Abstract
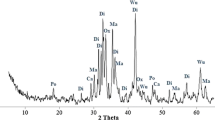
Rapid increase of CO2 concentration in the atmosphere has forced the international community towards adopting actions to restrain from the impacts of climate change. Moreover, in India, the dependence on fossil fuels is projected to increase in the future, implying the necessity of capturing CO2 in a safe manner. Alkaline solid wastes can be utilized for CO2 sequestration by which its disposal issues in the country could also be met. The present work focuses to study direct mineral carbonation of steelmaking slag (SS) at room temperature and low-pressure conditions (<10 bar). Direct mineral carbonation of SS was carried out in a batch reactor with pure CO2 gas. The process parameters that may influence the carbonation of SS, namely, CO2 gas pressure, liquid to solid ratio (L/S) and reaction time were also studied. The results showed that maximum sequestration of SS was attained in the aqueous route with a capacity of 82 g of CO2/kg (6 bar, L/S ratio of 10 and 3 h). In the gas-solid route, maximum sequestration capacity of about 11.1 g of CO2/kg of SS (3 bar and 3 h) was achieved indicating that aqueous route is the better one under the conditions studied. These findings demonstrate that SS is a promising resource and this approach could be further developed and used for CO2 sequestration in the country. The carbonation process was evidenced using FT-IR, XRD, SEM and TG analysis.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baciocchi R, Costa G, Polettini A, Pomi R (2009) Influence of particle size on the carbonation of stainless steel slag for CO2 storage. Energy Procedia 1(1):4859–4866
Baciocchi R, Costa G, Bartolomeo ED, Polettini A, Pomi R (2010) Carbonation of stainless steel slag as a process for CO2 storage and slag valorization. Waste Biomass Valor 1:467–477
Bobicki ER, Liu Q, Xu Z, Zeng H (2012) Carbon capture and storage using alkaline industrial wastes. Prog Energy Combust Sci 38(2):302–320
Chang EE, Pan SY, Chen YH, Chu HW, Wang CF, Chiang PC (2011) CO2 sequestration by carbonation of steelmaking slags in an autoclave reactor. J Hazard Mater 195:107–114
Fernandez Bertos M, Li X, Simons JR, Hills CD, Carey PJ (2004) Investigation of accelerated carbonation for the stabilisation of MSW incinerator ashes and the sequestration of CO2. Green Chem 6(8):428–436
Global steel 2013: a new world, a new strategy (2013). Elliott M, Agrawal A, Assis C, Stall B, Mangers P, Beifus A. Ernst and Young, UK
Hetland J, Anantharaman R (2009) Carbon capture and storage (CCS) options for co-production of electricity and synthetic fuels from indigenous coal in an Indian context. Energy Sustain Dev 13(1):56–63
Huijgen WJJ, Witkamp GJ, Comans RNJ (2005) Mineral CO2 sequestration by steel slag carbonation. Environ Sci Technol 39:9676–9682
Huijgen WJJ, Ruijg GJ, Comans RNJ, Witkamp GJ (2006) Energy consumption and net CO2 sequestration of aqueous mineral carbonation. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:9184–9194
Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment (INCCA) (2010) Ministry of environment and forests. Greenhouse Gas Emissions, India
International Energy Agency (2013) World Energy Outlook 2013 (WEO 2013). OECD publishing, Paris. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/weo-2013-en
Mathew P, Stephen L, George J (2013) Steel slag ingredient for concrete pavement. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 2(3):710–714
Mazzotti M, Abanades JC, Allam R, Lackner KS, Meunier F, Rubin E et al (2005) Mineral carbonation and industrial uses of carbon dioxide. In: IPCC special report on carbon dioxide capture and storage. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, Chapter 7
Montes-Hernandez G, Perez-Lopez R, Renard F, Nietob JM, Charlet L (2009) Mineral sequestration of CO2 by aqueous carbonation of coal combustion fly-ash. J Hazard Mater 161(1-2):1347–1354
Nyambura MG, Mugera GW, Felicia PL, Gathura NP (2011) Carbonation of brine impacted fractionated coal fly ash: implications for CO2 sequestration. J Environ Manage 92(3):655–664
Palaciosw M, Puertas F (2006) Effect of carbonation on alkali-activated slag paste. J Am Ceram Soc 89(10):3211–3221
Pan SY, Chang EE, Chiang PC (2012) CO2 capture by accelerated carbonation of alkaline wastes: a review on its principles and applications. Aerosol Air Qual Res 12(5):770–791
Pappu A, Saxena M, Asolekar SR (2007) Solid wastes generation in India and their recycling potential in building materials. Build Environ 42(6):2311–2320
Pires JCM, Martins FG, Alvim-Ferraz MCM, Simoes M (2011) Recent developments on carbon capture and storage: an overview. Chem Eng Res Des 89:1446–1460
Sahu RC, Patel R, Ray BC (2010) Neutralization of red mud using CO2 sequestration cycle. J Hazard Mater 179(1-3):28–34
Salman M, Cizer O, Pontikes Y, Santos RM, Snellings R, Vandewalle L, Blanpain B, Balen KV (2014) Effect of accelerated carbonation on AOD stainless slag for its valorization as a CO2 sequestering construction material. Chem Eng J 246:39–52
Santos RM, Francois D, Mertens G, Elsen J, Gerven TV (2013) Ultra-sound intensified mineral carbonation. Appl Thermal Eng 57(1-2):154–163
Sarkar R, Singh N, Das SK (2010) Utilization of steel melting electric arc furnace slag for development of vitreous ceramic tiles. Bull Mater Sci 33(3):293–298
Tamilselvi Dananjayan RR, Kandasamy P, Andimuthu R (2015) Direct mineral carbonation of coal fly ash for CO2 sequestration. J Clean Prod. doi:10.10010.1016/ j.jclepro.2015.05.145.
Tian S, Jiang J, Chen X, Yan F, Li K (2013) Direct gas–solid carbonation kinetics of steel slag and the contribution to in situ sequestration of flue gas CO2 in steel-making plants. Chem Sus Chem 6(12):2348–2355
Tian S, Jiang J, Yan F, Li K, Chen X (2015) Synthesis of highly efficient CaO-based, self-stabilizing CO2 sorbents via structure reforming of steel slag. Environ Sci Technol 49:7464–7472
Uibu M, Kuusik R, Andreas L, Kirsimae K (2011) The CO2-binding by Ca-Mg-silicates in direct aqueous carbonation of oil shale ash and steel slag. Energy Procedia 4:925–932
Viebahn P, Holler S, Vallentin D, Liptow H, Villar A (2011) Future CCS implementation in India: a systemic and long-term Analysis. Energy Procedia 4:2708–2715
Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC 5th Assessment Report (AR5): Climate change 2013: the physical science basis (2013) Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA
Yadav VS, Prasad M, Khan J, Amritphale SS, Singh M, Raju CB (2010) Sequestration of carbon dioxide (CO2) using red mud. J Hazard Mater 176(1-3):1044–1050
Zevenhoven R, Teir S, Elonev S (2008) Heat optimization of a staged gas–solid mineral carbonation process for long-term CO2 storage. Energy 33(2):362–370
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to “Department of Science and Technology” (DST), New Delhi, India, for financial support (Ref N0.DST/IS-STAC/CO2-SR-56/09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rushendra Revathy, T.D., Palanivelu, K. & Ramachandran, A. Direct mineral carbonation of steelmaking slag for CO2 sequestration at room temperature. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 7349–7359 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5893-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5893-5