Abstract
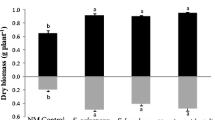
A greenhouse experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.), inoculated with the arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) species Acaulospora laevis, Glomus caledonium, and Glomus mosseae, on the soil bacterial community responsible for Aroclor 1242 dissipation. The dissipation rates of Aroclor 1242 and soil bacteria abundance were much higher with the A. laevis and G. mosseae treatments compared to the non-mycorrhizal control. The biphenyl dioxygenase (bphA) and Rhodococcus-like 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase (bphC) genes were more abundant in AM inoculated soils, suggesting that the bphA and Rhodococcus-like bphC pathways play an important role in Aroclor 1242 dissipation in the mycorrhizosphere. The soil bacterial communities were dominated by classes Betaproteobacteria and Actinobacteria, while the relative proportion of Actinobacteria was significantly (F = 2.288, P < 0.05) correlated with the PCB congener profile in bulk soil. Our results showed that AM fungi could enhance PCB dissipation by stimulating bph gene abundance and the growth of specific bacterial groups.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham WR, Nogales B, Golyshin PN, Pieper DH, Timmis KN (2002) Polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading microbial communities in soils and sediments. Curr Opin Microbiol 5:246–253
Alarcón A, Davies FT, Autenrieth RL, Zuberer DA (2008) Arbuscular mycorrhiza and petroleum-degrading microorganisms enhance phytoremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Int J Phytorem 10:251–263
Andrade G, Mihara KL, Linderman RG, Bethlenfalvay GJ (1997) Bacteria from rhizosphere and hyphosphere soils of different arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Soil 192:71–79
Biddle JF, Fitz-Gibbon S, Schuster SC, Brenchley JE, House CH (2008) Metagenomic signatures of the Peru Margin subseafloor biosphere show a genetically distinct environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:10583–10588
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
de Cárcer DA, Martín M, Karlson U, Rivilla R (2007) Changes in bacterial populations and in biphenyl dioxygenase gene diversity in a polychlorinated biphenyl-polluted soil after introduction of willow trees for rhizoremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6224–6232
Ding N, Guo H, Hayat T, Wu Y, Xu J (2009) Microbial community structure changes during Aroclor 1242 degradation in the rhizosphere of ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:149–158
Feng Y, Lin X, Jia Z, Zhu J (2012) Identification of formate-metabolizing bacteria in paddy soil by DNA-based stable isotope probing. Soil Sci Socie Am J 76:121–129
Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2008) Microbial transformation and degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ Pollut 155:1–12
Filion M, St-Arnaud M, Fortin JA (1999) Direct interaction between the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices and different rhizosphere microorganisms. New Phyto 141:525–533
Fuentes MS, Benimeli CS, Cuozzo SA, Amoroso MJ (2010) Isolation of pesticide-degrading actinomycetes from a contaminated site: bacterial growth, removal and dechlorination of organochlorine pesticides. Int Biodeterio Biodegrad 64:434–441
Giovannetti M, Mosse B (1980) An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phyto 84:489–500
Herman DJ, Firestone MK, Nuccio E, Hodge A (2012) Interactions between an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and a soil microbial community mediating litter decomposition. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 80:236–247
Hernandez B, Koh SC, Chial M, Focht D (1997) Terpene-utilizing isolates and their relevance to enhanced biotransformation of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil. Biodegradation 8:153–158
Johansson JF, Paul LR, Finlay RD (2004) Microbial interactions in the mycorrhizosphere and their significance for sustainable agriculture. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:1–13
Jordahl JL, Foster L, Schnoor JL, Alvarez PJJ (1997) Effect of hybrid poplar trees on microbial populations important to hazardous waste bioremediation. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1318–1321
Kittelmann S, Friedrich MW (2008a) Identification of novel perchloroethene-respiring microorganisms in anoxic river sediment by RNA-based stable isotope probing. Environ Microbiol 10:31–46
Kittelmann S, Friedrich MW (2008b) Novel uncultured Chloroflexi dechlorinate perchloroethene to trans-dichloroethene in tidal flat sediments. Environ Microbiol 10:1557–1570
Klironomos JN, McCune J, Hart M, Neville J (2000) The influence of arbuscular mycorrhizae on the relationship between plant diversity and productivity. Ecol Lett 3:137–141
Lee TK, Lee J, Sul WJ, Iwai S, Chai B, Tiedje JM, Park J (2011) Novel biphenyl-oxidizing bacteria and dioxygenase genes from a korean tidal mudflat. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3888–3891
Leigh MB, Fletcher JS, Fu X, Schmitz FJ (2002) Root turnover: an important source of microbial substrates in rhizosphere remediation of recalcitrant contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 36:1579–1583
Leigh MB, Prouzová P, Macková M, Macek T, Nagle DP, Fletcher JS (2006) Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-degrading bacteria associated with trees in a PCB-contaminated site. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2331–2342
Lillis L, Doyle E, Clipson N (2009) Comparison of DNA- and RNA-based bacterial community structures in soil exposed to 2,4-dichlorophenol. J App Microbiol 107:1883–1893
Macedo AJ, Timmis KN, Abraham WR (2007) Widespread capacity to metabolize polychlorinated biphenyls by diverse microbial communities in soils with no significant exposure to PCB contamination. Environ Microbiol 9:1890–1897
Mehmannavaz R, Prasher SO, Ahmad D (2002) Rhizospheric effects of alfalfa on biotransformation of polychlorinated biphenyls in a contaminated soil augmented with Sinorhizobium meliloti. Process Biochem 37:955–963
Narasimhan K, Basheer C, Bajic VB, Swarup S (2003) Enhancement of plant-microbe interactions using a rhizosphere metabolomics-driven approach and its application in the removal of polychlorinated biphenyls. Plant Physiol 132:146–153
Nuccio EE, Hodge A, Pett-Ridge J, Herman DJ, Weber PK, Firestone MK (2013) An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus significantly modifies the soil bacterial community and nitrogen cycling during litter decomposition. Environ Microbiol 15:1870–1881
Ohtsubo Y, Nagata Y, Kimbara K, Takagi M, Ohta A (2000) Expression of the bph genes involved in biphenyl/PCB degradation in Pseudomonas sp. KKS102 induced by the biphenyl degradation intermediate, 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoic acid. Gene 256:223–228
Oswald ET, Ferchau HA (1968) Bacterial associations of coniferous mycorrhizae. Plant Soil 28:187–192
Payne RB, Fagervold SK, May HD, Sowers KR (2013) Remediation of polychlorinated biphenyl impacted sediment by concurrent bioaugmentation with anaerobic halorespiring and aerobic degrading bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 47:3807–3815
Petrić I, Hršak D, Fingler S, Udiković-Kolić N, Bru D, Martin-Laurent F (2010) Insight in the PCB-degrading functional community in long-term contaminated soil under bioremediation. J Soils Sediments 11:290–300
Petric I, Bru D, Udikovic-Kolic N, Hrsak D, Philippot L, Martin-Laurent F (2011) Evidence for shifts in the structure and abundance of the microbial community in a long-term PCB-contaminated soil under bioremediation. J Hazard Mater 195:254–260
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2010) FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS One 5:e9490
Qin H, Brookes PC, Xu J (2014) Cucurbita spp. and Cucumis sativus enhance the dissipation of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners by stimulating soil microbial community development. Environ Pollut 184:306–312
Reeder J, Knight R (2010) Rapid denoising of pyrosequencing amplicon data: Exploiting the rank-abundance distribution. Nat Methods 7:668–669
Schreiner RP, Mihara KL, McDaniel H, Bethlenfalvay GJ (1997) Mycorrhizal fungi influence plant and soil functions and interactions. Plant Soil 188:199–209
Seto M, Kimbara K, Shimura M, Hatta T, Fukuda M, Yano K (1995) A novel transformation of polychlorinated biphenyls by Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3353–3358
Shaw LJ, Morris P, Hooker JE (2006) Perception and modification of plant flavonoid signals by rhizosphere microorganisms. Environ Microbiol 8:1867–1880
Smith SE, Read DJ (2010) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic press, London
Teng Y, Luo Y, Sun X, Tu C, Xu L, Liu W, Li Z, Christie P (2010) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhiza and rhizobium on phytoremediation by alfalfa of an agricultural soil contaminated with weathered PCBs: a field study. Int J Phytorem 12:516–533
Ter Braak C, Smilauer P (2002) Canoco for Windows version 4.5. Biometris–Plant Research International, Wageningen
Toljander JF, Artursson V, Paul LR, Jansson JK, Finlay RD (2006) Attachment of different soil bacteria to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal extraradical hyphae is determined by hyphal vitality and fungal species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 254:34–40
Toljander JF, Lindahl BD, Paul LR, Elfstrand M, Finlay RD (2007) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelial exudates on soil bacterial growth and community structure. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 61:295–304
Wang S, Zhang S, Huang H, Christie P (2011) Behavior of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in soil: effects of rhizosphere and mycorrhizal colonization of ryegrass roots. Environ Pollut 159:749–753
Acknowledgments
This work was supported jointly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41101243, 41090284, and 41271256), program of Shanghai Cooperative Centre for WEEE Recycling (ZF1224-09), and Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture (Grant No. 212000009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, H., Brookes, P.C., Xu, J. et al. Bacterial degradation of Aroclor 1242 in the mycorrhizosphere soils of zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 12790–12799 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3231-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3231-y