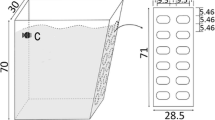
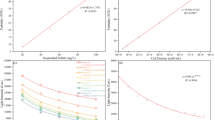
Abstract
Wind waves are responsible for some of the spatio-temporal gradients observed in the biotic and abiotic variables in large shallow lakes. However, their effects on the phytoplankton community composition are still largely unexplored especially in freshwater systems such as lakes. In this paper, using field observations and mesocosm bioassay experiments, we investigated the impact of turbulence generated by wind waves on the phytoplankton community composition (especially on harmful cyanobacteria) in Lake Taihu, a large, shallow eutrophic lake in China. The composition of the phytoplankton community varied with the intensity of wind waves in the different areas of the lake. During summer, when wind waves were strong in the central lake, diatoms and green algae seemed to dominate while harmful cyanobacteria dominated in the weakly influenced Meiliang Bay. Turbulence bioassays also showed that diatoms and green algae were favoured by turbulent mixing. The critical time for the shift of the phytoplankton community composition was approximately 10 days under turbulent conditions. However, short-term (6 days) turbulence is rather beneficial for the dominance of cyanobacteria. This study suggests that the duration of wind events and their associated hydrodynamics are key factors to understanding the temporal and spatial changes of phytoplankton communities.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arin L, Marrasé C, Maar M, Peters F, Sala MM, Alcaraz M (2002) Combined effects of nutrients and small-scale turbulence in a microcosm experiment. I. Dynamics and size distribution of osmotrophic plankton. Auat Microb Ecol 29:51–61
Barton AD, Ward BA, Williams RG, Follows MJ (2014) The impact of fine-scale turbulence on phytoplankton community structure. Limnol Oceanogr: Fluids Environ 4(1):34–49
Berger WH, Parker FL (1970) Diversity of planktonic foraminifera in deep-sea sediments. Science 168(3937):1345–1347
Cao HS, Kong FX, Luo LC, Sh XL, Yang Z, Zhang XF, Tao Y (2006) Effects of wind and wind-induced waves on vertical phytoplankton distribution and surface blooms of Microcystis aeruginosa in Lake Taihu. J Freshwater Ecol 21(2):231–238
Cardoso LS, Marques DM (2009) Hydrodynamics-driven plankton community in a shallow lake. Aquat Ecol 43(1):73–84
Carrick HJ, Aldridge FJ, Schelske CL (1993) Wind influences phytoplankton biomass and composition in a shallow, productive lake. Limnol Oceanogr 38(6):1179–1192
Clarke RD, Buskey EJ, Marsden KC (2005) Effects of water motion and prey behavior on zooplankton capture by two coral reef fishes. Mar Biol 146(6):1145–1155
Donaghay PL, Osborn TR (1997) Toward a theory of biological-physical control of harmful algal bloom dynamics and impacts. Limnol Ocennogr 42:1283–1296
Estrada M, Berdalet E (1997) Phytoplankton in a turbulent world. Sci Mar 61:125–140
Guadayol Ò, Peters F (2006) Analysis of wind events in a coastal area: a tool for assessing turbulence variability for studies on plankton. Sci Mar 70(1):9–20
Gulati RD, DeMott WR (1997) The role of food quality for zooplankton: remarks on the state-of-the-art, perspectives and priorities. Freshwater Biol 38(3):753–768
G-Tóth L, Parpala L, Balogh C, Tàtrai I, Baranyai E (2011) Zooplankton community response to enhanced turbulence generated by water-level decrease in Lake Balaton, the largest shallow lake in Central Europe. Limnol Ocennogr 56(6):2211–2222
Härkönen L, Pekcan-Hekim Z, Hellén N, Ojala A, Horppila J (2014) Combined effects of turbulence and different predation regimes on zooplankton in highly colored water—implications for environmental change in lakes. Plos One 9, e111942
Hu H, Li Y, Wei Y, Zhu H, Chen J, Shi Z (1980) Freshwater algae in China. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai (in Chinese)
Huisman J, Sharples J, Stroom JM, Visser PM, Kardinaal WEA, Verspagen JMH et al (2004) Changes in turbulent mixing shift competition for light between phytoplankton species. Ecology 85(11):2960–2970
Hunter PD, Tyler AN, Willby NJ, Gilvear DJ (2008) The spatial dynamics of vertical migration by Microcystis aeruginosa in a eutrophic shallow lake: a case study using high spatial resolution time-series airborne remote sensing. Limnol Oceanogr 53(6):2391–2406
Kundu PK, Cohen IM (2010) Fluid mechanics. San Diego Academic Press, California
Li YP, Feng Y, Liu XP, Luo LC, Xu QX (2008) Numerical modeling of waves in Lake Taihu. J Lake Sci 20(1):117–122 (In Chinese)
Moreno-Ostos E, Cruz-Pizarro L, Basanta A, George D (2009) The influence of wind-induced mixing on the vertical distribution of buoyant and sinking phytoplankton species. Aquat Ecol 43(2):271–284
Oliver RL (1994) Floating and sinking in gas-vacuolate cyanobacteria. J Phycol 30:161–173
Paerl HW, Xu H, McCarthy MJ, Zhu G, Qin B, Li Y, Gardner WS (2011) Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res 45:1973–1983
Pápista É, Ács É, Böddi B (2002) Chlorophyll-a determination with ethanol—a critical test. Hydroiologia 485:191–198
Pécseli HL, Trulsen JK, Fiksen Ø (2014) Predator-prey encounter and capture rates in turbulent environments. Limnol Oceanogr: Fluids Environ 4:85–105
Pekcan-Hekim Z, Joensuu L, Horppila J (2013) Predation by a visual planktivore perch (Perca fluviatilis) in a turbulent and turbid environment. Can J Fish Aqarat Sci 70(6):854–859
Peters F, Marrasé C (2000) Effects of turbulence on plankton: an overview of experimental evidence and some theoretical considerations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 205:291–306
Peters F, Redondo JM (1997) Turbulence generation and measurement: application to studies on plankton. Sci Mar 61:205–228
Prairie JC, Sutherland KR, Nickols KJ, Kaltenberg AM (2012) Biophysical interactions in the plankton: a cross-scale review. Limnol Oceanogr 2(1):121–145
Qin BQ, Xu PZ, Wu QL, Luo LC, Zhang YL (2007) Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581(1):3–14
Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao G, Zhang YL, Li W, Paerl HW, Carmichael WW (2010) A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ Manage 45(1):105–112
Romero E, Peters F, Marrasé C (2012) Dynamic forcing of coastal plankton by nutrient imbalances and match-mismatch between nutrients and turbulence. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 464:69–87
Ruiz J, Macias D, Peters F (2004) Turbulence increases the average settling velocity of phytoplankton cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(51):17720–17724
Sanford LP (1997) Turbulent mixing in experimental ecosystem studies. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 161:265–293
Wang P, Shen H, Xie P (2012) Can hydrodynamics change phosphorus strategies of diatoms?—nutrient levels and diatom blooms in lotic and lentic ecosystems. Microb Ecol 63(2):369–382
Wilson AE, Samelle O, Tillmanns AR (2006) Effects of cyanobacterial toxicity and morphology on the population growth of freshwater zooplankton: meta-analyses of laboratory experiments. Limnol Oceanogr 51(4):1915–1924
Wong KTM, Lee JHW, Hodgkiss IJ (2007) A simple model for forecast of coastal algal blooms. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 74:175–196
Wu T, Qin B, Zhu G, Luo L, Ding Y, Bian G (2013) Dynamics of cyanobacterial bloom formation during short-term hydrodynamic fluctuation in a large shallow, eutrophic, and wind-exposed Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(12):8546–8556
Wu X, Kong F, Chen Y, Qian X, Zhang L, Yu Y, Zhang M, Xing P (2010) Horizontal distribution and transport processes of bloom-forming Microcystis in a large shallow lake (Taihu, China). Limnologica 40(1):8–15
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol Oceanogr 55(1):420–432
Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Gao G, Zhang L, Luo LC, Zhang YL (2007) Effects of hydrodynamics on phosphorus concentrations in water of Lake Taihu, a large, shallow, eutrophic lake of China. Hydrobiologia 581(1):53–61
Zhu MY, Paerl HW, Zhu GW (2014) The role of tropical cyclones in stimulating cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 39:310–321
Zohary T (1985) Hyperscums of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa in a hypertrophic lake (Hartbeespoort Dam, South Africa). J Plankton Res 7(3):399–409
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the very thorough and constructive reviews provided by two anonymous reviewers. This research was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (41230744, 41471021) and Water Pollution Control and Management Project (2012ZX07503-002). We thank the Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research (TLLER) for providing the physical, chemical, and phytoplankton data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Qin, B., Casenave, C. et al. Effects of wind wave turbulence on the phytoplankton community composition in large, shallow Lake Taihu. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 12737–12746 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4535-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4535-2