Abstract
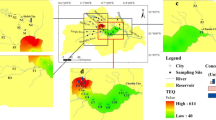
Surface sediment from large and eutrophic Lake Chaohu was investigated to determine the occurrence, spatial distribution, sources, and risks of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and heavy metals in one of the five biggest freshwater lakes in China. Total concentration of PCBs (Σ34PCBs) in Lake Chaohu was 672 pg g−1 dry weight (dw), with a range of 7 to 3999 pg g−1 dw, which was lower than other water bodies worldwide. The majority of heavy metals were detected at all sampling locations, except for Sr, B, and In. Concentrations of Al, Fe, Ca, Mn, Sr, Co, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Hg were similar to that reported for other lakes globally. Concentrations of K, Mg, Na, Li, Ga, and Ag were greater than the average, whereas those of Cr, Ni, and Cu were lower. Cluster analysis (CA) and positive matrix factorization (PMF) yielded accordant results for the source apportionment of PCBs. The technical PCBs and microbial degradation accounted for 34.2 % and 65.8 % of total PCBs using PMF, and PMF revealed that natural and anthropogenic sources of heavy metals accounted for 38.1 % and 61.8 %, respectively. CA indicated that some toxic heavy metals (e.g., Cd, In, Tl, and Hg) were associated with Ca–Na–Mg minerals rather than Fe–Mn minerals. The uncorrelated results between organic matter revealed by pyrolysis technology and heavy metals might be caused by the existence of competitive adsorption between organic matter and minerals. PCBs and heavy metals were coupling discharge without organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), but with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). No sediment sample exceeded the toxic threshold for dioxin-like PCBs (dl-PCBs) set at 20 pg toxicity equivalency quantity (TEQ) g−1, (max dl-PCBs, 10.9 pg TEQ g−1). However, concentrations of Ag, Cd, and Hg were at levels of environmental concern. The sediment in the drinking water source area (DWSA) was threatened by heavy metals from other areas, and some fundamental solutions were proposed to protect the DWSA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktumsek A, Gezgin S (2011) Seasonal variations of metal concentrations in muscle tissue of tench (Tinca tinca), water and sediment in Beysehir Lake (Turkey). Environ Technol 32:1479–1485
Allen-Gil SM, Gubala CP, Wilson R, Landers DH, Wade TL, Sericano JL, Curtis LR (1997) Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments and biota from four US Arctic lakes. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 33:378–387
Al-Taani AA, Batayneh AT, El-Radaideh N, Ghrefat H, Zumlot T, Al-Rawabdeh AM, Al-Momani T, Taani A (2015) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of trace metals in surface sediments of Ziqlab Reservoir. Jordan Environ Monit Assess 187
Bai J, Cui B, Chen B, Zhang K, Deng W, Gao H, Xiao R (2011) Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland, China. Ecol Model 222:301–306
Besser JM, Brumbaugh WG, Ivey CD, Ingersoll CG, Moran PW (2008) Biological and chemical characterization of metal bioavailability in sediments from Lake Roosevelt, Columbia River, Washington, USA. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:557–570
Brown JF, Bedard DL, Brennan MJ, Carnahan JC, Feng H, Wagner RE (1987) Polychlorinated biphenyl dechlorination in aquatic sediments. Science 236:709–712
Brown TM, Kuzyk ZZA, Stow JP, Burgess NM, Solomon SM, Sheldon TA, Reimery KJ (2013) Effects-based marine ecological risk assessment at a polychlorinated biphenyl-contaminated site in Saglek, Labrador, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:453–467
Bzdusek PA, Christensen ER, Lee CM, Pakdeesusuk U, Freedman DL (2006a) PCB congeners and dechlorination in sediments of Lake Hartwell, South Carolina, determined from cores collected in 1987 and 1998. Environ Sci Technol 40:109–119
Bzdusek PA, Lu JH, Christensen ER (2006b) PCB congeners and dechlorination in sediments of Sheboygan River, Wisconsin, determined by matrix factorization. Environ Sci Technol 40:120–129
Cacela D, Beltman DJ, Lipton J (2002) Polychlorinated biphenyl source attribution in Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA, using multivariate similarity among congener profiles in sediment samples. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1591–1599
Caeiro S, Costa MH, Ramos TB, Fernandes F, Silveira N, Coimbra A, Medeiros G, Painho M (2005) Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado Estuary sediment: an index analysis approach. Ecol Indic 5:151–169
Carrie J, Sanei H, Goodarzi F, Stern G, Wang F (2009) Characterization of organic matter in surface sediments of the Mackenzie River Basin, Canada. Int J Coal Geol 77:416–423
Chapman PM, Wang FY, Adams WL, Green A (1999) Appropriate applications of sediment quality values for metals and metalloids. Environ Sci Technol 33:3937–3941
Chevreuil M, Blanchard M, Teil MJ, Chesterikoff A (1998) Polychlorobiphenyl behaviour in the water/sediment system of the Seine River, France. Water Res 32:1204–1212
Clozel B, Ruban V, Durand C, Conil P (2006) Origin and mobility of heavy metals in contaminated sediments from retention and infiltration ponds. Appl Geochem 21:1781–1798
Dauvalter V (1994) Heavy metals in lake sediments of the Kola Peninsula, Russia. Sci Total Environ 158:51–61
Davis JA (1984) Complexation of trace metals by adsorbed natural organic matter. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:679–691
Du S, Belton TJ, Rodenburg LA (2008) Source apportionment of polychlorinated biphenyls in the tidal Delaware River. Environ Sci Technol 42:4044–4051
Eljarrat E, Caixach J, Rivera J, de Torres M, Ginebreda A (2001) Toxic potency assessment of non-and mono-ortho PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs, and PAHs in northwest Mediterranean sediments (Catalonia, Spain). Environ Sci Technol 35:3589–3594
Feng H, Cochran JK, Lwiza H, Brownawell BJ, Hirschberg DJ (1998) Distribution of heavy metal and PCB contaminants in the sediments of an urban estuary: the Hudson River. Mar Environ Res 45:69–88
Ferreira AM, Martins M, Vale C (2003) Influence of diffuse sources on levels and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in the Guadiana River estuary, Portugal. Mar Chem 83:175–184
Finley BL, Trowbridge KR, Burton S, Proctor DM, Panko JM, Paustenbach DJ (1997) Preliminary assessment of PCB risks to human and ecological health in the lower Passaic River. J Toxicol Environ Health 52:95–118
Frame GM, Cochran JW, Bøwadt SS (1996) Complete PCB congener distributions for 17 aroclor mixtures determined by 3 HRGC systems optimized for comprehensive, quantitative, congener-specific analysis. J High Resolut Chromatogr 19:657–668
Gadd GM, Griffiths AJ (1977) Microorganisms and heavy metal toxicity. Microb Ecol 4:303–317
Gao S, Chen J, Shen Z, Liu H, Chen Y (2013) Seasonal and spatial distributions and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Yangtze Estuary, China. Chemosphere 91:809–816
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
He W, Qin N, Kong X, Liu W, He Q, Ouyang H, Wang Q, Yang B, Yang C, Jiang Y, Xu F (2013a) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the surface sediments and suspended particulate matter (SPM) from Lake Chaohu, a large shallow Chinese lake. Sci Total Environ 463–464:1163–1173
He W, Qin N, Kong X, Liu W, He Q, Ouyang H, Yang C, Jiang Y, Wang Q, Yang B, Xu F (2013b) Spatio-temporal distributions and the ecological and health risks of phthalate esters (PAEs) in the surface water of a large, shallow Chinese lake. Sci Total Environ 461–462:672–680
Helm PA, Gewurtz SB, Whittle DM, Marvin CH, Fisk AT, Tomy GT (2008) Occurrence and biomagnification of polychlorinated naphthalenes and non- and mono-ortho PCBs in Lake Ontario sediment and biota. Environ Sci Technol 42:1024–1031
Hochella MF, Moore JN, Putnis CV, Putnis A, Kasama T, Eberl DD (2005) Direct observation of heavy metal-mineral association from the Clark Fork River Superfund Complex: implications for metal transport and bioavailability. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:1651–1663
Hong YW, Yu S, Yu GB, Liu Y, Li GL, Wang M (2012) Impacts of urbanization on surface sediment quality: evidence from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) contaminations in the Grand Canal of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1352–1363
Hou DK, He J, Lu CW, Ren LM, Fan QY, Wang JH, Xie ZL (2013) Distribution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd) in water and sediments from Lake Dalinouer, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 93:135–144
Ikem A, Adisa S (2011) Runoff effect on eutrophic lake water quality and heavy metal distribution in recent littoral sediment. Chemosphere 82:259–267
Iozza S, Mueller CE, Schmid P, Bogdal C, Oehme M (2008) Historical profiles of chlorinated paraffins and polychlorinated biphenyls in a dated sediment core from Lake Thun (Switzerland). Environ Sci Technol 42:1045–1050
Iqbal J, Tirmizi SA, Shah MH (2013) Statistical apportionment and risk assessment of selected metals in sediments from Rawal Lake (Pakistan). Environ Monit Assess 185:729–743
Kukrer S, Seker S, Abaci ZT, Kutlu B (2014) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of northern littoral zone of Lake Cildir, Ardahan, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 186:3847–3857
Li A, Rockne KJ, Sturchio N, Song W, Ford JC, Wei H (2009) PCBs in sediments of the Great Lakes—distribution and trends, homolog and chlorine patterns, and in situ degradation. Environ Pollut 157:141–147
Li F, Huang JH, Zeng GM, Yuan XZ, Li XD, Liang J, Wang XY, Tang XJ, Bai B (2013) Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. J Geochem Explor 132:75–83
Loska K, Cebula J, Pelczar J, Wiechuła D, Kwapuliński J (1997) Use of enrichment, and contamination factors together with geoaccumulation indexes to evaluate the content of Cd, Cu, and Ni in the Rybnik water reservoir in Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut 93:347–365
MacDonald DD, MacFarlane M (1999) Criteria for managing contaminated sediment in British Columbia. British Columbia Ministry of Environment, Lands, and Parks, Victoria
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger T (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Müller G, Grimmer G, Böhnke H (1977) Sedimentary record of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Lake Constance. Naturwissenschaften 64:427–431
Niu H, Deng W, Wu Q, Chen X (2009) Potential toxic risk of heavy metals from sediment of the Pearl River in South China. J Environ Sci 21:1053–1058
Odhiambo BK, Brown V, Armentrout G, Giancarlo LC, Wegner C (2013) Sediment trace metals and PCB input history in Lake Anna, Virginia. USA Environ Earth Sci 69:2103–2117
Ok G, Shirapova G, Matafonova G, Batoev V, Lee SH (2013) Characteristics of PAHs, PCDD/Fs, PCBs and PBDEs in the Sediment of Lake Baikal. Russia Polycycl Aromat Compd 33:173–192
Omwoma S, Lalah JO, Virani M, Schramm KW, Henkelmann B (2015) Dioxin-like PCBs and PCDD/Fs in surface sediments near the shore of Winam Gulf, Lake Victoria. Chemosphere 118:143–147
Persaud DR, Jaagumagi R, Hayton A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment in Ontario. Standards Development Branch. Ontario Ministry of Environment and Energy, Toronto
Qi M, Bierenga S, Carson J (1997) Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in Bear Lake sediment. In: Subramanian KS, Iyengar GV (Editors), Environmental Biomonitoring: Exposure Assessment and Specimen Banking. ACS Symposium Series, pp. 83–94
Qin N, He W, Kong X-Z, Liu W-X, He Q-S, Yang B, Wang Q-M, Yang C, Jiang Y-J, Jorgensen SE, Xu F-L, Zhao X-L (2014) Distribution, partitioning and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water–SPM–sediment system of Lake Chaohu, China. Sci Total Environ 496:414–423
Samara F, Tsai CW, Aga DS (2006) Determination of potential sources of PCBs and PBDEs in sediments of the Niagara River. Environ Pollut 139:489–497
Selvam AP, Priya SL, Banerjee K, Hariharan G, Purvaja R, Ramesh R (2012) Heavy metal assessment using geochemical and statistical tools in the surface sediments of Vembanad Lake, Southwest Coast of India. Environ Monit Assess 184:5899–5915
Ssebugere P, Kiremire BT, Henkelmann B, Bernhooft S, Wasswa J, Kasozi GN, Schramm KW (2013) PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in surface sediments from Lake Victoria, East Africa. Sci Total Environ 454:528–533
Swarnalatha K, Letha J, Ayoob S (2013) An investigation into the heavy metal burden of Akkulam-Veli Lake in south India. Environ Earth Sci 68:795–806
Tsakovski S, Kudiak B, Simeonov V, Wolska L, Namiesnik J (2009) Ecotoxicity and chemical sediment data classification by the use of self-organising maps. Anal Chim Acta 631:142–152
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Hakansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93:223–241
van Drooge BL, Grimalt JO, Stuchlik E (2013) Spatial distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in High Tatras lake sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6594–6600
Vanier C, Sylvestre M, Planas D (1996) Persistence and fate of PCBs in sediments of the Saint Lawrence River. Sci Total Environ 192:229–244
Wan X, Pan X, Wang B, Zhao S, Hu P, Li F, Boulanger B (2011) Distributions, historical trends, and source investigation of polychlorinated biphenyls in Dianchi Lake, China. Chemosphere 85:361–367
Wang Q, Shen W, Ma Z (2000) Estimation of mercury emission from coal combustion in China. Environ Sci Technol 34:2711–2713
Wang Y-B, Liu C-W, Wang S-W (2015) Characterization of heavy-metal-contaminated sediment by using unsupervised multivariate techniques and health risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:469–476
Wu F, Xu L, Sun Y, Liao H, Zhao X, Guo J (2012) Exploring the relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and sedimentary organic carbon in three Chinese lakes. J Soils Sediments 12:774–783
Xu F-L, Jørgensen SE, Tao S, Li B-G (1999) Modeling the effects of ecological engineering on ecosystem health of a shallow eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chao). Ecol Model 117:239–260
Yang ZF, Wang Y, Shen ZY, Niu JF, Tang ZW (2009) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J Hazard Mater 166:1186–1194
Young DR, McDermott DJ, Heesen TC (1976) Marine inputs of polychlorinated biphenyls off southern California, National Conference on Polychlorinated Biphenyls, November 1975, Chicago, Illinois: conference proceedings. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Toxic Substances, p 199
Yu GB, Liu Y, Yu S, Wu SC, Leung AOW, Luo XS, Xu B, Li HB, Wong MH (2011) Inconsistency and comprehensiveness of risk assessments for heavy metals in urban surface sediments. Chemosphere 85:1080–1087
Yun XY, Yang YY, Liu MX, Wang J (2015) Concentrations and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface sediments from the East Lake, China. Ecotoxicology 24:172–180
Zaharescu DG, Hooda PS, Soler AP, Fernandez J, Burghelea CI (2009) Trace metals and their source in the catchment of the high altitude Lake Respomuso, Central Pyrenees. Sci Total Environ 407:3546–3553
Zhang Y, Shi TR, Zhang Y, Yu T (2014) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from a hypertrophic plateau lake Dianchi, China. Environ Monit Assess 186:1219–1234
Zhao S, Feng CH, Yang YR, Niu JF, Shen ZY (2012) Risk assessment of sedimentary metals in the Yangtze Estuary: New evidence of the relationships between two typical index methods. J Hazard Mater 241:164–172
Zhao G, Li K, Zhou H, Liu X, Zhang P, Wen W, Yu Y, Yuan H (2013) Polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from Three Gorges Reservoir. J Environ Sci Health A-Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 48:136–144
Acknowledgments
The funding for this study was provided by the National Project for Water Pollution Control (2012ZX07103-002) and the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC; 41503083, 41271462, 41030529). This work is also supported by a grant from the 111 Project (B14001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roland Kallenborn
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 552 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, W., Bai, ZL., Liu, WX. et al. Occurrence, spatial distribution, sources, and risks of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in surface sediments from a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 10335–10348 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-6001-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-6001-6