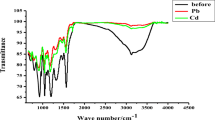
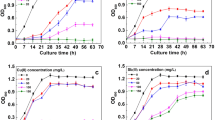
Abstract
In the present study, we investigated structural effects of various ionic liquids (ILs) on microalgal growth inhibition and microbial biodegradability. For this, we tested pyridinium- and pyrrolidinium-based ILs with various alkyl chain lengths and bromide anion, and compared the toxicological effects with log EC50 values of imidazolium-based IL with the same alkyl chains and anion from literature. Comparing determined EC50 values of cationic moieties with the same alkyl chain length, pyridinium-based ILs were found to be slightly more toxic towards the freshwater green alga, Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, than a series of pyrrolidinium and imidazolium except to 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide. Concerning the biodegradation study of 12 ILs using the activated sludge microorganisms, the results showed that the pyridinium derivatives except to 1-propyl-3-methylpyridinium cation were degraded. Whereas in case of imidazolium- and pyrrolidinium-based compounds, only n-hexyl and n-octyl substituted cations were fully degraded but no significant biodegradation was observed for the short chains (three and four alkyl chains).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernot RJ, Kennedy EE, Lamberti GA (2005) Acute and chronic toxicity of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on photosynthetic response of Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. J Biosci Bioeng 105:425–428
Biczak R, Pawlowska B, Balczewski P, Rychter P (2014) The role of the anion in the toxicity of imidazolium ionic liquids. J Hazard Mater 274:181–190
Blaise CR (1993) In: Richardson ML (ed) Ecotoxicology monitoring. VCH, Weinheim, pp 83–108
Bond HC (1950) Problems in the cultivation of algae. In: Brunel J, Prescott GW, Tiffany LH (eds) The culturing of algae. Antioch, Yellow Springs, OH, pp 11–17
Cho C-W, Pham TPT, Jeon Y-C, Vijayaraghavan K, Choe W-S, Yun Y-S (2007) Toxicity of imidazolium salt with anion bromide to a phytoplankton Selenastrum capricornutum: effect of alkyl-chain length. Chemosphere 69:1003–1007
Cho C-W, Jeon YC, Pham TPT, Vijayaraghavan K, Yun Y-S (2008a) The ecotoxicity of ionic liquids and traditional organic solvents on microalgal Selenastrum capricornutum. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:166–171
Cho C-W, Pham TPT, Jeon Y-C, Yun Y-S (2008b) Influence of anions on the toxic effects of ionic liquids to a phytoplankton Selenastrum capricornutum. Chemosphere 10:67–72
Deng Y, Beadham I, Ghavre M, Costa Gomes MF, Gathergood N, Husson P, Légeret B, Quilty B, Sancelme M, Besse-Hoggan P (2015) When can ionic liquids be considered readily biodegradable? Biodegradation pathways of pyridinium, pyrrolidinium and ammonium-based ionic liquids. Green Chem 17:1479–1491
Docherty KM, Dixon JK, Kulpa CF (2007) Biodegradability of imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquids by an activated sludge microbial community. Biodegradation 18:481–493
Docherty KM, Joyce MV, Kulacki KJ, Kulpa CF (2010) Microbial biodegradation and metabolite toxicity of three pyridinium-based cation ionic liquids. Green Chem 12:701–712
Freemantle M (2003) BASF’s smart ionic liquids—process scavenges acid on a large scale without producing solids. Chem Eng News 81:9
Garcia MT, Gathergood N, Scammells PJ (2005) Biodegradable ionic liquids: part II. Effect of the anion and toxicology. Green Chem 7:9–14
Gathergood N, Garcia MT, Scammells PJ (2004) Biodegradable ionic liquids: part I. Concept, preliminary targets and evaluation. Green Chem 6:166–175
Gathergood N, Scammells PJ, Garcia MT (2006) Biodegradable ionic liquids: part III. The first readily biodegradable ionic liquids. Green Chem 8:156–160
Harjani JR, Singer RD, Garcia MT, Scammells PJ (2008) The design and synthesis of biodegradable pyridinium ionic liquids. Green Chem 10:436–438
Kulacki KJ, Lamberti GA (2008) Toxicity of imidazolium ionic liquids to freshwater algae. Green Chem 10:104–110
Larson JH, Frost PC, Lamberti GA (2008) Variable toxicity of ionic liquid-forming chemicals to Lemna minor and the influence of dissolved organic matter. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:676–681
Latala A, Stepnowski P, Nedzi M, Mrozik W (2005) Marine toxicity assessment of imidazolium ionic liquids: acute effects on the Baltic algae Oocystis submarina and Cyclotella meneghiniana. Aquat Toxicol 73:91–98
Latała A, Nędzi M, Stepnowski P (2009a) Toxicity of imidazolium and pyridinium based on ionic liquids towards algae, Chlorella vulgaris, Oocystis submarina (green algae) and Cyclotella meneghiniana, Skeletonema marinoi (diatoms). Green Chem 11:580–588
Latała A, Nędzi M, Stepnowski P (2009b) Toxicity of imidazolium and pyridinium based on ionic liquids towards algae, Bavillaria paxillifer (a microphytobenthic diatom) and Geitlerinema amphibium (a microphytobenthic blue green alga). Green Chem 11:1371–1376
Latała A, Nędzi M, Stepnowski P (2010) Toxicity of imidazolium ionic liquids towards algae. Influence of salinity variations. Green Chem 12:60–64
Lewis MA (1995) In: Rand GM (ed) Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology: effects, environmental fate, and risk assessment, 2nd edn. Taylor and Francis, Washington, DC, pp 135–170
Ma J, Dong X, Fang Q, Li X, Wang J (2014) Toxicity of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on Physa acuta and the snail antioxidant stress response. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 28:69–75
Matzke M, Stolte S, Thiele K, Juffernholz T, Arning J, Ranke J, Welz-Biermann U, Jastorff B (2007) The influence of anion species on the toxicity of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids observed in an (eco)toxicological test battery. Green Chem 9:1198–1207
Matzke M, Stolte S, Arning J, Uebers U, Filsers J (2009) Ionic liquids in soils: effect of different anion species of imidazolium based ionic liquids on wheat (Triticum aestivum) as affected by different clay minerals and clay concentrations. Ecotoxicology 18:197–203
Modelli A, Sali A, Galletti P, Samori C (2008) Biodegradation of oxygenated and non-oxygenated imidazolium-based ionic liquids in soil. Chemosphere 73:1322–1327
Neumann J, Steudte S, Cho C-W, Thöming J, Stolte S (2014) Biodegradability of 27 pyrrolidinium, morpholinium, piperidinium, imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquid cations under aerobic conditions. Green Chem 16:2174–2184
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (2002) Freshwater alga and cyanobacteria growth inhibition test, 2011 updated, OECD guideline 201
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (1992) Modified OECD screening, ready biodegradability, OECD guideline 301E
Pham TPT, Cho C-W, Min J, Yun Y-S (2008) Alkyl-chain length effects of imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquids on photosynthesis response of Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. J Biosci Bioeng 105:425–428
Pham TPT, Cho C-W, Jeon C-O, Chung Y-J, Lee M-W, Yun Y-S (2009) Identification of metabolites involved in the biodegradation of the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylpyridinium bromide by activated sludge microorganisms. Environ Sci Technol 43:516–521
Pham TPT, Cho C-W, Yun Y-S (2010) Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: a review. Water Res 44:352–372
Ranke J, Mölter K, Stock F, Bottin-Weber U, Poczobutt J, Hoffmann J, Ondruschka B, Filser J, Jastorff B (2004) Biological effects of imidazolium ionic liquids with varying chain lengths in acute Vibrio fischeri and WST-1 cell viability assays. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 58:394–404
Rogers RD, Seddon KR (2005) Ionic liquids IIIB: fundamentals, process, challenges, and opportunities. ACS, Washington DC
Romero A, Santos A, Tojo J, Rodriguez A (2008) Toxicity and biodegradability of imidazolium ionic liquids. J Harzard Mater 151:268–273
Stepnowski P, Składanowski AC, Ludwiczak A, Łaczyńska E (2004) Evaluating the cytotoxicity of ionic liquids using human cell line HeLa. Hum Exp Toxicol 23:513–517
Stolte S, Abdulkarim S, Arning J, Blomeyer-Nienstedt A-K, Bottin-Weber U, Matzke M, Ranke J, Jastorff B, Thöming J (2008) Primary biodegradation of ionic liquid cations, identification of degradation products of 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium chloride and electrochemical wastewater treatment of poorly biodegradable compounds. Green Chem 10:214–224
Stolte S, Schulz T, Cho C-W, Arning J, Strassner T (2013) Synthesis, toxicity and biodegradation of tunable aryl alkyl ionic liquids. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 1:410–418
Stolte S, Steudte S, Igartua A, Stepnowski P (2011) The biodegradation of ionic liquids—the view from a chemical structure perspective. Curr Org Chem 15:1946–1978
Torrecilla JS, Garcia J, Rojo E, Rodriguez F (2009) Estimation of toxicity of ionic liquids in Leukemia Rat Cell Line and Acetylcholinesterase enzyme by principal component analysis, neutral networks and multiple linear regression. J Hazard Mater 164:182–194
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (1994) Ecological effect test guidelines, Algal toxicity, Tiers I and II, OPPTS 850.5400
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (1998) Fate, transport, and transformation test guidelines, OPPTS 835.3110, Ready biodegradability
van der Gast CJ, Whiteley AS, Thompson IP (2004) Temporal dynamics and degradation activity of an bacterial inoculum for treating waste metal-working fluid. Environ Microbiol 6:254–263
van der Gast CJ, Ager D, Lilley AK (2008) Temporal scaling of bacterial taxa is influenced by both stochastic and deterministic ecological factors. Environ Microbiol 10:1411–1418
Well AS, Coomber VT (2006) On the freshwater exotoxicology and biodegradation properties of some common ionic liquids. Org Process Res Dev 10:794–798
Yun Y-S, Park JM (1997) Development of gas recycling photobioreactor system for microalgal carbon dioxide fixation. Korean J Chem Eng 14:1297–1300
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Korean Government through NRF (2014R1A2A1A09007378, 2014R1A1A2008337) grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, T.P.T., Cho, CW. & Yun, YS. Structural effects of ionic liquids on microalgal growth inhibition and microbial degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 4294–4300 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5287-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5287-8