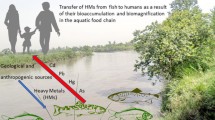
Abstract
From the concentration in water and sediments, bioconcentration and bioaccumulation of copper (Cu), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), cadmium (Cd), chrome (Cr), silver (Ag), lead (Pb), nickel (Ni), aluminum (Al), and arsenic (As) were determined in the gills, liver, and muscles of Geophagus brasiliensis in the Alagados Reservoir, Ponta Grossa, Paraná, Brazil. Metals were quantified through AAS, and a study was carried out on the existing relations between metal and body weight, size, and genre of this species. The level of metal in the water of the reservoir was lower than the maximum set forth in the legislation, except for that of Cd and Fe. In sediments, Cu, Cd, Cr, and Ni presented concentrations above the threshold effect level (TEL). Pb and Cr were above the limits for the G. brasiliensis. The tendency of metals present in the muscles of G. brasiliensis was Al > Cu > Zn > Fe > Co > Mn > Cr > Ag > Ni > Pb > Cd > As. In the gills, it was Al > Fe > Zn > Mn > Co > Ag > Cr > Ni > Cu > As > Pb > Cd, and the liver presented Al > Cu > Zn > Co > Fe > Mn > Pb > Ag > Ni > Cr > As > Cd. The bioconcentration and bioaccumulation of metal in the tissues follow the global tendency liver > gills > muscle. The statistical analysis did not point to significant differences in the metal concentration and body weight, size, and gender of the species in the three tissues under analysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel PD (2002) Water pollution biology. CRC
Abelha MC, Goulart E (2004) Oportunismo trófico de Geophagus brasiliensis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1824) (Osteichthyes, Cichlidae) no reservatório de Capivari, Estado do Paraná, Brasil. Acta Sci Biol Sci 26(1):37–45
Alloway BJ, Ayres DC (1997) Chemical principles of environmental pollution, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, p. 395
Alvorado NE, Quesada I, Hylland K, Marigómez I, Soto M (2006) Quantitative changes in metallothionein expression in target cell-types in the gills of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) exposed to Cd, Cu, Zn and after a depuration treatment. Aquat Toxicol 77:64–77
Al-Yousuf MH, El-Shahawi MS, Al-Ghais SM (2000) Trace metals in liver, skin and muscle of Lethrinus lentjan fish species in relation to body length and sex. Sci Total Environ 256(2–3):87–94
ANVISA (2014) Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. http://www.anvisa.gov.br/alimentos/legis/especifica/contaminantes.htm.
Asuquo FE, Ewa-Oboho I, Asuquo EF, Udo PJ (2004) Fish species used as biomarker for heavy metal and hydrocarbon contamination for Cross River, Nigeria. Environmentalist 2:29–37
Bastos RF, Condini MV, Varela Junior AS, Garcia AM (2011) Diet and food consumption of the pearl cichlid Geophagus brasiliensis (Teleostei: Cichlidae): relationships with gender and sexual maturity. Neotropical Ichthyol 9(4):825–830
Benincá C, Ramsdorf W, Vicari T, de Oliveira Ribeiro CA, de Almeida MI, de Assis HCS, Cestari MM (2012) Chronic genetic damages in Geophagus brasiliensis exposed to anthropic impact in Estuarine Lakes at Santa Catarina Coast–Southern of Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 184(4):2045–2056
Botté SE, Hugo Freije R, Marcovecchio JE (2007) Dissolved heavy metal (Cd, Pb, Cr, Ni) concentrations in surface water and porewater from Bahia Blanca estuary tidal flats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:415–421
Brekhovskikh VF, Volkova ZV, Katunin DN, Kazmiruk VD, Kazmiruk TN, Ostrovskaya EV (2002) Heavy metals in bottom sediment in the upper and lower Volga. Water Resour 29(5):539–547
Buratini SV, Brendelli A (2006) Bioacumulação, In: P. A. Zagatto & E. Bertoletti: Ecotoxicologia Aquática Princípios e Aplicações. Rima, pp. 55–87
Canli M, Atli G (2003) The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ Pollut 121(1):129–136
Carranza-Álvarez C, Alonso-Castro AJ, Alfaro-de La Torre MC, García-de La Cruz RF (2008) Accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in Scirpus americanus and Typha latifolia from an artificial Lagoon in San Luis Potosí, México. Water Air Soil Pollut 188:297–309
Carvalho CEV, Di Beneditto APM, Souza CMM, Ramos RMA, Rezende CE (2008) Heavy metal distribution in two cetacean species from Rio de Janeiro State, south-eastern Brazil. J Mar Biol Assoc U K 88(6):1117–1120
Clemente Z, Busato RH, de Oliveira Ribeiro CA, Cestari MM, Ramsdorf WA, Magalhães VF, Wosiack AC, de Assis HCS (2010) Analyses of paralytic shellfish toxins and biomarkers in a southern Brazilian reservoir. Toxicon 55(2):396–406
CONAMA (2011) Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. Resolução 357, de 17 de março de 2005, Publicada no DOU n° 053, de 18/03/2005, págs. 58–63. Alterada pela Resolução 410/2009 e pela 430/2011. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/res/res05/res35705.pdf.
Davies OA, Allison ME, Uyi HS (2006) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in water, sediment and periwinkle (Tympanotonus fuscatus var radula) from the Elechi Creek, Niger Delta. Afr J Biotechnol 5(10):968–973
Di Giulio RT, Hinton DE (2008) The toxicology of fishes. CRC
Ebrahimi M, Taherianfard M (2010) Pathological and hormonal changes in freshwater fishes duo to exposure to heavy metals pollutants. Water Air Soil Pollut 217(1):47–55
Ebrahimpour M, Mushrifah I (2008) Heavy metal concentrations (Cd, Cu and Pb) in five aquatic plant species in Tasik Chini, Malaysia. Environ Geol 54:689–698
Environment Canada (1999) Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life summary tables. http://www.ec.gc.ca.
FAO/WHO (2014) Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization. Contaminants & food additives. Limit test for heavy metals in food additive specifications—explanatory note. http://www.fao.org/food/food-safety-quality/scientific-advice/jecfa/guidelines0/en/
Förstner U, Wittmann GTW (1983) Metal pollution in the aquatic environment, 2ath edn. Springer, Berlin, p 486
Fowler BA, Nordberg GF, Nordberg M, Friberg L (2011) Handbook on the toxicology of metals. Academic
Giannakopoulou L, Neofitou C (2014) Heavy metal concentrations in Mullus barbatus and Pagellus erythrinus in relation to body size, gender, and seasonality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(11):7140–53
Gomes ID, Nascimento AA, Sales A, Araújo FG (2012) Can fish gill anomalies be used to assess water quality in freshwater Neotropical systems? Environ Monit Assess 184:5523–5531
Hidetoshi N (1984) Dicionário dos Peixes do Brasil. Editora Editerra, 1° Edição, 482 p
IPARDES (2010) Instituto Paranaense de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Social. Cadernos Municipais – Ponta Grossa. Paraná
Jarić I, Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Cvijanović G, Gačić Z, Jovanović LJ, Skorić S, Lenhardt M (2011) Determination of differential heavy metal and trace element accumulation in liver, gills, intestine and muscle of starlet (Acipenser ruthenus) from the Danube River in Serbia by ICP-OES. Microchem J 98:77–81
Kehrig HA, Costa M, Malm O (2007) Estudo da contaminação por metais pesados em peixes e mexilhão da Baia de Guanabara—Rio de Janeiro. Trop Oceanogr 35(1):32–50
Khan R, Israili SH, Ahmad H, Mohan A (2005) Heavy metal pollution assessment in surface water bodies and its suitability for irrigation around the Neyevli lignite mines and associated industrial complex, Tamil Nadu, India. Mine Water Environ 24:155–161
Kullander SO, Cichlidae (Cichlids) (2003) In: Checklist of the freshwater fishes of South and Central America, Reis RE, Kullander SO, Ferraris Jr. CJ. Porto Alegre: EDIPUCRS, Brasil, 605–654
Licata P, Trombetta D, Cristiani MT, Naccari C, Martino D, Cal M, Naccari IF (2005) Heavy metals in liver and muscles of bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) caught in the straits of Messina (Sicily, Italy). Environ Monit Assess 107:239–48
Lau S, Mohammed MA, Yen TC, Su’ut S (1998) Accumulation of heavy metals in fresh water molluscs. Sci Total Environ 214:113–121
Malik RN, Hashmi MZ, Huma Y (2014) Heavy metal accumulation in edible fish species from Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1188–1196
Marsden ID, Smith BD, Rainbow PS (2014) Effects of environmental and physiological variables on the accumulated concentrations of trace metals in the New Zealand cockle Austrovenus stutchburyi. Sci Total Environ 470–471:324–339
Martinez CBR, Nagae MY, ZaiaCTBV ZDAM (2004) Acute morphological and physiological effects of lead in the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Braz J Biol 64:797–807
Monroy M, Maceda-Veiga A, de Sostoa A (2014) Metal concentration in water, sediment and four fish species from Lake Titicaca reveals a large-scale environmental concern. Sci Total Environ 487(1):233–244
Monteiro V, Cavalcante DGSM, Viléla MBFA, Sfia SH, Martinez CBR (2011) In vivo and in vitro exposures for the evaluation of the genotoxic effects of lead on the Neotropical freshwater fish Prochilodus lineatus. Aquat Toxicol 104:291–298
Osório FHT, Silva LFO, Piancini LDS, Azevedo ACB, Liebel S, Yamamoto FY, Philippi VP, Silva Oliveira ML, Ortolani-Machado CF, Filipak Neto F, Cestari MM, Silva de Assis HC, Oliveira Ribeiro CA (2013) Water quality assessment of the Tubarão River through chemical analysis and biomarkers in the Neotropical fish Geophagus brasiliensis. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1512-5
Palaniappan PL, Karthikeyan S (2009) Bioaccumulation and depuration of chromium in the selected organs and whole body tissues of freshwater fish Cirrhinus mrigala individually and in a binary solution with nickel. J Environ Sci 21:229–236
Papagiannis I, Kagalou I, Leonardos J, Petridis D, Kalfakakou V (2004) Copper and zinc in four freshwater fish species from Lake Pamvotis (Greece). Environ Int 30:357–362
Peakall D, Burger J (2003) Methodologies for assessing exposure to metals: speciation, bioavailability of metals, and ecological host factors. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 56:110–121
Pereira MO, Calza C, Anjos MJ, Lopes RT, Araújo FG (2006) Metal concentrations in surface sediments of Paraíba do Sul River (Brazil). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 269(3):707–709
Poleksić V, Lenhardt M, Jarić I, Đorđević D, Gačić Z, Cvijanović G, Rašković B (2010) Liver, gills, and skin histopathology and heavy metal content of the Danube starlet (Acipenser ruthenus Linnaeus, 1758). Environ Toxicol Chem 29(3):515–521
Ramalho JFGP, Amaral Sobrinho NMB, Velloso ACX (2000) Contaminação da microbacia de Caetés com metais pesados pelo uso de agroquímicos. Pesq Agrop Brasileira 35(7):1289–1303
Rocha O, Espíndola ELG, Fenerich-Verani N, Verani JR, Rietzler AC (2005) Espécies invasoras em águas doces: estudos de caso e propostas de manejo, 416 p
Salomons W, Förstner U (1984) Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer. p. 349
Shah AQ, Kazi TG, Arain MB, Jamali MK, Afridi HI, Jalbani N, Baig JA, Kandhro GA (2009) Accumulation of arsenic in different fresh water fish species—potential contribution to high arsenic intakes. Food Chem 112:520–524
Shrivastava P, Saxena A, Swarup A (2003) Heavy metal pollution in a sewage-fed lake of Bhopal, (M. P.) India. Lakes Reserv Res Manag 8:1–4
Singh AK, Srivastava SC, Ansari A, Kumar D, Singh R (2012) Environmental monitoring and health risk assessment of African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) cultured in rural ponds, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:1142–1147
Singh AK, Srivastava SC, Verma P, Ansari A, Verma A (2014) Hazard assessment of metals in invasive fish species of the Yamuna River, India in relation to bioaccumulation factor and exposure concentration for human health Implications. Environ Monit Assess 2186(6):3823–36
Subotić S, Spasić S, Višnjić-Jeftić Z, Hegediš A, Krpo-Ćetković J, Mićković B, Skorić S, Lenhardt M (2013) Heavy metal and trace element bioaccumulation in target tissues of four edible fish species from the Danube River (Serbia). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:196–202
Terra BF, Araújo FG, Calza CF, Lopes RT, Teixeira P (2008) Heavy metal in tissues of three fish species from different trophic levels in a tropical Brazilian River. Water Air Soil Pollut 187:275–284
US EPA (1992) Environmental Protection Agency of United States. Acid digestion of waters for total recoverable or dissolved metals for analysis by FLAA or ICP spectroscopy. Method EPA-3005A. http://www.epa.gov/osw/hazard/testmethods/sw846/pdfs/3005a.pdf
US EPA (1996) Environmental Protection Agency of United States. Acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soils. Method EPA-3050B. http://www.epa.gov/wastes/hazard/testmethods/sw846/pdfs/3050b.pdf
US EPA (2001). Methods for collection, storage and manipulation of sediments for chemical and toxicological analyses: technical manual. EPA 823-B-01-002. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Washington, DC. http://water.epa.gov/polwaste/sediments/cs/upload/toc.pdf
US EPA (2014a) Environmental Protection Agency of United States. Ecological screening values for surface water, sediment, and soil. WSRC-TR-98–00110, http://www.osti.gov/bridge/purl.cover.jsp?purl=/47642uJvjR/webviewable/4764.PDF.
US EPA (2014b) Environmental Protection Agency of United States. Water quality criteria. National recommended water quality criteria. http://water.epa.gov/scitech/swgidance/standards/criteria/current/index.cfm#C.
Uysal K, Köse E, Bülbül M, Dönmez M, Erdoğan Y, Koyun M, Ömeroğlu C, Özmal F (2009) The comparison of heavy metal accumulation ratios of some fish species in Enne Dame Lake (Kütahya/Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 157:355–362
Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Jari I, Jovanović LJ, Skorić S, Smederevac-Lalić M, Nikčević M, Lenhardt M (2010) Heavy metal and trace element accumulation in muscle, liver and gills of the Ponticshad (Alosa immaculata Bennet 1835) from the Danube River (Serbia). Microchem J 95:341–344
Vukosav P, Mlakar M, Cukrov N, Kwokal Z, Pižeta I, Pavlus N, Špoljarić I, Vurnek M, Brozinčević A, Omanović D (2014) Heavy metal contents in water, sediment and fish in a karst aquatic ecosystem of the Plitvice Lakes National Park (Croatia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3826–3839
WHO (2011) World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking water quality, 4th edn. WHO, 564
Wood CM, Farrell AP, Brauner CJ (2011) Fish physiology: homeostasis and toxicology of essential metals, Vol. 31. Academic
Yilmaz F, Özdemir N, Demirak A, LeventTuna A (2007) Heavy metal levels in two fish species Leuciscus cephalus and Lepomis gibbosus. Food Chem 100:830–835
Zheng N, Wang Q, Liang Z, Zheng D (2008) Characterization of heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, Northeast China. Environ Pollut 154:135–142
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Araucaria Foundation by funding the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Highlights
Bioaccumulation and bioconcentration of 12 metals in the Geophagus brasiliensis in the reservoir in the state of Paraná, Brazil were determined.
The muscle showed lower bioconcentration and bioaccumulation of metals when compared to the gills and liver.
The liver presented higher bioconcentration of metals Cu, Co, Cd, Cr, Ag, and Ni and higher bioaccumulation of metals Cu, Co, Cd, Cr, Ag, Pb, Ni, and As when compared to the gills.
The gills presented higher bioaccumulation of Zn and Al and higher bioconcentration of Zn when compared to the muscle and liver.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voigt, C.L., da Silva, C.P., Doria, H.B. et al. Bioconcentration and bioaccumulation of metal in freshwater Neotropical fish Geophagus brasiliensis . Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 8242–8252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3967-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3967-4