Abstract
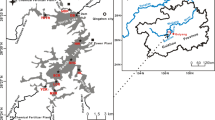
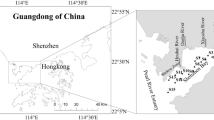
Bosten Lake, a typical rump lake in an oasis in northwest China, was chosen to evaluate the distribution, sources, pollution status, and potential ecological risk of heavy metals. Sediment samples were collected from the lake, and results showed that the values of the eight heavy metals all fell within the Second Soil National Standard, while the average and maximum values of the metals were higher than the background values of the study. Multivariate statistical analysis showed that sediment concentrations of Cd, Pb, Hg, and Zn were mainly influenced by man sources. In comparison, Cu, Ni, Cr, and As were primarily natural in origin. Enrichment factor analysis (EF) and the geo-accumulation index evaluation method (I geo) showed that Cd, Hg, and Pb fell under low and partial serious pollution levels, while Zn, As, Cr, Ni, and Cu mainly were characterized under no pollution and low pollution levels. The potential ecological hazards index (RI) showed that among the eight heavy metals, Pb, Hg, and Cd posed the highest potential ecological risk, with potential ecological hazards indices (RI) of 29.06, 27.71, and 21.54 %, respectively. These findings demonstrated that recent economic development in the area of the basin has led to heavy metal accumulation in the surface sediments of the lake.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bing H, Wu Y, Sun Z, Yao S (2011) Historical trends of heavy metal contamination and their sources in lacustrine sediment from Xijiu Lake, Taihu Lake Catchment, China. J Environ Sci 23(10):1671–1678 (In Chinese)
Chandra SK, Charya S, Kamala CT, Suman RDS, Sreenivasa RA (2003) Fractionation studies and bioaccumulation of sediment-bound heavy metals in Kolleru Lake by edible fish. Environ Int 29:1001–100
Chen J, Li SF (2007) Chemical speciation and total concentration of heavy metals for sediments from lake Chaohu. Henan Sci 25(2):303–307 (In Chinese)
Chen YZ, Yang H, Zhang ZK, Qin MZ, Jin F, Lü JJ (2007) Application of equilibrium partitioning approach to the derivation of sediment quality guidelines for metals in Dianchi Lake. Pedosphere 17(3):284–294
Chen J, He F, Zhang X, Sun X, Zheng J, Zheng J (2014) Heavy metal pollution decreases microbial abundance, diversity and activity within particle-size fractions of a paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87(1):164–181
Dauvalter V, Rognerud S (2001) Heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pasvik River drainage. Chemosphere 42(1):9–18
Ezeilo FE, Agunwamba JC (2014) Analysis of heavy metal pollution status of Amadi creek, port Harcourt, Nigeria. Health, Safety Environ (HSE) 2(3):88–96
Fang M, Wu YJ, Liu H, Jia Y, Zhang Y, Wang XT, Wu MH et al (2013) Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River estuary. Acta Sci Circumst 33(2):563–569 (In Chinese)
Gao JP, Maguhn J, Spitzauer P, Kettrup A (1998) Sorption of pesticides in the sediment of the Teufelsweiher pond (Southern Germany). I: equilibrium assessments, effect of organic carbon content and pH. Water Res 32(5):1662–1672
Govers LL, de-Brouwer JH, Suykerbuyk W, Bouma TJ, Lamers LP, Smolders AJ, van-Katwijk MM (2014) Toxic effects of increased sediment nutrient and organic matter loading on the seagrass Zostera noltii. Aquat Toxicol 155:253–260
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Horn MK, Adams JAS (1966) Computer-derived geochemical balances and element abundances. Aquat Toxicol 30(3):279–297
Hu RJ (2004) Chinese Tianshan mountains natural geography. China Environmental Science Press (In Chinese)
Hung CC, Gong GC, Ko FC, Lee HJ, Chen HY, Wu JM, Santschi PH (2011) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of the East China Sea and their relationship with carbonaceous materials. Mar Pollut Bull 63(5):464–470
Kankiliç GB, Tüzün İ, Kadıoğlu YK (2013) Assessment of heavy metal levels in sediment samples of Kapulukaya Dam Lake (Kirikkale) and lower catchment area. Environ Monit Assess 185(8):6739–6750
Krooss BM, Littke R, Müller B, Frielingsdorf J, Schwochau K, Idiz EF (1995) Generation of nitrogen and methane from sedimentary organic matter: implications on the dynamics of natural gas accumulations. Chem Geol 126(3):291–318
Kükrer S, Şeker S, Abacı ZT, Kutlu B (2014) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of northern littoral zone of Lake Çildir, Ardahan, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 186(6):3847–3857
Li X, Poon C, Liu PS (2001) Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Appl Geochem 16(11):1361–1368
Li BC, He LS, Yang M, Meng R, Yuan DM, Xi BD, Shu JM (2012) Speciation and vertical distribution of heavy metals in sediments of Baiyangdian Lake. Chinese J Environ Sci 33(7):2376–2383 (In Chinese)
Li M, Zang S, Xiao H, Wu C (2014) Speciation and distribution characteristics of heavy metals and pollution assessments in the sediments of Nashina Lake, Heilongjiang, China. Ecotoxicology 23(4):681–688
Liu ZK, Zhang SH (2005) The analysis of pollution changing trend of heavy metals in Hongze Lake’s bottom material. Jiang Su Environ Sci Technol 4:016 (In Chinese)
Lu (2000) Soil agricultural chemical analysis methods. China’s Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing, In Chinese
Mamat Z, Yimit H, Eziz A (2014a) Oasis land-use change and its effects on the eco-environment in Yanqi basin, Xinjiang, China. Environ Monit Assess 186(1):335–348
Mamat Z, Yimit H, Rouzi AJ, Eziz M (2014b) Source identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metal contamination in Yanqi basin, northwest China. Sci Total Environ 493:1098–1111
Muller G (1969) Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 2(3):108–118
Nguyen HL, Leermakers M, Osán J, Török S, Baeyens W (2005) Heavy metals in Lake Balaton: water column, suspended matter, sediment and biota. Sci Total Environ 340(1):213–230
Ren W, Xue B, Geng Y, Sun L, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Zhang L (2014) Inventorying heavy metal pollution in redeveloped brown field and its policy contribution: case study from Tiexi District, Shenyang, China. Land Use Policy 38:138–146
Schartup AT, Mason RP, Balcom PH, Hollweg TA, Chen CY (2012) Methylmercury production in estuarine sediments: role of organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 47(2):695–700
Sheela AM, Letha J, Joseph S, Thomas J (2012) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in coastal lake sediments associated with urbanization: Southern Kerala, India. Lakes Reservoirs Res Manage 17(2):97–112
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39(6):611–627
Tam NFY, Wong YS (2000) Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environ Pollut 110(2):195–205
Tang W, Shan B, Zhang H, Mao Z (2010) Heavy metal sources and associated risk in response to agricultural intensification in the estuarine sediments of Chaohu Lake Valley, East China. J Hazard Mater 176(1):945–951
The State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) (1990) China’s soil element background values. China environmental Science Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
The State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) (1995) The national standard of soil environmental quality standard of the People’s Republic of China (GB15618-1995). The People’s Republic of China State Environmental Protection Agency, Beijing (In Chinese)
The Statistics Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (SBXUA) (2013) The statistical yearbook of Bayingolin Mongol autonomous prefecture. China Statistics Press, Xinjiang (In Chinese)
Wu JL, Ma L, Zeng HA (2013) Water quality and quantity characteristics and its evolution in Lake Bosten, Xinjiang over the past 50 years. Sci Geogr Sin 33(2):231–237 (In Chinese)
Xiong J, Liu Y, Lin X, Zhang H, Zeng J, Hou J, Chu H (2012) Geographic distance and pH drive bacterial distribution in alkaline lake sediments across Tibetan Plateau. Environ Microbiol 14(9):2457–2466
Xu HL, Chen YN, Li WH (2003) Analysis on the pollution situation of Boston Lake. J Arid Land Resources Environ 17(03):95–97 (In Chinese)
Xu ZQ, Ni J, Tuo XG, Zhang CJ (2008) Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. China Environ Sci Technol 31(2):112–115 (In Chinese)
Yang SQ, Liu GQ, Zhang AP, Wang YS, Yang ZL (2010) Analysis on accumulation characters of 5 kinds of heavy metals in orchard topsoil in typical production zone in China. Acta Ecol Sin 30(22):6201–6207 (In Chinese)
Yao Z, Bao Z, Gao P (2006) Environmental assessments of trace metals in sediments from Dongting Lake, Central China. J China Univ Geosci 17(4):310–319
Yin H, Gao Y, Fan C (2011a) Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Taihu, China. Environ Res Lett 6(4):044012
Yin Y, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhu G, Qin B, Shi Z, Feng L (2011b) Temporal and spatial variations of chemical oxygen demand in Lake Taihu, China from 2005 to 2009. Hydrobiologia 665(1):129–141
Yu WH, Wang JJ, Zang SY (2012) The spatial variability characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals of lake sediments in the Songnen Plain. Sci Geogr Sin 32(8):1001–1005 (In Chinese)
Yuan H, Liu E, Shen J, Zhou H, Geng Q, An S (2014) Characteristics and origins of heavy metals in sediments from Ximen Co Lake during summer monsoon season, a deep lake on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. J Geochem Explor 136:76–83
Zhan YZ, Jin XC, Zhao Z (2011) Speciation distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake. China Environ Sci 31(11):1842–1848 (In Chinese)
Zhang Z, Abuduwaili J, Jiang F (2013) Determination of occurrence characteristics of heavy metals in soil and water environments in Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Anal Lett 46(13):2122–2131
Zhang ZZ, Abuduwaili J, Jiang FQ (2015) Sources identification and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface water environment of Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Environ Monit Assess 187:4191
Zhao SP, Chen LX (2011) Soil heavy content analysis and ecological risk assessment of different landuse types in Daqing Region. J Soil Water Conserv 25(5):195–199 (In Chinese)
Zhong XL, Zhou SL, Li JT, Zhao QG (2010) Evaluation of soil heavy metals accumulation in the fast economy development region. Environ Sci 31(6):1608–1616 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Open Project of Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Lake Environment and Resources in Arid Zone, Xinjiang Normal University (X2014KL0106), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41501541), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2015M570867). We are extremely thanked for the reviewer’s advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamat, Z., Haximu, S., Zhang, Z.y. et al. An ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Bosten Lake, northwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 7255–7265 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-6020-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-6020-3