Abstract
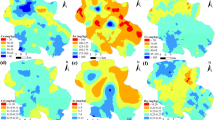
A total of 59 samples consisting of 45 topsoils samples and 14 subsoils samples were collected from urban soils of Donggang and were analyzed for soil properties and 12 trace elements. The mean contents of As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, Se, V, and Zn in topsoils were 5.76, 0.20, 9.88, 44.82, 17.69, 0.05, 578.96, 19.98, 28.38, 0.21, 58.88, and 58.32 mg kg−1, respectively. The mean enrichment factor results suggested that Hg, Cd, Pb, Cu, Se, and Zn were enriched in topsoils compared with subsoils. Spatial distribution maps of trace elements indicated that Hg, Cd, Pb, Cu, Se, and Zn had similar patterns, with the highest values in the industrial region. There were no significant associations displayed between spatial distributions of As, Co, Cr, Mn, Ni, and V and the industrial region. Through correlation analysis, stepwise regression analysis, and redundancy analysis, three main sources of 12 trace elements were identified. Cd, Hg, and Se originated from industrial emissions and coal combustion, and As, Co, Cr, Mn, Ni, and V had a lithogenic origin. The combination of human activities and natural sources contributed to the contents of Cu, Pb, and Zn, and the human activities included industrial and traffic emissions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta JA, Faz A, Martinez-Martinez S (2010) Identification of heavy metal sources by multivariable analysis in a typical Mediterranean city (SE Spain). Environ Monit Assess 169:519–530
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2004) Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ Int 30:1009–1017
Al-Khashman OA (2004) Heavy metal distribution in dust, street dust and soils from the work place in Karak Industrial Estate, Jordan. Atmos Environ 38:6803–6812
Alloway B (1995) Heavy metals in soils. Chapman and Hall, London
Bai X, Li W, CHen Y, Jiang Y (2007) The general distributions of trace elements in Chinese coals. Coal Qual Technol 22:1–4
Cachada A, Pereira ME, da Silva EF, Duarte AC (2012) Sources of potentially toxic elements and organic pollutants in an urban area subjected to an industrial impact. Environ Monit Assess 184:15–32
Cai LM et al (2012) Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:2–8
Chen TB, Wong JWC, Zhou HY, Wong MH (1997) Assessment of trace metal distribution and contamination in surface soils of Hong Kong. Environ Pollut 96:61–68
Chen HM, Zheng CR, Tu C, Zhu YG (1999) Heavy metal pollution in soils in China: status and countermeasures. Ambio 28:130–134
Chen TB et al (2005) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 60:542–551
Chen T, Liu XM, Zhu MZ, Zhao KL, Wu JJ, Xu JM, Huang PM (2008) Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban-rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 151:67–78
Chen X, Xia XH, Zhao Y, Zhang P (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 181:640–646
Chen XD, Lu XW, Yang G (2012) Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an Second Ringroad, NW China using multivariate statistical methods. Catena 98:73–78
Dai JR, Pang XG, Yu C, Wang CL, Wang ZH, Hu XP (2011) Geochemical baselines and background values and element enrichment characteristics in soils in eastern Shandong Province. Geochimica 40:577–587
Davis HT, Aelion CM, McDermott S, Lawson AB (2009) Identifying natural and anthropogenic sources of metals in urban and rural soils using GIS-based data, PCA, and spatial interpolation. Environ Pollut 157:2378–2385
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324
Franco-Uria A, Lopez-Mateo C, Roca E, Fernandez-Marcos ML (2009) Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J Hazard Mater 165:1008–1015
Jenny H (1941) Factors of soil formation. A system of quantitative pedology. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Jiang J, Hao J, Wu Y, Strret DG, Duan L, Tian H (2005) Development of mercury emission inventory from coal combustion in China. Environ Sci 26:34–39
Jiries AG, Hussein HH, Halaseh Z (2001) The quality of water and sediments of street runoff in Amman, Jordan. Hydrol Process 15:815–824
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants. CSC press, London
Lee CS, Li XD, Shi WZ, Cheung SC, Thornton I (2006) Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci Total Environ 356:45–61
Li XY et al (2013) Heavy metal contamination of urban soil in an old industrial city (Shenyang) in Northeast China. Geoderma 192:50–58
Lin YP, Teng TP, Chang TK (2002) Multivariate analysis of soil heavy metal pollution and landscape pattern in Changhua county in Taiwan. Landsc Urban Plan 62:19–35
Liu Y, Lv JS, Zhang B, Bi J (2013) Spatial multi-scale variability of soil nutrients in relation to environmental factors in a typical agricultural region, Eastern China. Sci Total Environ 450:108–119
Llorens JF, Fernandez-Turiel JL, Querol X (2001) The fate of trace elements in a large coal-fired power plant. Environ Geol 40:409–416
Lu RK (2000) Analysis method of soil and agricultural chemistry. China Agricultural Science & Technology Press, Beijing
Lu LT, Chang IC, Hsiao TY, Yu YH, Ma HW (2007a) Identification of pollution source of cadmium in soil - Application of material flow analysis and a case study in Taiwan. Environ Sci Pollut R 14:49–59
Lu Y, Zhu F, Chen J, Gan HH, Guo YB (2007b) Chemical fractionation of heavy metals in urban soils of Guangzhou, China. Environ Monit Assess 134:429–439
Lu AX, Wang JH, Qin XY, Wang KY, Han P, Zhang SZ (2012) Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 425:66–74
Lv J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Dai B (2014a) Multivariate geostatistical analyses of heavy metals in soils: spatial multi-scale variations in Wulian, Eastern China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 107:140–147
Lv JS, Zhang ZL, Li S, Liu Y, Sun YY, Dai B (2014b) Assessing spatial distribution, sources, and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Nansi Lake, Eastern China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299:1671–1681
Lv J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Dai J, Dai B, Zhu Y (2015) Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in soils of Ju country (Eastern China) using multivariate and geostatistical approach. J Soils Sediments 15:163–178
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A, Neri R, Sprovieri M (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci Total Environ 300:229–243
McDermott S, Wu JL, Cai B, Lawson A, Aelion CM (2011) Probability of intellectual disability is associated with soil concentrations of arsenic and lead. Chemosphere 84:31–38
McGrath D, Zhang CS, Carton OT (2004) Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in Silvermines area, Ireland. Environ Pollut 127:239–248
Nanos N, Rodríguez Martín JA (2012) Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in soils: spatial variability in the Duero river basin (Spain). Geoderma 189:554–562
Norra S, Lanka-Panditha M, Kramar U, Stuben D (2006) Mineralogical and geochemical patterns of urban surface soils, the example of Pforzheim, Germany. Appl Geochem 21:2064–2081
Nriagu JO, Pacyna JM (1988) Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace-metals. Nature 333:134–139
Otero-Rey JR, Lopez-Vilarino JM, Moreda-Pineiro J, Alonso-Rodriguez E, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, Lopez-Mahia P, Prada-Rodriguez D (2003) As, Hg, and Se flue gas sampling in a coal-fired power plant and their fate during coal combustion. Environ Sci Technol 37:5262–5267
Querol X, Fernandezturiel JL, Lopezsoler A (1995) Trace-elements in coal and their behavior during combustion in a large power-station. Fuel 74:331–343
Rizhao Municipal Bureau of Statistics (2012) Rizhao statistical year book in 2012. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Rodríguez Martín JA, Ramos-Miras JJ, Boluda R, Gil C (2013) Spatial relations of heavy metals in arable and greenhouse soils of a Mediterranean environment region (Spain). Geoderma 200:180–188
Rodriguez JA, Nanos N, Grau JM, Gil L, Lopez-Arias M (2008) Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in Spanish agricultural topsoils. Chemosphere 70:1085–1096
Shi GT, Chen ZL, Xu SY, Zhang J, Wang L, Bi CJ, Teng JY (2008) Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 156:251–260
Shpirt MY, Punanova SA (2011) Accumulation of mercury in petroleum, coal, and their conversion products. Solid Fuel Chem 45:330–336
Smolders E, Degryse F (2002) Fate and effect of zinc from tire debris in soil. Environ Sci Technol 36:3706–3710
Swaine DJ (1990) Trace elements in coal. Butterworth-Heinemann, London
Tian HZ, Wang Y, Xue ZG, Cheng K, Qu YP, Chai FH, Hao JM (2010) Trend and characteristics of atmospheric emissions of Hg, As, and Se from coal combustion in China, 1980–2007. Atmos Chem Phys 10:11905–11919
Wei BG, Yang LS (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94:99–107
Weinberg SL, Abramowitz SK (2008) Statistics using SPSS: an integrative approach. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Xu W, Zeng X, Ye D, Querol X (2005) Distributions and environmental impacts of selenium in wastes of coal from a power plant. Environ Sci 26:64–68
Yang ZP, Lu WX, Long YQ, Bao XH, Yang QC (2011) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City, China. J Geochem Explor 108:27–38
Zhang CS (2006) Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ Pollut 142:501–511
Zhang XY, Lin FF, Wong MTF, Feng XL, Wang K (2009) Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County, China. Environ Monit Assess 154:439–449
Zheng YM, Chen TB, He JZ (2008) Multivariate geostatistical analysis of heavy metals in topsoils from Beijing, China. J Soils Sediments 8:51–58
Acknowledgments
This study was jointly funded by China State-Sponsored Postgraduate Study Abroad Program (No. 201306190053), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41101079), and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. Y2008E13), the Program B for Outstanding PhD Candidate of Nanjing University (No. 2014001B008), and the Program for Graduate Student’s Research Innovation of Jiangsu Province (CXLX13-051). We are grateful to the two anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z. et al. Distinguishing anthropogenic and natural sources of trace elements in soils undergoing recent 10-year rapid urbanization: a case of Donggang, Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 10539–10550 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4213-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4213-4