, Inui H, Nakazawa M, Ueda M, Watanabe H, Mori C, Iguchi T, Miyatake K (2003) Effect of UV screens and preservatives on vitellogenin and choriogenin production in male medaka (Oryzias latipes). Toxicology 194:43–50
Janzen N, Banzhaf S, Scheytt T, Bester K (2009) Vertical flow soil filter for the elimination of micro pollutants from storm and waste water. Chemosphere 77:1358–65
Jin X, Wang S, Bu Q et al (2006) Laboratory experiments on phosphorous release from the sediments of 9 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River region, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 176(1-4):233–51
Kameda Y, Kimura K, Miyazaki M (2011) Occurrence and profiles of organic sun-blocking agents in surface waters and sediments in Japanese rivers and lakes. Environmental Pollut 159:1570–6
Kim S, Choi K (2014) Occurrences, toxicities, and ecological risks of benzophenone-3, a common component of organic sunscreen products: a mini-review. Environ Int 70:143–57
Kunisue T, Chen Z, Buck Louis GM, Sundaram R, Hediger ML, Sun L, Kannan K (2012) Urinary concentrations of benzophenone-type UV filters in US women and their association with endometriosis. Environ Sci Technol 46:4624–32
Kupper T, Plagellat C, Brändli R, de Alencastro LF, Grandjean D, Tarradellas J (2006) Fate and removal of polycyclic musks, UV filters and biocides during wastewater treatment. Water Res 40:2603–12
La HL, Vieno N, Temmink H, Zeeman G, Buisman CJ (2010) Occurrence of xenobiotics in gray water and removal in three biological treatment systems. Environ Sci Technol 44:6835–42
Lin AY-C, Lin C-A, Tung H-H, Chary NS (2010) Potential for biodegradation and sorption of acetaminophen, caffeine, propranolol and acebutolol in lab-scale aqueous environments. J Hazard Mater 183:242–50
Manová E, von Goetz N, Hauri U, Bogdal C, Hungerbühler K (2013) Organic UV filters in personal care products in Switzerland: a survey of occurrence and concentrations. Int J Hyg Environ Heal 216:508–14
Martínez-Hernández V, Meffe R, Herrera S, Arranz E, de Bustamante I (2014) Sorption/desorption of non-hydrophobic and ionisable pharmaceutical and personal care products from reclaimed water onto/from a natural sediment. Sci Total Environ 472:273–81
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeny DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Inc, Madison
OECD (2000) Test No. 106: Adsorption-desorption using a batch equilibrium method. OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, 1–45. doi:10.1787/9789264069602-en
OECD (2002) Test No. 308: Aerobic and anaerobic transformation in aquatic sediment systems. OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, 1–19. doi:10.1787/9789264070523-en
Ozáez I, Martínez-Guitarte JL, Morcillo G (2013) Effects of in vivo exposure to UV filters (4-MBC, OMC, BP-3, 4-HB, OC, OD-PABA) on endocrine signaling genes in the insect Chironomus riparius. Sci Total Environ 456:120–6
Pestotnik K, Kosjek T, Heath E (2014) Transformation products of personal care products: UV filters case studies. Transformation products of emerging contaminants in the environment: analysis, processes, occurrence, effects and risks 459–492
Ramil M, El Aref T, Fink G, Scheurer M, Ternes TA (2009) Fate of beta blockers in aquatic-sediment systems: sorption and biotransformation. Environ Sci Technol 44:962–70
Rodil R, Moeder M, Altenburger R, Schmitt-Jansen M (2009) Photostability and phytotoxicity of selected sunscreen agents and their degradation mixtures in water. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1513–24
Rodríguez-Fuentes G, Sandoval-Gío JJ, Arroyo-Silva A, Noreña-Barroso E, Escalante-Herrera KS, Olvera-Espinosa F (2015) Evaluation of the estrogenic and oxidative stress effects of the UV filter 3-benzophenone in zebrafish (Danio rerio) eleuthero-embryos. Ecotox Environ Safe 115:14–8
Schlumpf M, Kypke K, Vökt CC, Birchler M, Durrer S, Faass O, Ehnes C, Fuetsch M, Gaille C, Henseler M (2008) Endocrine active UV filters: developmental toxicity and exposure through breast milk. CHIMIA Int J Chem 62:345–51
Schmitt C, Oetken M, Dittberner O, Wagner M, Oehlmann J (2008) Endocrine modulation and toxic effects of two commonly used UV screens on the aquatic invertebrates Potamopyrgus antipodarum and Lumbriculus variegatus. Environ Pollut 152:322–9
Schreurs R, Lanser P, Seinen W, van der Burg B (2002) Estrogenic activity of UV filters determined by an in vitro reporter gene assay and an in vivo transgenic zebrafish assay. Arch Toxicol 76:257–61
Schwarzenbach R P, Gschwend P M, Imboden D M (2003) Environmental organic chemistry, 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ
Sinkkonen S, Paasivirta J (2000) Degradation half-life times of PCDDs, PCDFs and PCBs for environmental fate modeling. Chemosphere 40:943–9
Tsui MM, Leung H, Lam PK, Murphy MB (2014a) Seasonal occurrence, removal efficiencies and preliminary risk assessment of multiple classes of organic UV filters in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 53:58–67
Tsui MM, Leung H, Wai T-C, Yamashita N, Taniyasu S, Liu W, Lam PK, Murphy MB (2014b) Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk assessment of multiple classes of UV filters in surface waters from different countries. Water Res 67:55–65
Wijekoon KC, Hai FI, Kang J, Price WE, Guo W, Ngo HH, Nghiem LD (2013) The fate of pharmaceuticals, steroid hormones, phytoestrogens, UV-filters and pesticides during MBR treatment. Bioresource Technol 144:247–54
Xu J, Wu L, Chang AC (2009) Degradation and adsorption of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in agricultural soils. Chemosphere 77:1299–305
Yamamoto H, Nakamura Y, Moriguchi S, Nakamura Y, Honda Y, Tamura I, Hirata Y, Hayashi A, Sekizawa J (2009) Persistence and partitioning of eight selected pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: laboratory photolysis, biodegradation, and sorption experiments. Water Res 43:351–62
Yu Y, Liu Y, Wu L (2013) Sorption and degradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in soils. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:4261–7
Zhao D, Pignatello JJ, White JC, Braida W, Ferrandino F (2001) Dual‐mode modeling of competitive and concentration‐dependent sorption and desorption kinetics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils. Water Resources Res 37:2205–12
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51279061), the National Science Funds for Creative Research Groups of China (Grant No. 51421006), and by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roland Kallenborn
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 298 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Lu, G., Xie, Z. et al. Sorption and degradation of selected organic UV filters (BM-DBM, 4-MBC, and OD-PABA) in laboratory water-sediment systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 9679–9689 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6126-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6126-2