Abstract
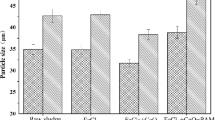
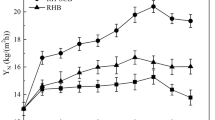
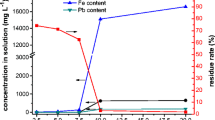
Fenton’s reagent and sawdust were used on the dewaterability of the raw oily sludge in this study. The result shows that the combination of the two treatment processes is favorable, although the application of Fenton’s reagent only is not so good. The capillary suction time (CST) and specific resistance to filtration (SRF) were used to evaluate the effect of dewaterability of the raw oily sludge, and the CST and SRF values are reduced from 1,760 s and 13.8 × 1012 m/kg to 185 s and 1.5 × 1012 m/kg, respectively. The dry matter contents of sludge cakes and properties of the supernatant all gained when using only the Fenton’s reagent and when using the combined treatment with Fenton’s reagent and sawdust respectively were investigated. The results indicate that the oily sludge is more suitable for further treatment after combined process with Fenton’s reagent and sawdust.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartha R (1986) Biotechnology of petroleum pollutant biodegradation. Microb Ecol 12:155–172
Buyukkamaci N, Kucukselek E (2007) Improvement of dewatering capacity of a petrochemical sludge. J Hazard Mater 144:323–327
Chen W-S, Chang F-C, Shen Y-H, Tsai M-S (2011) The characteristics of organic sludge/sawdust derived fuel. Bioresour Technol 102:5406–5410
Da Rocha ORS, Dantas RF, Duarte MMMB, Duarte MML, Da Silva VL (2010) Oil sludge treatment by photocatalysis applying black and white light. Chem Eng J 157:80–85
da Silva LJ, Alves FC, de Frana FP (2012) A review of the technological solutions for the treatment of oily sludges from petroleum refineries. Waste Manag Res 30:1016–1030
Eaton AD, Franson MAH (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater
Guo S, Li G, Qu J, Liu X (2011) Improvement of acidification on dewaterability of oily sludge from flotation. Chem Eng J 168:746–751
Hu G, Li J, Zeng G (2013) Recent development in the treatment of oily sludge from petroleum industry: a review. J Hazard Mater 261:470–490
Jing G, Luan M, Han C, Chen T, Wang H (2012) An effective process for removing organic compounds from oily sludge using soluble metallic salt. J Ind Eng Chem 18:1446–1449
Lin Y-F, Jing S-R, Lee D-Y (2001) Recycling of wood chips and wheat dregs for sludge processing. Bioresour Technol 76:161–163
Liu H, Yang J, Zhu N, Zhang H, Li Y, He S, Yang C, Yao H (2013) A comprehensive insight into the combined effects of Fenton’s reagent and skeleton builders on sludge deep dewatering performance. J Hazard Mater 258:144–150
Long X, Zhang G, Han L, Meng Q (2013) Dewatering of floated oily sludge by treatment with rhamnolipid. Water Res 47:4303–4311
Luo H, Ning X-a, Liang X, Feng Y, Liu J (2013) Effects of sawdust-CPAM on textile dyeing sludge dewaterability and filter cake properties. Bioresour Technol 139:330–336
Majuste D, Mansur MB (2008) Characterization of the fine fraction of the argon oxygen decarburization with lance (AOD-L) sludge generated by the stainless steelmaking industry. J Hazard Mater 153:89–95
Tahhan RA, Ammari TG, Goussous SJ, Al-Shdaifat HI (2011) Enhancing the biodegradation of total petroleum hydrocarbons in oily sludge by a modified bioaugmentation strategy. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65:130–134
USEPA (2007) Test method for evaluating solid waste, 3rd edn. USEPA, Washington, DC, SW-846, vol. VIA
Zhao L, Gu W-M, He P-J, Shao L-M (2011) Biodegradation potential of bulking agents used in sludge bio-drying and their contribution to bio-generated heat. Water Res 45:2322–2330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Feng, S., Jiang, J. et al. Application of Fenton’s reagent combined with sawdust on the dewaterability of oily sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 10706–10712 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3070-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3070-x