Abstract
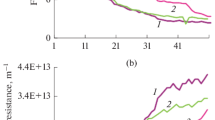
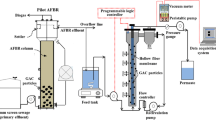
A novel dead-end mode operation for filtering anaerobic suspensions was investigated. In this mode, the filtration system automatically adjusted backwashing frequency to a preselected transmembrane pressure set-point. This paper discusses the effectiveness of the backwashing conditions on membrane fouling. Anaerobic suspensions from a conventional wastewater treatment plant digester were used as model suspensions for the trials carried out at lab-scale. Gas sparging aided backwashing significantly enhanced membrane cleaning efficiency. No effect of gas sparging on internal fouling was detected. Also, the cleaning efficiency linearly decreased with permeate flux. Nevertheless, due to a high increase in the reversible fouling, a reasonable net permeate flux (7.2–6.8 L/h m2) can be achieved when intermediate fluxes (12–16 L/h m2) were imposed and the higher transmembrane pressure set-point value (50 kPa) was applied. Both backwashing duration and flux exhibited similar influence on cake fouling removal for a given volume of permeate produced.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (2005) Water Environment Federation Standard Methods for the examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed. Washington DC USA
Bacchin P, Aimar P, Field RW (2006) Critical and sustainable fluxes: theory, experiments and applications. J Membr Sci 281:42–69
Bessiere Y, Guigui C, Remize P, Cabassud C (2009) Coupling air-assisted backwash and rising steps: a new way to improve ultrafiltration process operation for inside-out hollow fibre modules. Desalination 240:71–77
Bolton G, LaCasse D, Kuriyel R (2006) Combined models of membrane fouling: development and application to microfiltration and ultrafiltration of biological fluids. J Membr Sci 277:75–84
Busch J, Marquardt W (2009) Model-based control of MF/UF filtration processes: pilot plant implementation and results. Water Sci Tech 59:1713–1720
Defrance L, Jaffrin MY (1999) Reversibility of fouling formed in activated sludge filtration. J Membr Sci 157:73–84
Delgado S, Vera L, González E, Martínez M, Vera LM, Bravo L (2012) Effect of previous coagulation in direct ultrafiltration of primary settled municipal wastewater. Desalination 304:41–48
Diez V, Ezquerra D, Cabezas JL, García A, Ramos C (2014) A modified method for evaluation of critical flux, fouling rate and in situ determination of resistance and compressibility in MBR under different fouling conditions. J Membr Sci 453:1–11
Do K-U, Banu R, Son D-H, Yeom I-T (2012) Influence of ferrous sulfate on thermochemical sludge disintegration and on performances of wastewater treatment in a new process: Anoxic-oxic membrane bioreactor coupled with sludge disintegration step. Biochem Eng J 66:20–26
Drews A (2010) Membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors—characterisation, contradictions, causes and cures. J Membr Sci 363:1–28
Hu A, Stuckey D (2006) Treatment of dilute wastewaters using a novel submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. J Environ Eng ASCE 132:190–198
Jeison D, van Betuw W, van Lier JB (2008) Feasibility of anaerobic membrane bioreactors for the treatment of wastewaters with particulate organic matter. Sep Sci Technol 43:3417–3431
Jeison D, van Lier JB (2007) Cake formation and consolidation: main factors governing the applicable flux in anaerobic submerged membrane bioreactors (AnSMBR) treating acidified wastewaters. Sep Purif Technol 56:71–78
Kraume M, Wedi D, Schaller J, Iversen V, Drews A (2009) Fouling in MBR: what use are lab investigations for full scale operation? Desalination 236:94–103
Le-Clech P, Chen V, Fane TAG (2006) Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J Membr Sci 284:17–53
Lew B, Tarre S, Beliavski M, Dosoretz C, Green M (2009) Anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) for domestic wastewater treatment. Desalination 243:251–257
Liao BQ, Kraemer JT, Bagley DM (2006) Anaerobic membrane bioreactors: applications and research directions. Crít Rev Environ Sci Technol 36:489–530
Martin I, Pidou M, Soares A, Judd S, Jefferson B (2011) Modelling the energy demands of aerobic and anaerobic membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment. Environ Technol 32:921–932
Martin-Garcia I, Monsalvo V, Pidou M, Le-Clech P, Judd SJ, McAdam EJ, Jefferson B (2011) Impact of membrane configuration on fouling in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. J Membr Sci 382:41–49
Meng F, Chae SR, Drews A, Kraume M, Shin HS, Yang F (2009) Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res 43:1489–1512
Ozgun H, Dereli R, Ersahin M, Kinaci C, Spanjers H, van Lier J (2013) A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment: Integration options, limitations and expectations. Sep Pur Tech 118:89–104
Robles A, Ruano MV, Ribes J, Ferrer J (2013) Factors that affect the permeability of commercial hollow-fibre membranes in a submerged anaerobic MBR (HF-SAnMBR) system. Water Res 47:1277–1288
Smith A, Stadler L, Love N, Skerlos S, Raskin L (2012) Perspectives on anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 122:149–159
Smith PJ, Vigneswaran S, Ngo HH, Ben-Aim R, Nguyen H (2006) A new approach to backwash initiation in membrane systems. J Membr Sci 278:381–389
Stuckey D (2012) Recent developments in anaerobic membrane reactors. Bioresour Technol 122:137–148
Vera L, González E, Díaz O, Delgado S (2014) Performance of a tertiary submerged membrane bioreactor operated at supra-critical fluxes. J Membr Sci 457:1–8
Villarroel R, Delgado S, González E, Morales M (2013) Physical cleaning initiation controlled by transmembrane pressure set-point in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Sep Pur Tech 104:55–63
Wu J, He C, Zhang Y (2012) Modelling membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor by considering the role of solid, colloidal and soluble components. J Membr Sci 397–398:102–111
Ye Y, Chen V, Le-Clech P (2011) Evolution of fouling deposition and removal on hollow fibre membrane during filtration with periodical backwash. Desalination 283:198–205
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the N.R.C. (MINECO project CTM2011-27307). Mr Ruigómez acknowledges a predoctoral fellowship supported by MINECO, BES-2012-060920. The authors are grateful to GE Water & Process Technologies for membrane module supply and also to the Water Analysis Laboratory of the ULL Chemical Engineering Department for its analytical advice. We also thank EMMASA for supplying the sludge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vera, L., González, E., Ruigómez, I. et al. Analysis of backwashing efficiency in dead-end hollow-fibre ultrafiltration of anaerobic suspensions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 16600–16609 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4857-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4857-0