Abstract
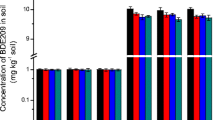
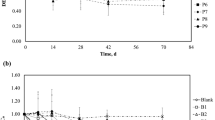
Decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209) and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) are the main contaminants at electronic waste (e-waste) recycling sites (EWRSs), and their potential toxicological effects have received extensive attention. However, the impact on soil microorganism of joint exposure to the two chemicals remains almost unknown. Therefore, indoor incubation tests were performed on control and contaminated soil samples to determine the response of soil bacterial community structure in the joint presence of BDE209 and TBBPA for the first time. The results have demonstrated that the soil bacterial diversity generally declined with increasing BDE209 and TBBPA concentrations and moderate and high doses of both chemicals can cause inhibitory effects. PCR-DGGE analysis indicated that the correlations between Shannon-Weaver index and contaminant concentrations could be well represented by a second-order polynomial model. The combined toxicity of the two chemicals was antagonistic during the first 14 days and then synergistic. Pectobacterium carotovorum, Sinorhizobium fredii HH103, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia were highly tolerant to joint exposure during the entire incubation period. Moreover, some Staphylococcus strains were enriched after 90 days exposed to TBBPA or low concentrations of BDE209, indicating that they might degrade the two chemicals effectively. The results of these observations have provided some basic understanding of potential ecological effects of joint exposure to BDE209 and TBBPA on soil microorganism at EWRSs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
An S (2013) Toxic effects of decabromodiphenyl ether and tetrabromobisphenol A on soil microbe. Dissertation, East China University of Science and Technology, 12-13
Battin TJ, Kaplan LA, Findlay S, Hopkinson CS, Marti E, Packman AI, Newbold JD, Sabater F (2008) Biophysical controls on organic carbon fluxes in fluvial networks. Nat Geosci 1:95–100
Bronislava U, Roland L, Jana P, Ladislav H, Ludmila L, Miroslav Š, Alena P, Fatima E, Helena P, Daniela M, Vladimír K, Dietmar H, Ludmila M (2011) Biodegradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by oxidases in basidiomycetous fungi and estrogenic activity of the biotransformation products. Bioresour Technol 102:9409–9415
Cremonesi L, Firpo S, Ferrari M, Righetti PG, Gelfi C (1997) Double-gradient DGGE for optimized detection of DNA point mutations. Biotechniques 22:326–330
Fang YW, Lu ZX, Lv FX, Bie XM, Liu S, Ding ZY, Xu WF (2006) A newly isolated organic solvent tolerant Staphylococcus saprophyticus M36 produced organic solvent-stable lipase. Curr Microbiol 53:510–515
Jenny RN, Charlott L, Patrik LA (2010) Biodegradation kinetics of selected brominated flame retardants in aerobic and anaerobic soil. Environ Pollut 158:2235–2240
Juhasz AL, Stanley GA, Britz ML (2000) Microbial degradation and detoxification of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain VUN 10003. Lett Appl Microbiol 30:396–401
Langford K, Scrimshaw M, Lester J (2007) The impact of process variables on the removal of PBDEs and NPEOs during simulated activated sludge treatment. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53:1–7
Li HZ, Bai JM, Li YT, Cheng HF, Zeng EY, You J (2011) Short-range transport of contaminants released from e-waste recycling site in South China. J Environ Monit 13:836–843
Liang YT, Van Nostrand JD, Wang J, Zhang X, Zhou JZ, Li GH (2009) Microarray-based functional gene analysis of soil microbial communities during ozonation and biodegradation of crude oil. Chemosphere 75:193–199
Liu L, Zhu W, Xiao L, Yang LY (2011) Effect of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209) and dibromodiphenyl ether (BDE15) on soil microbial activity and bacterial community composition. J Hazard Mater 186:883–890
Luo Y, Luo XJ, Lin Z, Chen SJ, Liu J, Mai BX, Yang ZY (2009) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in road and farmland soils from an e-waste recycling region in Southern China, concentrations, source profiles, and potential dispersion and deposition. Sci Total Environ 407:1105–1113
Nübel U, Engelen B, Felske A, Snaidr J, Wieshuber A, Amann RI, Ludwig W, Backhaus H (1996) Sequence heterogeneities of genes encoding 16S rRNAs in Paenibacillus polymyxa detected by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol 78:5636–5643
Nweke CO, Okpokwasili GC (2003) Drilling fluid base oil biodegradation potential of a soil Staphylococcus species. Afr J Biotechnol 2:293–295
Poorna V, Kulkarni PR (1995) Full factorial design to study fermentative production of inulinase using inulin from kuth (Saussurea lappa) root power by Aspergillus niger van Teighem UV11 mutant. Bioresour Technol 54:117–121
Sabeen S, Samia A, Syed AS, Munazza AS, Ajaz R (2004) Hydrocarbon degrading bacteria from Pakistani soil: isolation, identification, screening and genetical studies. Pak J Biol Sci 7:1518–1522
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Shen GQ, Lu YT, Hong JB (2006) Combined effect of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon on urease activity in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:474–480
Stephanie KL, Jenny CF, Eduardo AR, Michael HY, Duane PM (2010) Microbially mediated aerobic and anaerobic degradation of acrylamide in a western united states irrigation canal. J Environ Qual 39:1563–1569
Suresh KD, Anil KT, Siddh NU (2006) Exploration of soil bacterial communities for their potential as bioresource. Bioresour Technol 97:2217–2224
Tang XJ, Shen CF, Shi DZ, Cheema SA, Khan MI, Zhang CK, Chen YX (2010) Heavy metal and persistent organic compound contamination in soil from Wenling, an emerging e-waste recycling city in Taizhou area, China. J Hazard Mater 173:653–660
Xie XC, Qian Y, Wu YX, Yin J, Zhai JP (2013) Effects of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) on the avoidance response, survival, growth and reproduction of earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 90:21–27
Zak JC, Willig MR, Moorhead DL, Wildman HG (1994) Functional diversity of microbial communities, a quantitative approach. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1101–1108
Zhang XL, Luo XJ, Chen SJ, Wu JP, Mai BX (2009) Spatial distribution and vertical profile of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, tetrabromobisphenol A, and decabromodiphenyl ethane in river sediment from an industrialized region of South China. Environ Pollut 157:1917–1923
Zhang W, Zhang M, An S, Xiong B, Li H, Cui CZ, Lin KF (2012) Ecotoxicological effects of decabromodiphenyl ether and cadmium contamination on soil microbe and enzyme. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82:71–79
Zheng J, Luo XJ, Yuan JG, Wang J, Wang YT, Chen SJ, Mai BX, Yang ZY (2011) Levels and sources of brominated flame retardants in human hair from urban, e-waste, and rural areas in South China. Environ Pollut 159:3706–3713
Zhou XY, Guo J, Zhang W, Zhou P, Deng JJ, Lin KF (2014) Tetrabromobisphenol A contamination and emission in printed circuit board production and implications for human exposure. J Hazard Mater 273:27–35
Zhu W, Liu L, Zou P, Xiao L, Yang LY (2010) Effect of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) on soil microbial activity and bacterial community composition. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:1891–1899
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41371467, 40901148, 21307030), the Science and Technology Committee Research Program of Shanghai (12DZ0502700), the National Environmental Protection Public Welfare Science and Technology Research Program of China (201409037, 201409076, 201309047, 201309030), the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (2011CB200904), and the Scientific Project on Treatment and Control of Water Pollution (2014ZX07104006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Chen, L., An, S. et al. Effects of the joint exposure of decabromodiphenyl ether and tetrabromobisphenol A on soil bacterial community structure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 1054–1065 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3344-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3344-3