Abstract
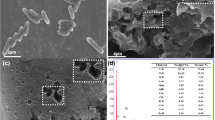
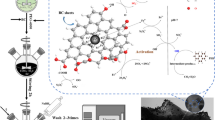
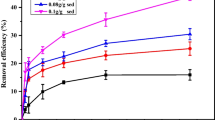
In this study, an aerobic strain identified as Rhodococcus sp. was isolated from the sediment of a typical electronic waste disassemble site, Taizhou, China. This strain could use BDE-209 as the sole carbon and energy source and degrade 65.1 % of BDE-209 (initial concentration being 50 mg/L) within 144 h. To explore the BDE-209 degradation properties of this strain with the co-existed electronic donor, zerovalent iron/activated carbon (ZVI/AC) was introduced to build a microbial-chemical coupling system, which was found to promote the degradation of BDE-209 slightly (74.7 % in 144 h). Moreover, the debromination products in both of the batch experiments were determined with GC/MS, which showed that lower brominated PBDE congeners were produced almost in order of the number of bromine ions, ranged from nona- to di-BDEs. In addition, the possible debromination pathways of BDE-209 for each system were proposed respectively, which confirmed the microbial activity of BDE-209 debromination. Since some of the lower-brominated BDE congeners are much toxic than BDE-209, these microbial activities might bring potential hazards to the environment with BDE-209 contamination. It is the first time to investigate the transformation of BDE-209 with microbial-chemical coupling system, which is universal in the nature, thus suggesting that the ecological safety of environment exposed to PBDEs should be focused in the future.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bramwell L, Fernandes A, Rose M, Harrad S, Pless-Mulloli T (2014) PBDEs and PBBs in human serum and breast milk from cohabiting UK couples. Chemosphere 116:67–74
Chen WF, Pan L, Chen LF, Wang Q, Yan CC (2014a) Dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene by nano zero-valent iron/activated carbon composite: iron loading, kinetics and pathway. RSC Adv 4:46689–46696
Chen XJ, Chen GL, Qiu MD, Sun GP, Guo J, Xu MY (2014b) Synergistic degradation of deca-BDE by an enrichment culture and zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7856–7862
Chou HL, Chang YT, Liao YF, Lin CH (2013) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by bacterial mixed cultures in a soil/water system. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 85:671–682
Chow KL, Man YB, Zheng JS, Liang Y, Tam NFY, Wong MH (2012) Characterizing the optimal operation of photocatalytic degradation of BDE-209 by nano-sized TiO2. J Environ Sci 24:1670–1678
Deng DY, Guo J, Sun GP, Chen XJ, Qiu MD, Xu MY (2011) Aerobic debromination of deca-BDE: Isolation and characterization of an indigenous isolate from a PBDE contaminated sediment. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65:465–469
Egorova DO, Demakov VA, Plotnikova EG (2011) Destruction of mixture of tri-hexa-chlorinated biphenyls by Rhodococcus genus strains. Appl Biochem Microbiol 47:599–606
Gerecke AC, Hartmann PC, Heeb NV, Kohler H-PE, Giger W, Schmid P, Zennegg M, Kohler M (2005) Anaerobic degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether. Environ Sci Technol 39:1078–1083
Huang K, Lin KF, Guo J, Zhou XY, Wang JX, Zhao JH, Zhou P, Xu F, Liu LL, Zhang W (2013) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in birds from Chongming Island, Yangtze estuary, China: insight into migratory behavior. Chemosphere 91:1416–1425
Ikonomou MG, Rayne S, Addison RF (2002) Exponential increases of the brominated flame retardants, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, in the Canadian Arctic from 1981 to 2000. Environ Sci Technol 36:1886–1892
Keum YS, Li QX (2005) Reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39:2280–2286
Kierkegaard A, Bignert A, Sellström U, Olsson M, Asplund L, Jansson B, De Wit CA (2004) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and their methoxylated derivatives in pike from Swedish waters with emphasis on temporal trends, 1967–2000. Environ Pollut 130:187–198
Lagalante AF, Shedden CS, Greenbacker PW (2011) Levels of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in dust from personal automobiles in conjunction with studies on the photochemical degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209). Environ Int 37:899–906
Li Y, Duan YP, Huang F, Yang J, Xiang N, Meng XZ, Chen L (2013) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in e-waste: level and transfer in a typical e-waste recycling site in Shanghai, Eastern China. Waste Manag 34:1059–1065
Li Y, Niu S, Hai R, Li M (2015) Concentrations and distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in soils and plants from a deca-BDE manufacturing factory in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1133–1143
Liu LL, Li H, Wang ZP, Liu RH, Zhang YC, Lin KF (2015) Insights into spatially and temporally co-occurring polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the East China Sea. Chemosphere 123:55–63
Lu M, Zhang ZZ, Wu XJ, Xu YX, Su XL, Zhang M, Wang JX (2013) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by a metal resistant strain, Bacillus cereus JP12. Bioresour Technol 149:8–15
Luo Q, Cai ZW, Wong MH (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish and sediment from river polluted by electronic waste. Sci Total Environ 383:115–127
Luo S, Yang SG, Xue YG, Liang F, Sun C (2011) Two-stage reduction/subsequent oxidation treatment of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether in aqueous solutions: kinetic, pathway and toxicity. J Hazard Mater 192:1795–1803
Luo S, Yang SG, Sun C, Gu JD (2012) Improved debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by bimetallic iron–silver nanoparticles coupled with microwave energy. Sci Total Environ 429:300–308
Nose K, Hashimoto S, Takahashi S, Noma Y, Sakai SI (2007) Degradation pathways of decabromodiphenyl ether during hydrothermal treatment. Chemosphere 68:120–125
Qiu MD, Chen XJ, Deng DY, Guo J, Sun GP, Mai BX, Xu MY (2012) Effects of electron donors on anaerobic microbial debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Biodegradation 23:351–361
Robrock KR, Korytár P, Alvarez-Cohen L (2008) Pathways for the anaerobic microbial debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Environ Sci Technol 42:2845–2852
Robrock KR, Coelhan M, Sedlak DL, Alvarez-Cohen L (2009) Aerobic biotransformation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) by bacterial isolates. Environ Sci Technol 43:5705–5711
Ross PS, Couillard CM, Ikonomou MG, Johannessen SC, Lebeuf M, Macdonald RW, Tomy GT (2009) Large and growing environmental reservoirs of Deca-BDE present an emerging health risk for fish and marine mammals. Mar Pollut Bull 58:7–10
Shi GY, Yin H, Ye JS, Peng H, Li J, Luo CL (2013) Aerobic biotransformation of decabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-209) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chemosphere 93:1487–1493
Shih YH, Tai YT (2010) Reaction of decabrominated diphenyl ether by zerovalent iron nanoparticles. Chemosphere 78:1200–1206
Sjödin A, Jones RS, Focant JF, Lapeza C, Wang RY, Mcgahee EE, Zhang YL, Turner WE, Slazyk B, Needham LL, Patterson DG (2004) Retrospective time-trend study of polybrominated diphenyl ether and polybrominated and polychlorinated biphenyl levels in human serum from the United States. Environ Health Perspect 112:654–658
Stiborova H, Vrkoslavova J, Lovecka P, Pulkrabova J, Hradkova P, Hajslova J, Demnerova K (2015) Aerobic biodegradation of selected polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in wastewater sewage sludge. Chemosphere 118:315–321
Su GJ, Liu YX, Huang LY, Shi YL, Zhang AQ, Zhang LX, Liu WB, Gao LR, Zheng MH (2013a) Synergetic effect of alkaline earth metal oxides and iron oxides on the degradation of hexachlorobenzene and its degradation pathway. Chemosphere 90:103–111
Su YF, Cheng YL, Shih YH (2013b) Removal of trichloroethylene by zerovalent iron/activated carbon derived from agricultural wastes. J Environ Manag 129:361–366
Tang ZW, Huang QF, Cheng JL, Yang YF, Yang J, Guo W, Nie ZQ, Zeng N, Jin L (2014) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soils, sediments, and human hair in a plastic waste recycling area: a neglected heavily polluted area. Environ Sci Technol 48:1508–1516
Wang JX, Liu LL, Wang JF, Pan BS, Fu XX, Zhang G, Zhang L, Lin KF (2015) Distribution of metals and brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in sediments, soils and plants from an informal e-waste dismantling site, South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1020–1033
Xiao JN, Yue QY, Gao BY, Sun YY, Kong JJ, Gao Y, Li Q, Wang Y (2014) Performance of activated carbon/nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of trihalomethanes (THMs) at infinitesimal concentration in drinking water. Chem Eng J 253:63–72
Xie YY, Fang ZQ, Cheng W, Tsang PE, Zhao DY (2014) Remediation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soil using Ni/Fe bimetallic nanoparticles: influencing factors, kinetics and mechanism. Sci Total Environ 485–486:363–370
Xu GY, Wang JB (2014) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by white-rot fungus Phlebia lindtneri. Chemosphere 110:70–77
Xu L, Huo X, Zhang YL, Li WQ, Zhang JQ, Xu XJ (2015) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human placenta associated with neonatal physiological development at a typical e-waste recycling area in China. Environ Pollut 196:414–422
Yu ZQ, Liao RE, Li HR, Mo LG, Zeng XY, Sheng GY, Fu JM (2011) Particle-bound dechlorane plus and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in ambient air around Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 159:2982–2988
Zhuang Y, Ahn S, Luthy RG (2010) Debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by nanoscale zerovalent iron: pathways, kinetics, and reactivity. Environ Sci Technol 44:8236–8242
Zhuang Y, Jin L, Luthy RG (2012) Kinetics and pathways for the debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by bimetallic and nanoscale zerovalent iron: effects of particle properties and catalyst. Chemosphere 89:426–432
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41001316, 51108262), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WB1214059), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014 M551415).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Liu, R. et al. Aerobic debromination of BDE-209 by Rhodococcus sp. coupled with zerovalent iron/activated carbon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 3925–3933 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5663-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5663-4