Abstract
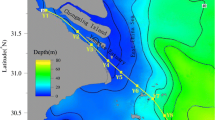
Toxicity evaluation is an important segment in sediment quality monitoring in order to protect aquatic organisms and human health. The purpose of this study is to assess the toxicity of sediments from three sediment cores in Yangtze River Estuary, China, using the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo tests. Fertilized zebrafish eggs were exposed to both whole sediments and sediment organic extracts prepared from collected sediments, in order to provide a comprehensive and realistic insight into the bioavailable toxicity potential of the sediments. As end points, development parameters (mortality, hatching rate, and abnormality) in the developing embryos were recorded during the 96-h exposure. The results showed that some samples increased mortality, inhibited the hatching of embryos, and induced morphological abnormalities. The embryonic toxicities presented serrated changes and irregular distribution with depth, which may be related to hydrodynamic effect and unstable environmental input. However, lethal and sub-lethal effects were more significant at the sub-surface sediments (10∼40 cm), which indicated that the pollution is more serious in recent decades.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Q, Wu Y, Wang J, Li Z (2009) Heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Yangtze River estuary, China. Environ Earth Sci 59:363–370. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0034-4
Atalar M, Kucuksezgin F, Duman M, Gonul LT (2013) Heavy metal concentrations in surficial and core sediments from Izmir bay: an assessment of contamination and comparison against sediment quality benchmarks. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:69–75. doi:10.1007/s00128-013-1008-5
Barjhoux I, Baudrimont M, Morin B, Landi L, Gonzalez P, Cachot J (2012) Effects of copper and cadmium spiked-sediments on embryonic development of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79:272–282. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.01.011
Blaber SJM, Cyrus DP, Albaret JJ, Ching CV, Day JW, Elliott M, Fonseca MS, Hoss DE, Orensanz J, Potter IC, Silvert W (2000) Effects of fishing on the structure and functioning of estuarine and nearshore ecosystems. ICES J Mar Sci 57:590–602. doi:10.1006/jmsc.2000.0723
Chapman PM, Ho KT, Munns WR, Solomon K, Weinstein MP (2002) Issues in sediment toxicity and ecological risk assessment. Mar Pollut Bull 44:271–278. doi:10.1016/s0025-326x (01)00329-0
Chen ZY, Li JF, Shen HT, Wang ZH (2001) Yangtze River of China: historical analysis of discharge variability and sediment flux. Geomorphology 41:77–91. doi:10.1016/s0169-555x (01)00106-4
Chen JF, Chen YH, Liu W, Bai CL, Liu XX, Liu K, Li R, Zhu JH, Huang CJ (2012) Developmental lead acetate exposure induces embryonic toxicity and memory deficit in adult zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:581–586. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2012.09.001
Domingues I, Oliveira R, Lourenco J, Grisolia CK, Mendo S, Soares AMVM (2010) Biomarkers as a tool to assess effects of chromium (VI): comparison of responses in zebrafish early life stages and adults. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 152:338–345. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.05.010
Eklund B, Elfstrom M, Gallego I, Bengtsson BE, Breitholtz M (2010) Biological and chemical characterization of harbour sediments from the Stockholm area. J Soils Sediments 10:127–141. doi:10.1007/s11368-009-0149-y
Feiler U, Hoss S, Ahlf W, Gilberg D, Hammers-Wirtz M, Hollert H, Meller M, Neumann-Hensel H, Ottermanns R, Seiler TB, Spira D, Heininger P (2013) Sediment contact tests as a tool for the assessment of sediment quality in German waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:144–155. doi:10.1002/etc.2024
Floehr T, Xiao HX, Scholz-Starke B, Wu LL, Hou JL, Yin DQ, Zhang XW, Ji R, Yuan XZ, Ottermanns R, Ross-Nickoll M, Schaffer A, Hollert H (2013) Solution by dilution?—a review on the pollution status of the Yangtze River. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6934–6971. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1666-1
Fu J, Hu X, Tao XC, Yu HX, Zhang XW (2013) Risk and toxicity assessments of heavy metals in sediments and fishes from the Yangtze River and Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 93:1887–1895. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.061
Geffard O, His E, Budzinski H, Chiffoleau JF, Coynel A, Etcheber H (2004) Effects of storage method and duration on the toxicity of marine sediments to embryos of Crassostrea gigas oysters. Environ Pollut 129:457–465. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2003.11.014
Hallare AV, Kosmehl T, Schulze T, Hollert H, Kohler HR, Triebskorn R (2005) Assessing contamination levels of Laguna Lake sediments (Philippines) using a contact assay with zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Sci Total Environ 347:254–271. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.12.002
Haring HJ, Smith ME, Lazorchak JM, Crocker PA, Euresti A, Wratschko MC, Schaub MC (2010) Comparison of bulk sediment and sediment elutriate toxicity testing methods. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:676–683. doi:10.1007/s00244-009-9447-z
Ho KT, Burgess RM (2013) What’s causing toxicity in sediments? Results of 20 years of toxicity identification and evaluations. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:2424–2432. doi:10.1002/etc.2359
Hollert H, Durr M, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T (2000) Cytotoxicity of settling particulate matter and sediments of the Neckar River (Germany) during a winter flood. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:528–534. doi:10.1897/1551-5028
Hollert H, Keiter S, König N, Rudolf M, Ulrich M, Braunbeck T (2003) A new sediment contact assay to assess particle-bound pollutants using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. J Soils Sediments 3:197–207
Hui YM, Zheng MH, Liu ZT, Gao LR (2009) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from yellow river estuary and Yangtze River estuary, China. J Environ Sci (China) 21:1625–1631. doi:10.1016/s1001-0742(08)62465-1
Incardona JP, Collier TK, Scholz NL (2004) Defects in cardiac function precede morphological abnormalities in fish embryos exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196:191–205
Johnson A, Carew E, Sloman KA (2007) The effects of copper on the morphological and functional development of zebrafish embryos. Aquat Toxicol 84:431–438. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.07.003
Keiter S, Rastall A, Kosmehl T, Wurm K, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of sediment, suspended matter and water samples in the upper Danube River—a pilot study in search for the causes for the decline of fish catches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:308–319. doi:10.1065/espr2006.04.300
Kienle C, Koehler HR, Filser J, Gerhardt A (2008) Effects of nickel chloride and oxygen depletion on behaviour and vitality of zebrafish (Danio rerio, Hamilton, 1822) (Pisces, Cypriniformes) embryos and larvae. Environ Pollut 152:612–620. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.069
Kosmehl T, Hallare AV, Reifferscheid G, Manz W, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2006) A novel contact assay for testing genotoxicity of chemicals and whole sediments in zebrafish embryos. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2097–2106. doi:10.1897/05-460r.1
Kosmehl T, Hallare AV, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2008) DNA damage induced by genotoxicants in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos after contact exposure to freeze-dried sediment and sediment extracts from Laguna Lake (The Philippines) as measured by the comet assay. Mutat Res 650:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.09.009
Long ER, Macdonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manage 19:81–97. doi:10.1007/bf02472006
Pane L, Giacco E, Corra C, Greco G, Mariottini GL, Varisco F, Faimali M (2008) Ecotoxicological evaluation of harbour sediments using marine organisms from different trophic levels. J Soils Sediments 8:74–79. doi:10.1065/jss2008.02.272
Rocha PS, Bernecker C, Strecker R, Mariani CF, Pompeo MLM, Storch V, Hollert H, Braunbeck T (2011) Sediment-contact fish embryo toxicity assay with Danio rerio to assess particle-bound pollutants in the Tiete River Basin (Sao Paulo, Brazil). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1951–1959. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.07.009
Scholz S, Fischer S, Gundel U, Kuster E, Luckenbach T, Voelker D (2008) The zebrafish embryo model in environmental risk assessment—applications beyond acute toxicity testing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:394–404. doi:10.1007/s11356-008-0018-z
Sisman T, Geyikoglu F, Atamanalp M (2007) Early life-stage toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) following embryonal exposure to selected polychlorinated biphenyls. Toxicol Ind Health 23:529–536. doi:10.1177/0748233708089042
Strecker R, Seiler TB, Hollert H, Braunbeck T (2011) Oxygen requirements of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos in embryo toxicity tests with environmental samples. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 153:318–327. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.12.002
Tuikka AI, Schmitt C, Hoss S, Bandow N, von der Ohe PC, de Zwart D, de Deckere E, Streck G, Mothes S, van Hattum B, Kocan A, Brix R, Brack W, Barcelo D, Sormunen AJ, Kukkonen JVK (2011) Toxicity assessment of sediments from three European river basins using a sediment contact test battery. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:123–131. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.08.038
Wang CH, Peng B (2002) Analysis of micro organic compound pollution in major city river reaches of the main stem of the Changjiang River. Yangtze River 33:4–9 (in Chinese)
Wang L, Jia HL, Liu XJ, Sun YQ, Yang M, Hong WJ, Qi H, Li YF (2013) Historical contamination and ecological risk of organochlorine pesticides in sediment core in northeastern Chinese river. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 93:112–120. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.04.009
Wu LL, Chen L, Hou JL, Zhang YL, Zhao JF, Gao HW (2010) Assessment of sediment quality of Yangtze River estuary using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Toxicol 25:234–242. doi:10.1002/tox.20501
Yang HY, Zhuo SS, Xue B, Zhang CL, Liu WP (2012) Distribution, historical trends and inventories of polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments from Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent East China Sea. Environ Pollut 169:20–26. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2012.05.003
Zhou GH, Sun BB, Zeng DM, Wei HL, Liu ZY, Zhang BM (2014) Vertical distribution of trace elements in the sediment cores from major rivers in east China and its implication on geochemical background and anthropogenic effects. J Geochem Explor 139:53–67. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.03.007
Zielke H, Seiler TB, Niebergall S, Leist E, Brinkmann M, Spira D, Streck G, Brack W, Feiler U, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2011) The impact of extraction methodologies on the toxicity of sediments in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo test. J Soils Sediments 11:352–363. doi:10.1007/s11368-010-0317-0
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41101499) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (No. 0400219213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Zhang, L., Liu, L. et al. Toxicity of sediment cores from Yangtze River estuary to zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 16423–16433 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3484-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3484-5