Abstract
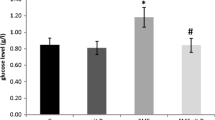
In the present study, we investigate the effects of a possible protective role of vitamin E (vit E) or selenium (Se) on glucose metabolism disruption induced by static magnetic field (SMF) in rats. Rats have been exposed to SMF (128 mT, 1 h/day during 5 days). Our results showed that SMF failed to alter body weight and relative liver weight. Our data demonstrated that exposure to SMF increased (+21 %) blood glucose level and caused a decrease (−15 %) in liver glycogen content. Moreover, the same treatment induced a reduction of pancreatic islet area. Interestingly, supplementation with vit E (DL α-tocopherol acetate, 150 mg/kg per os during 5 days) prevented alterations induced by SMF on glucose metabolism and liver glycogen content, whereas supplementation with Se (Na2SeO3, 0.20 mg/l, in drinking water for 4 weeks) restored only hepatic glycogen contents. By contrast, both vit E and Se failed to correct the area of pancreatic islets.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmelek H, Molnar S, Servais S et al (2006) Skeletal muscle HSP72 and norepinephrine response to static magnetic field in rat. J Neural Transm 113:821–827
Amara S, Abdelmelek H, Garrel C et al (2007) Zinc supplementation ameliorates static magnetic field-induced oxidative stress in rat tissues. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 23:193–197
Amara S, Douki T, Garel C et al (2009) Effects of static magnetic field exposure on antioxidative enzymes activity and DNA in rat brain. Gen Physiol Biophys 28:260–265
Atli T, Keven K, Avci A et al (2004) Oxidative stress and antioxidant status in elderly diabetes mellitus and glucose intolerance patients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 39:269–275
Barnes FS, Greenebaum B (2006) In: Bioengineering and biophysical aspects of electromagnetic fields. Third ed. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, Introduction
Chater S, Abdelmelek H, Pequignot JM et al (2006a) Effects of sub-acute exposure to a static magnetic field on hematologic and biochemical parameters in pregnant rats. Electromagn Biol Med 25:1–10
Chater S, Abdelmelek H, Douki T et al (2006b) Exposure to static magnetic field of pregnant rats induces hepatic GSH elevation but not oxidative DNA damage in liver and kidney. Archices Med Res 37:941–946
Elferchichi M, Mercier J, Coisy-Quivy M et al (2010) Effects of exposure to a 128-mT static magnetic field on glucose and lipid metabolism in serum and skeletal muscle of rats. Archices Med Res 41:309–314
Ghodbane S, Amara S, Garrel C et al (2011a) Selenium supplementation ameliorates static magnetic field-induced disorders in antioxidant status in rat tissues. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 31:100–106
Ghodbane S, Amara S, Arnaud J et al (2011b) Effect of selenium pre-treatment on plasma antioxidant vitamins A (Retinol) and E (α-Tocopherol) in static magnetic field-exposed rats. Toxicol Ind Health 27(10):949–955
Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Paolisso G (1996) Oxidative stress and diabetic vascular complications. Diabetes Care 19:257–267
Hashish AH, El-Missiry MA, Abdelkader HI et al (2008) Assessment of biological changes of continuous whole body exposure to static magnetic field and extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:895–902
Hayek A, Guardian C, Guardian J et al (1984) Homogeneous magnetic fields influence pancreatic islet function in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122:191–196
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29(4):577–580
Jajte J, Grzegorczyk J, Zmyślony M et al (2002) Effect of 7 mT static magnetic field and iron ions on rat lymphocytes: apoptosis, necrosis and free radical processes. Bioelectrochemistry 57:107–111
Jajte J, Zmyslony M, Rajkowska E (2003) Protective effect of melatonin and vitamin E against prooxidative action of iron ions and static magnetic field. Med Pr 54(1):23–28
Kanety H, Hemi R, Paz K et al (1998) Cellular stress impairs insulin signalling. Diabetologia 41(Suppl):A34, Abstract
Lahbib A, Elferchichi M, Ghodbane S et al (2010) Time-dependent effects of exposure to static magnetic field on glucose and lipid metabolism in rat. Gen Physiol Biophys 29:390–395
Lo S, Russell JC, Taylor AW (1970) Determination of glycogen in small tissue samples. J Appl Physiol 28:234–236
Lombardi AM, Fabris R, Bassetto F et al (1999) Hyperlactatemia reduces muscle glucose uptake and GLUT-4 mRNA while increasing (E1alpha) PDH gene expression in rat. Am J Physiol 276:922–929
Lyan B, Azais-Braesco V, Cardinault N et al (2001) Simple method for clinical determination of 13 carotenoids in human plasma using an isocratic high-performance liquid chromatographic method. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 751:297–303
Mazur A, Remesy C, Gueux E et al (1990) Effects of diets rich in fermentable carbohydrates on plasma lipoprotein levels and on lipoprotein catabolism in rats. J Nutr 120:1037–1045
Miller BF, Fattor JA, Jacobs KA et al (2002) Lactate and glucose interactions during rest and exercise in men: effect of exogenous lactate infusion. J Physiol 544:963–975
Miyakoshi J (2005) Effects of static magnetic fields at the cellular level. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 87:213–223
Miyakoshi J (2006) Biological responses to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields. J Dermatol Sci Suppl 2:S23–S30
Monfared AS, Jorsaraei SG, Abdi R (2009) Protective effects of vitamins C and E on spermatogenesis of 1.5 Tesla magnetic field exposed rats. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:1047–1051
Okano H (2008) Effects of static magnetic fields in biology: role of free radicals. Front Biosci 13:6106–6125
Ozkan Y, Yilmaz O, Oztürk AI et al (2005) Effects of triple antioxidant combination (vitamin E, vitamin C and alpha-lipoic acid) with insulin on lipid and cholesterol levels and fatty acid composition of brain tissue in experimental diabetic and non-diabetic rats. Cell Biol Int 29:754–760
Paolisso G, D’amore A, Giugliano D et al (1993) Pharmacologic doses of vitamin E improve insulin action in healthy subjects and non-insulin dependent diabetic patients. Am J Clin Nutr 57:650–656
Rosen AD (2003) Mechanism of action of moderate-intensity static magnetic fields on biological systems. Cell Biochem Biophys 39:163–173
Rosen AD, Chastney EE (2009) Effect of long term exposure to 0.5 T static magnetic fields on growth and size of GH3 cells. Bioelectromagnetics 30:114–119
Rudich A, Tirosh A, Khamaisi M et al (1998) Putative role of oxidative stress in adipocyte and skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Diabetologia 41(Suppl):A34, Abstract
Srinivasan S, Pari L (2012) Ameliorative effect of diosmin, a citrus flavonoid against streptozotocin-nicotinamide generated oxidative stress induced diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact 195(1):43–51
Stapleton SR (2000) Selenium: an insulin-mimetic. CMLS Cell Mol Life Sci 57:1874–1879
Tiwari V, Kuhad A, Bishnoi M et al (2009) Chronic treatment with tocotrienol, an isoform of vitamin E, prevents intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative-nitrosative stress in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93:183–189
Vettor R, Lombardi AM, Fabris R et al (2000) Substrate competition and insulin action in animal models. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:S22–S24
Xu S, Okano H, Ohkubo C (1998) Subchronic effects of static magnetic fields on cutaneous microcirculation in rabbits. Vivo 12:383–389
Yuge L, Kataoka K (2000) Differentiation of myoblasts is accelerated in culture in a magnetic field. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 36:383–386
Acknowledgments
We thank Bechir Azib for his excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghodbane, S., Amara, S., Lahbib, A. et al. Vitamin E prevents glucose metabolism alterations induced by static magnetic field in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 12731–12738 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3224-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3224-x