Abstract
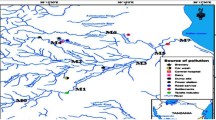
Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are toxic environmental pollutants that are often found in sediments. The Yangtze and Yellow rivers in China are two of the largest rivers in Asia and are therefore important aquatic ecosystems; however, few studies have investigated the PCDD/F and PCB content in the sediments of these rivers. Accordingly, this study was conducted to generate baseline data for future environmental risk assessments. In the present study, 26 surface sediments from the middle reaches of the Yellow and Yangtze rivers were analyzed for PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like (dl) PCBs by high-resolution gas chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry. The ranges of PCDD/F, dl-PCB, and WHO-TEQ content in sediments from the Yellow River were 2.1–19.8, 1.11–9.9, and 0.08–0.57 pg/g (dry weight), respectively. The ranges of PCDD/F, dl-PCB, and WHO-TEQ content in sediments from the Yangtze River were 6.1–84.9, 1.8–24.1, and 0.13–0.29 pg/g (dry weight), respectively. Total organic carbon and dl-PCB contents in the Yellow River were significantly correlated (Spearman’s correlation coefficient, r = 0.64, P < 0.05). It is well known that total organic carbon plays a role in the transport and redistribution of dl-PCB. Principal component analysis indicated that PCDD/Fs may arise from pentachlorophenol, sodium pentachlorophenate, and atmospheric deposition, while dl-PCBs likely originate from burning of coal and wood for domestic heating. The dioxin levels in the river sediments examined in this study were relatively low. These findings advance our knowledge regarding eco-toxicity and provide useful information regarding contamination sources.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aries E, Anderson DR, Ordsmith N, Hall K, Fisher R (2004) Development and validation of a method for analysis of “dioxin-like” PCBs in environmental samples from the steel industry. Chemosphere 54:23–31. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(03)00762-8
Bao Z, Wang K, Kang J, Zhao L (1995) Analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans in pentachlorophenol and sodium pentachlorophenate. Chinese Journal of Environmental Chemistry 14:317–321
Bouloubassi I, Fillaux J, Saliot A (2001) Hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Changjiang (Yangtze river) estuary, East China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 42:1335–1346
Buckley-Golder D (1999) Compilation of EU Dioxins Exposure and Health Data, Summary Report for European Commission DG Environment and the UK Department of the Environmental Transport and the Regions. AEAT/EEQC/0016. http://ec.europa.eu/environment/archives/dioxin/pdf/dioxin.pdf
Castro-Jimenez J et al (2008) Atmospheric input of POPs into Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): PCDD/F and dioxin-like PCB profiles and fluxes in the atmosphere and aquatic system. Chemosphere 73:S122–S130. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.097
Cornelissen G, Gustafsson Ö, Bucheli TD, Jonker MT, Koelmans AA, van Noort PC (2005) Extensive sorption of organic compounds to black carbon, coal, and kerogen in sediments and soils: mechanisms and consequences for distribution, bioaccumulation, and biodegradation. Environ Sci Technol 39:6881–6895. doi:10.1021/es050191b
Da C, Liu G, Tang Q, Liu J (2013) Distribution, sources, and ecological risks of organochlorine pesticides in surface sediments from the Yellow River Estuary, China. Environ Sci-Proc Imp 15:2288–2296. doi:10.1039/c3em00369h
Eljarrat E, Caixach J, Rivera J, de Torres M, Ginebreda A (2001) Toxic potency assessment of non-and mono-ortho PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs, and PAHs in northwest Mediterranean sediments (Catalonia, Spain). Environ Sci Technol 35:3589–3594. doi:10.1021/es010041a
El-Kady AA, Abdel-Wahhab MA, Henkelmann B, Belal MH, Morsi MK, Galal SM, Schramm KW (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyl, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and polychlorinated dibenzofuran residues in sediments and fish of the River Nile in the Cairo region. Chemosphere 68:1660–1668. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.066
Environment CCOMOT (2001) Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Summary Tables. Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, 1999. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Winnipeg. https://www.elaw.org/system/files/sediment_summary_table.pdf
Fattore E, Viganò L, Mariani G, Guzzi A, Benfenati E, Fanelli R (2002) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in River Po sediments. Chemosphere 49:749–754
Gui Z-f, Xue B, Yao S-c, Wei W-j, Yi S (2012) Organic carbon burial in lake sediments in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin, China. Hydrobiologia 710:143–156. doi:10.1007/s10750-012-1365-9
He MC, Sun Y, Li XR, Yang ZF (2006) Distribution patterns of nitrobenzenes and polychlorinated biphenyls in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from mid- and down-stream of the Yellow River (China). Chemosphere 65:365–374. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.033
Hosomi M, Matsuo T, Dobashi S, Katou S, Abe H (2003) Survey of dioxins in Tokyo Bay bottom sediment. Mar Pollut Bull 47:68–73. doi:10.1016/s0025-326x(02)00417-4
Hui Y, Zheng M, Liu Z, Gao L (2009) PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in sediments from Yellow Estuary and Yangtze Estuary, China. B Environ Contam Tox 83:614–619. doi:10.1007/s00128-009-9832-3
Jiang K, Li L, Chen Y, Jin J (1997) Determination of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in Chinese commercial PCBs and emissions from a testing PCB incinerator. Chemosphere 34:941–950
Josefsson S, Karlsson OM, Malmaeus JM, Cornelissen G, Wiberg K (2011) Structure-related distribution of PCDD/Fs, PCBs and HCB in a river-sea system. Chemosphere 83:85–94. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.019
Kannan K, Ramu K, Kajiwara N, Sinha RK, Tanabe S (2005) Organochlorine pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in Irrawaddy dolphins from India. Arch Environ Con Tox 49:415–420. doi:10.1007/s00244-005-7078-6
Kim KS et al (2009) Survey on organochlorine pesticides, PCDD/Fs, dioxin-like PCBs and HCB in sediments from the Han river, Korea. Chemosphere 75:580–587. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.01.075
Koh CH, Khim JS, Kannan K, Villeneuve DL, Senthilkumar K, Giesy JP (2004) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzofurans (PCDFs), biphenyls (PCBs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and 2,3,7,8-TCDD equivalents (TEQs) in sediment from the Hyeongsan River, Korea. Environ Pollut 132:489–501. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.001
Lee RG, Coleman P, Jones JL, Jones KC, Lohmann R (2005) Emission factors and importance of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, PCNs, PAHs and PM10 from the domestic burning of coal and wood in the UK. Environ Sci Technol 39:1436–1447. doi:10.1021/es048745i
Li C, Zheng M, Gao L, Zhang B, Liu L, Xiao K (2013) Levels and distribution of PCDD/Fs, dl-PCBs, and organochlorine pesticides in sediments from the lower reaches of the Haihe River basin, China. Environ Monit Assess 185:1175–1187. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2624-y
Li H-W, Lee W-J, Huang K-L, Chang-Chien G-P (2007) Effect of raw materials on emissions of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from the stack flue gases of secondary aluminum smelters. J Hazard Mater 147:776–784. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.078
Liu M, Yang Y, Hou L, Xu S, Ou D, Zhang B, Liu Q (2003) Chlorinated organic contaminants in surface sediments from the Yangtze Estuary and nearby coastal areas, China. Mar Pollut Bull 46:672–676. doi:10.1016/s0025-326x(03)000500-x
Montuori P, Cirillo T, Fasano E, Nardone A, Esposito F, Triassi M (2014) Spatial distribution and partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyl and organochlorine pesticide in water and sediment from Sarno River and Estuary, Southern Italy. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:5023–5035. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-2419-x
Nam JJ, Gustafsson O, Kurt-Karakus P, Breivik K, Steinnes E, Jones KC (2008) Relationships between organic matter, black carbon and persistent organic pollutants in European background soils: Implications for sources and environmental fate. Environ Pollut 156:809–817. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.05.027
Neamtu M et al (2009) Chemical, biological, and ecotoxicological assessment of pesticides and persistent organic pollutants in the Bahlui River, Romania. Environ Sci Pollut R16:76–85. doi:10.1007/s11356-009-0101-0
Nie Z et al (2013) Occurrence, possible sources, and temporal trends of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in water and sediment from the lower Yangtze River basin, Jiangsu and Shanghai areas of Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:8751–8762. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1832-5
Nunes M, Vernisseau A, Marchand P, Le Bizec B, Ramos F, Pardal MA (2014) Occurrence of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in superficial sediment of Portuguese estuaries. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:9396–9407. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-2891-y
Ren M, Peng P, Chen D, Chen P, Li X (2009) Patterns and sources of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in surface sediments from the East River, China. J Hazard Mater 170:473–478. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.072
Ren M et al (2007) Atmospheric deposition of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in Guangzhou, China. Atmos Environ 41:592–605. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.08.025
Sakai M, Seike N, Kobayashi J, Kajihara H, Takahashi Y (2008) Mass balance and long-term fate of PCDD/Fs in a lagoon sediment and paddy soil, Niigata, Japan. Environ Pollut 156:760–768. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.004
Shih SI, Wang YF, Chang JE, Jang JS, Kuo FL, Wang LC, Chang-Chien GP (2006) Comparisons of levels of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans in the surrounding environment and workplace of two municipal solid waste incinerators. J Hazard Mater 137:1817–1830. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.022
Song Y, Ji J, Mao C, Yang Z, Yuan X, Ayoko GA, Frost RL (2010) Heavy metal contamination in suspended solids of Changjiang River—environmental implications. Geoderma 159:286–295. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.07.020
Stone R (2009) Confronting a toxic blowback from the electronics trade. Science 325:1055–1055. http://www.kysq.org/docs/1055.pdf
Van den Berg M et al (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and Mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93:223–241. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfl055
Wang G-l, Ma L-m, Sun J-h, Zhang G (2010) Occurrence and distribution of organochlorine pesticides (DDT and HCH) in sediments from the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China. Environ Monit Assess 168:511–521. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-1131-2
Wen S, Hui Y, Yang F, Liu Z, Xu Y (2008) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and dibenzofurans (PCDFs) in surface sediment and bivalve from the Changjiang Estuary. Chin J Oceanol and Limn 26:35–44. doi:10.1007/s00343-008-0035-2
Wen Y, Yang Z, Xia X (2013) Dissolved and particulate zinc and nickel in the Yangtze River (China): distribution, sources and fluxes. Appl Geochem 31:199–208. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.01.004
Yang H, Zhuo S, Xue B, Zhang C, Liu W (2012) Distribution, historical trends and inventories of polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments from Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent East China Sea. Environ Pollut 169:20–26. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2012.05.003
Zhang H et al (2008) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in soils and sediments from Daliao River Basin, China. Chemosphere 73:1640–1648. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.067
Zhang Q, Jiang G (2005) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments and aquatic organisms from the Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 61:314–322. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.099
Zhang S, Peng P, Huang W, Li X, Zhang G (2009) PCDD/PCDF pollution in soils and sediments from the Pearl River Delta of China. Chemosphere 75:1186–1195. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.02.032
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 21377140 and 21321004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Concentrations (pg/g dw) of PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs in the sediments from the middle reaches of the Yellow River (DOCX 27 kb)
Table S2
Concentrations (pg/g dw) of PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs in the sediments from the middle reaches of the Yangtze River (DOCX 27 kb) (DOCX 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, L., Huang, H., Liu, L. et al. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments from the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 19804–19813 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5175-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5175-2