Abstract
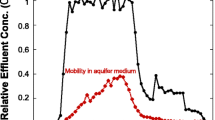
Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) has recently gained great interest in the scientific community as in situ reagent for installation of permeable reactive barriers in aquifer systems, since nZVI is highly reactive with chlorinated compounds and may render them to harmless substances. However, nZVI has a high tendency to agglomerate and sediment; therefore it shows very limited transport ranges. One new approach to overcome the limited transport of nZVI in porous media is using a suited carrier colloid. In this study we tested mobility of a carbon colloid supported nZVI particle “Carbo-Iron Colloids” (CIC) with a mean size of 0.63 μm in a column experiment of 40 cm length and an experiment in a two-dimensional (2D) aquifer test system with dimensions of 110 × 40 × 5 cm. Results show a breakthrough maximum of 82 % of the input concentration in the column experiment and 58 % in the 2D-aquifer test system. Detected residuals in porous media suggest a strong particle deposition in the first centimeters and few depositions in the porous media in the further travel path. Overall, this suggests a high mobility in porous media which might be a significant enhancement compared to bare or polyanionic stabilized nZVI.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold WA, Roberts AL (2000) Pathways and kinetics of chlorinated ethylene and chlorinated acetylene reaction with Fe(0) particles. Environ Sci Technol 34:1794–1805
Baumann T (2010) Nanoparticles in groundwater – occurrence and applications. In: Frimmel FH, Niessner R (eds) Nanoparticles in the water cycle. Springer, Berlin, pp 23–34
Bleyl S, Kopinke F-D, Mackenzie K (2012) Carbo-Iron ® synthesis and stabilization of Fe(0)-doped colloidal activated carbon for in situ groundwater treatment. Chem Eng J 191:588–595
Bradford SA, Bettahar M (2006) Concentration dependent transport of colloids in saturated porous media. J Contam Hydrol 82:99–117
Bradford SA, Torkzaban S (2008) Colloid transport and retention in unsaturated porous media: a review of interface-, collector-, and pore-scale processes and models. Vadose Zone J 7:667–681
Bradford SA, Yates SR, Bettahar M, Simunek J (2002) Physical factors affecting the transport and fate of colloids in saturated porous media. Water Resour Res 38
Busch J, Meißner T, Potthoff A, Oswald SE (2014) Transport of carbon colloid supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in saturated porous media. J Contam Hydrol, in revision
Comba S, Di Molfetta A, Sethi R (2011) A comparison between field applications of nano-, micro-, and millimetric zero-Valent iron for the remediation of contaminated aquifers. Water Air Soil Pollut 215:595–607
Crane RA, Scott TB (2012) Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater 211–212:112–125
Gillham RW, O'Hannesin SF (1994) Enhanced degradation of halogenated aliphatics by zero-valent Iron. Ground Water 32:958–967
He F, Zhang M, Qian T, Zhao D (2009) Transport of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized iron nanoparticles in porous media: column experiments and modeling. J Colloid Interface Sci 334:96–102
He F, Zhao D, Paul C (2010) Field assessment of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized iron nanoparticles for in situ destruction of chlorinated solvents in source zones. Water Res 44:2360–2370
Hoch LB, Mack EJ, Hydutsky BW, Hershman JM, Skluzacek JM, Mallouk TE (2008) Carbothermal synthesis of carbon-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron particles for the remediation of hexavalent chromium. Environ Sci Technol 42:2600–2605
Jiemvarangkul P, Zhang WX, Lien HL (2011) Enhanced transport of polyelectrolyte stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in porous media. Chem Eng J 170:482–491
Johnson RL, Nurmi JT, O’Brien Johnson GS, Fan D, O’Brien Johnson RL, Shi Z, Salter-Blanc AJ, Tratnyek PG, Lowry GV (2013) Field-scale transport and transformation of carboxymethylcellulose-stabilized nano zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 47:1573–1580
Kanel SR, Goswami RR, Clement TP, Barnett MO, Zhao D (2008) Two dimensional transport characteristics of surface stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles in porous media. Environ Sci Technol 42:896–900
Loveland JP, Bhattacharjee S, Ryan JN, Elimelech M (2003) Colloid transport in a geochemically heterogeneous porous medium: aquifer tank experiment and modeling. J Contam Hydrol 65:161–182
Lowry GV (2007) Nanomaterials for groundwater remediation. In: Wiesner MR, Bottero JY (eds) Environmental nanotechnology. Applications and impacts of nanomaterials. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 297–336
Mackenzie K, Bleyl S, Georgi A, Kopinke F-D (2012) Carbo-Iron An Fe/AC composite As alternative to nano-iron for groundwater treatment. Water Res 46:3817–3826
Matheson LJ, Tratnyek PG (1994) Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated methanes by iron metal. Environ Sci Technol 28:2045–2053
McMahon PB, Dennehy KF, Sandstrom MW (1999) Hydraulic and geochemical performance of a permeable reactive barrier containing zero-valent iron, Denver Federal Center. Ground Water 37:396–404
Meißner T, Oelschlägel K, Potthoff A (2014) Dispersion of nanomaterials used in toxicological studies: a comparison of sonication approaches demonstrated on TiO2 P25. J Nanoparticle Res 16:1–13
Misra SK, Dybowska A, Berhanu D, Luoma SN, Valsami-Jones E (2012) The complexity of nanoparticle dissolution and its importance in nanotoxicological studies. Sci Total Environ 438:225–232
Mueller NC, Nowack B (2010) Nanoparticles for remediation: solving big problems with little particles. Elements 6:395–400
O'Hannesin SF, Gillham RW (1998) Long-term performance of an in situ "iron wall" for remediation of VOCs. Ground Water 36:164–170
Phenrat T, Saleh N, Sirk K, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2007) Aggregation and sedimentation of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions. Environ Sci Technol 41:284–290
Phenrat T, Saleh N, Sirk K, Kim HJ, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2008) Stabilization of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions by anionic polyelectrolytes: adsorbed anionic polyelectrolyte layer properties and their effect on aggregation and sedimentation. J Nanoparticle Res 10:795–814
Phenrat T, Cihan A, Kim HJ, Mital M, Illangasekare T, Lowry GV (2010) Transport and deposition of polymer-modified Fe–O nanoparticles in 2-D heterogeneous porous media: effects of particle concentration, Fe–O content, and coatings. Environ Sci Technol 44:9086–9093
Quinn J, Geiger C, Clausen C, Brooks K, Coon C, O'Hara S, Krug T, Major D, Yoon W-S, Gavaskar A, Holdsworth T (2005) Field demonstration of DNAPL dehalogenation using emulsified zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39:1309–1318
Raychoudhury T, Tufenkji N, Ghoshal S (2012) Aggregation and deposition kinetics of carboxymethyl cellulose-modified zero-valent iron nanoparticles in porous media. Water Res 46:1735–1744
Savage N, Diallo MS (2005) Nanomaterials and water purification: opportunities and challenges. J Nanoparticle Res 7:331–342
Schrick B, Hydutsky BW, Blough JL, Mallouk TE (2004) Delivery vehicles for zerovalent metal nanoparticles in soil and groundwater. Chem Mater 16:2187–2193
Stroo HF (2010) Remedial technology selection for chlorinated solvent plumes. In: Stroo HF, Ward CH (eds) In situ remediation of chlorinated solvent plumes. Springer Science + Business Media, New York
Stroo HF, Ward CH (2010) In situ remediation of chlorinated solvent plumes. Springer Science + Business Media, New York
Sunkara B, Zhan JJ, He JB, McPherson GL, Piringer G, John VT (2010) Nanoscale zerovalent iron supported on uniform carbon microspheres for the in situ remediation of chlorinated hydrocarbons. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:2854–2862
Sunkara B, Zhan JJ, Kolesnichenko I, Wang YQ, He JB, Holland JE, McPherson GL, John VT (2011) Modifying metal nanoparticle placement on carbon supports using an aerosol-based process, with application to the environmental remediation of chlorinated hydrocarbons. Langmuir 27:7854–7859
Tiraferri A, Sethi R (2009) Enhanced transport of zerovalent iron nanoparticles in saturated porous media by guar gum. J Nanoparticle Res 11:635–645
Tong M, Johnson WP (2006) Colloid population heterogeneity drives hyperexponential deviation from classic filtration theory. Environ Sci Technol 41:493–499
Tufenkji N, Elimelech M (2004) Correlation equation for predicting single-collector efficiency in physicochemical filtration in saturated porous media. Environ Sci Technol 38:529–536
Zhan JJ, Kolesnichenko I, Sunkara B, He JB, McPherson GL, Piringer G, John VT (2011) Multifunctional iron–carbon nanocomposites through an aerosol-based process for the in situ remediation of chlorinated hydrocarbons. Environ Sci Technol 45:1949–1954
Zhang WX (2003) Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview. J Nanoparticle Res 5:323–332
Zhang H, Jin Z-H, Han L, Qin C-H (2006) Synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on exfoliated graphite for removal of nitrate. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 16:345–349
Zheng TH, Zhan JJ, He JB, Day C, Lu YF, McPherson GL, Piringer G, John VT (2008) Reactivity characteristics of nanoscale zerovalent iron–silica composites for trichloroethylene remediation. Environ Sci Technol 42:4494–4499
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the German Ministry for Education and Research (Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, BMBF) in the project Fe-NANOSIT (Iron based nanoparticles and nano-composite structures for remediation of ground- and wastewater). We want to thank Stefan Scholz from the department Bioanalytical Ecotoxicology and the staff of the department Environmental Engineering from the Helmholtz-Centre for Environmental Research UFZ (Leipzig, Germany) for provision of particles and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Busch, J., Meißner, T., Potthoff, A. et al. Investigations on mobility of carbon colloid supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in a column experiment and a laboratory 2D-aquifer test system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 10908–10916 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3049-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3049-7