Abstract
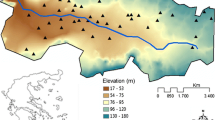
In this work, kriging with covariates is used to model and map the spatial distribution of salinity measurements gathered by an autonomous underwater vehicle in a sea outfall monitoring campaign aiming to distinguish the effluent plume from the receiving waters and characterize its spatial variability in the vicinity of the discharge. Four different geostatistical linear models for salinity were assumed, where the distance to diffuser, the west-east positioning, and the south-north positioning were used as covariates. Sample variograms were fitted by the Matèrn models using weighted least squares and maximum likelihood estimation methods as a way to detect eventual discrepancies. Typically, the maximum likelihood method estimated very low ranges which have limited the kriging process. So, at least for these data sets, weighted least squares showed to be the most appropriate estimation method for variogram fitting. The kriged maps show clearly the spatial variation of salinity, and it is possible to identify the effluent plume in the area studied. The results obtained show some guidelines for sewage monitoring if a geostatistical analysis of the data is in mind. It is important to treat properly the existence of anomalous values and to adopt a sampling strategy that includes transects parallel and perpendicular to the effluent dispersion.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bivand RS, Pebesma EJ, Gómez-Rubio V (2008) Applied spatial data analysis with R. ISBN: 97-0-387-78170-9
Carvalho JLB, Roberts PJW, Roldão J (2002) Field observations of the Ipanema Beach outfall. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 128(2):151– 160
Daviero GJ, Roberts PJW (2006) Marine wastewater discharges from multiport diffusers. III: stratified stationary water. J Hydraul Eng 132(4):404–410
Diggle PJ, Ribeiro Jr. PJ (2007) Model based geostatistics
Goovaerts P (1997) Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. Applied geostatistics series. ISBN13: 9780195115383, ISBN10: 0195115384
Hunt CD, Mansfield AD, Mickelson MJ, Albro CS, Geyer WR, Roberts PJW (2010) Plume tracking and dilution of effluent from the Boston sewage outfall. Mar Environ Res 70:150–161
Isaaks EH, Srivastava RM (1989) Applied geostatistics. New York Oxford, ISBN 0-19-505012-6-ISBN 0-19-505013-4 (pbk.)
Kitanidis P (1997) Introduction to geostatistics: applications in hydrogeology. New York (USA)
Lloyd C (2011) Local models for spatial analysis
Niu H, Husain T, Veitch B, Bose N, Adams S, He M, Lee K (2007) Ocean outfall mapping using an autonomous underwater vehicle. In: MTS/IEEE Oceans
Pardo-Igúzquiza E, Mardia KV, Chica-Olmo M (2009) Mlmatern: a computer program for maximum likelihood inference with the spatial Matérn covariance model. Comput Geosci 35(6):1139–1150. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2008.09.009. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300408002756
Petrenko AA, Jones BH, Dickey TD (1998) Shape and initial dilution of sand island, Hawaii sewage plume. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 124(6):565–571
R Development Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R version 3.00. http://www.R-project.org/.
Ramos P, Abreu N (2010) Environmental monitoring of wastewater discharges using an autonomous underwater vehicle. In: Workshop on Robotics for Environmental Monitoring, IEEE/RSJInternational Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. IROS2010, Taipei
Ramos P, Neves MV (2009) Environmental impact assessment and management of sewage outfall discharges using AUVs. In: Underwater vehicles
Ramos P, Neves MV, Pereira FL (2007) Mapping and initial dilution estimation of a sewage outfall plume using an autonomous underwater vehicle. Cont Shelf Res 27:583–593
Ribeiro PJ, Diggle PJ (2001) geoR: a package for geostatistical analysis
Rogowski P, Terrill EJ, Otero MP, Hazard L, Middleton WF (2012) Mapping ocean outfall plumes and their mixing using autonomous underwater vehicles. J.Geophys Res Oceans 117
Tian X, Roberts PJW, Daviero GJ (2004a) Marine wastewater discharges from multiport diffusers. I: unstratified stationary water. J Hydraul Eng 130(12):1137–1146
Tian X, Roberts PJW, Daviero GJ (2004b) Marine wastewater discharges from multiport diffusers. II: unstratified flowing water. J Hydraul Eng 130(12):1147–1155
Tian X, Roberts PJW, Daviero GJ (2006) Marine wastewater discharges from multiport diffusers. IV: stratified flowing water. J Hydraul Eng 132(4):411–419
Wackernagel H. (2003) Multivariate geostatistics: an introduction with applications. Berlin
Washburn L, Jones BH, Bratkovich A, Dickey TD, Chen MS (1992) Mixing, dispersion, and resuspension in vicinity of ocean wastewater plume. J Hydraul Eng ASCE 118(1):38–58
Webster R, Oliver M (2007) Geostatistics for environmental scientists, 2nd ed. ISBN-13: 978-0-470-02858-2(HB)
Wu Y, Washburn L, Jones BH (1994) Buoyant plume dispersion in a coastal environment: evolving plume structure and dynamics. Cont Shelf Res 14(9):1001–1023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Michael Matthies
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Del Monego, M., Ribeiro, P.J. & Ramos, P. Comparing the performance of geostatistical models with additional information from covariates for sewage plume characterization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 5850–5863 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3709-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3709-7