Abstract
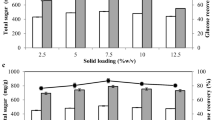
The present investigation demonstrated pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass rice straw using natural deep eutectic solvents (NADESs), and separation of high-quality lignin and holocellulose in a single step. Qualitative analysis of the NADES extract showed that the extracted lignin was of high purity (>90 %), and quantitative analysis showed that nearly 60 ± 5 % (w/w) of total lignin was separated from the lignocellulosic biomass. Addition of 5.0 % (v/v) water during pretreatment significantly enhanced the total lignin extraction, and nearly 22 ± 3 % more lignin was released from the residual biomass into the NADES extract. X-ray diffraction studies of the untreated and pretreated rice straw biomass showed that the crystallinity index ratio was marginally decreased from 46.4 to 44.3 %, indicating subtle structural alterations in the crystalline and amorphous regions of the cellulosic fractions. Thermogravimetric analysis of the pretreated biomass residue revealed a slightly higher T dcp (295 °C) compared to the T dcp (285 °C) of untreated biomass. Among the tested NADES reagents, lactic acid/choline chloride at molar ratio of 5:1 extracted maximum lignin of 68 ± 4 mg g−1 from the rice straw biomass, and subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis of the residual holocellulose enriched biomass showed maximum reducing sugars of 333 ± 11 mg g−1 with a saccharification efficiency of 36.0 ± 3.2 % in 24 h at 10 % solids loading.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NADESs:
-
Natural deep eutectic solvents
- T dcp :
-
Thermal onset of decomposition
- IL:
-
Ionic liquid
- DESs:
-
Deep eutectic solvents
- CMC:
-
Carboxymethyl cellulose
- PNPG:
-
p-Nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
- LA:
-
Lactic acid
- BE:
-
Betaine
- LC:
-
Lactic acid/choline chloride
- CC:
-
Choline chloride
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffractometer
- CrI:
-
Crystallinity index
- I cry :
-
Intensity of crystalline region
- I amp :
-
Intensity of amorphous region
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- KBr:
-
Potassium bromide
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetric analysis
- NREL:
-
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
- FPU:
-
Filter paper unit
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- PES:
-
Polyether sulfone
- HCl:
-
Hydrochloric acid
- H2SO4 :
-
Sulfuric acid
- [Bmim][Cl]:
-
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride
References
Abbott AP, Bell TJ, Handa S, Stoddart B (2006) Cationic functionalisation of cellulose using a choline based ionic liquid analogue. Green Chem 8:784–786
Alvira P, Tomas-Pejo M, Ballesteros M, Negro MJ (2010) Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4851–4861
Anwar Z, Gulfraz M, Irshad M (2014) Agro-industrial lignocellulosic biomass a key to unlock the future bioenergy: a brief review. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7(2):163–173
Belal BE (2013) Bioethanol production from rice straw residues. Braz J Microbiol 44:225–234
Binod P, Sindhu R, Singhania RR, Vikram S, Devi L, Nagalakshmi S, Kurien N, Sukumaran RK, Pandey A (2010) Bioethanol production from rice straw: an overview. Bioresour Technol 101:4767–4774
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Choi YH, Spronsen JV, Dai Y, Verberne M, Hollmann F, Arends IWCE, Witkamp GJ, Verpoorte R (2011) Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology. Plant Physiol 156:1710–1705
Dai Y, Spronsen JV, Witkamp GJ, Verpoorte R, Choi YH (2013a) Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal Chim Acta 766:61–68
Dai Y, Witkamp GJ, Verpoorte R, Choi YH (2013b) Natural deep eutectic solvents as a new extraction media for phenolic metabolites in Carthamus tinctorius L. Anal Chem 85:6272–6278
Dowe N, McMillan J (2008) SSF experimental protocols – Lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis and fermentation. Laboratory analytical procedure (LAP). Technical report NREL/TP-510-42630
Ehrman T (1996) Determination of acid-soluble lignin in biomass. Laboratory analytical procedure (LAP). Technical Report NREL/TP-510-42618
Francisco M, Gonzalez ASB, de Dios SLG, Weggemans W, Kroon MC (2013a) Comparison of a low transition temperature mixture (LTTM) formed by lactic acid and choline chloride with choline lactate ionic liquid and the choline chloride salt: physical properties and vapour-liquid equilibria of mixtures containing water and ethanol. RSC Adv 3:23553–23561
Francisco M, van den Bruinhorst A, Zubeir LF, Peter CJ, Kroon MC (2013b) A new low transition temperature mixture (LTTM) formed by choline chloride+lactic acid: characterization as solvent for CO2 capture. Fluid Phase Equilib 340:77–84
Ghandi K (2014) A review of ionic liquids, their limits and applications. Green Sustain Chem 4:44–53
Ghose TK (1994) Measurement of cellulase activities. In: Commission on Biotechnology. IUPAC, New York, pp. 1–12
Goering HK, Van Soest PJ (1970) Forage fiber analysis (apparatus, reagents, procedures and some applications). In: USDA Agricultural Handbook No. 379
Grasvik J, Winestrand S, Normark M, Jonsson LJ, Mikkola JP (2014) Evaluation of four ionic liquids for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. BMC Biotechnol 14:34
Gunny AAN, Arbain D, Nashef EM, Jamal P (2015) Applicability evaluation of deep eutectic solvents-Cellulase system for lignocellulosic hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 181:297–302
Hendriks ATWM, Zeeman G (2009) Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 100:10–18
Hsu TC, Gou GL, Chen WH, Hwang WS (2010) Effect of acid pretreatment of rice straw on structural properties and enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 101:4907–4913
Huang ZL, Wu BP, Wen Q, Yang TX, Yang Z (2013) Deep eutectic solvents can be viable enzyme activators and stabilizers. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. doi:10.1002/jctb.4285
Kline LM, Hayes DG, Womac AR, Labbe N (2010) Simplified determination of lignin content in hard and soft woods via UV-spectrophotometric analysis of biomass dissolved in ionic liquids. Bioresources 5:1366–1383
Kroon MC, Casal MF, Vanden Bruinhorst A (2014) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass and recovery of substituents using natural deep eutectic solvents/compound mixtures with low transition temperatures. International Patent. Publication Number: WO 2013/153203 A1
Kumar AK, Parikh BJ (2015) Cellulose degrading enzymes from Aspergillus terreus D34 and enzymatic saccharification of mild-alkali and dilute-acid pretreated lignocellulosic biomass residues. Bioresour Bioprocess. doi:10.1186/s40643-015-0038-8
Lee HV, Hamid SBA, Zain SK (2014) Conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to nanocellulose: structure and chemical process. Sci World J. doi:10.1155/2014/631013
Liu Z, Xu A, Zhao T (2011) Energy from combustion of rice straw: status and challenges to china. Energy Power Eng 3:325–331
Liu YT, Chen YA, Xing YJ (2014) Synthesis and characterization of novel ternary deep eutectic solvents. Chin Chem Lett 25:104–106
Melero JA, Iglesias J, Garcia A (2012) Biomass as renewable feedstock in standard refinery units: feasibility, opportunities and challenges. Energy Environ Sci 5:7393–7420
Mood SH, Golfeshan AH, Tabatabaei M, Jouzani GS, Najafi GH, Gholami M, Ardjmand M (2013) Lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol, a comprehensive review with a focus on pretreatment. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 27:77–93
Paiva A, Craveiro R, Aroso I, Martins M, Reis RL (2014) Natural deep eutectic solvents – Solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 2:1063–1071
Rahanama N, Mamat S, Kalsom U, Foo S, Ling H, Aini N, Rahman A, Ariff AB (2013) Effect of alkali pre-treatment of rice straw on cellulase and xylanase production by local Trichoderma harzianum SNRS3 under solid state fermentation. Bioresources 8:2881–2896
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE Jr, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the x-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794
Sun Y, Lin L, Pang C, Deng H, Peng H, Li J (2007) Hydrolysis of cotton fiber cellulose in formic acid. Energy Fuel 21:2386–2389
Tadesse H, Luque R (2011) Advances on biomass pretreatment using ionic liquids: an overview. Energy Environ Sci 4:3913–3929
Tang S, Baker GA, Zhao H (2014) Ether- and alcohol-functionalized task-specific ionic liquids: attractive properties and applications, Chem Soc Rev. 41:4030–4066
Wyman CE, Dale BE, Elander RT, Holtzapple M, Ladisch MR, Lee YY (2005) Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies. Bioresour Technol 96:1959–1966
Xia S, Baker GA, Ravula S, Zhao H (2014) Aqueous ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents saccharification for cellulosic biomass pretreatment and saccharification. RSC Adv 4:10586–10596
Yingying Z, Xiaohua L, Xin F, Yijin S, Xiaoyan J (2013) Properties and applications of choline-based deep eutectic solvents. Prog Chem 25:881–892
Zeng Q, Wang Z, Huang Y, Ding X, Chen J, Xu K (2014) Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for protein partitioning. Analyst 139:2565–2573
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Director, Sardar Patel Renewable Energy Research Institute, Gujarat, India, for the financial support through Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR-ACRIP) project code VVN/RES/LBT/2014/5 to carry out the research. The authors acknowledge helpful discussions with Prof. Datta Madambar, BRD School of Biosciences, Sardar Patel University, Gujarat, India. The authors are thankful to Er. Farha Tinwala, Thermochemical Conversion Division, SPRERI for helpful discussions on viscosity measurement of NADES reagents.
Author contributions
BSP and MP performed research experiments; AKK designed, supervised the research work, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Angeles Blanco
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A.K., Parikh, B.S. & Pravakar, M. Natural deep eutectic solvent mediated pretreatment of rice straw: bioanalytical characterization of lignin extract and enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated biomass residue. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 9265–9275 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4780-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4780-4