Abstract
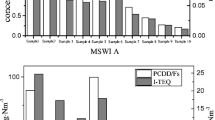
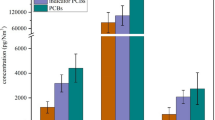
Unintentionally produced persistent organic pollutants (UP-POPs) including polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) were characterized and quantified in stack gas and fly ash from the second ventilation systems in five typical converters in five different steelmaking plants. The 2378-substituted PCDD/Fs (2378-PCDD/Fs) and dioxin-like PCB (dl-PCBs) toxic equivalents (TEQs) were 1.84–10.3 pg WHO-TEQ Nm−3 in the stack gas and 5.59–87.6 pg WHO-TEQ g−1 in the fly ash, and the PCN TEQs were 0.06–0.56 pg TEQ Nm−3 in the stack gas and 0.03–0.08 pg TEQ g−1 in the fly ash. The concentrations of UP-POPs in the present study were generally lower than those in other metallurgical processes, such as electric arc furnaces, iron ore sintering, and secondary metallurgical processes. Adding scrap metal might increase UP-POP emissions, indicating that raw material composition was a key influence on emissions. HxCDF, HpCDF, OCDF, HpCDD, and OCDD were the dominant PCDD/Fs in the stack gas and fly ash. TeCB and PeCB were dominant in the stack gas, but HxCB provided more to the total PCB concentrations in the fly ash. The lower chlorinated PCNs were dominant in all of the samples. The 2378-PCDD/F, dl-PCB, and PCN emission factors in stack gases from the steelmaking converter processes (per ton of steel produced) were 1.88–2.89, 0.14–0.76, and 229–759 μg t−1, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DR, Fisher R (2002) Sources of dioxins in the United Kingdom the steel industry and other sources. Chemosphere 46:371–381
Aries E, Anderson DR, Fisher R, Fray TA, Hemfrey D (2006) PCDD/F and “Dioxin-like” PCB emissions from iron ore sintering plants in the UK. Chemosphere 65:1470–1480
Ba T, Zheng M, Zhang B, Liu W, Su G, Liu G, Xiao K (2010) Estimation and congener-specific characterization of polychlorinated naphthalene emissions from secondary non ferrous metallurgical facilities in China. Environ Sci Technol 44:2441–2446
Buekens A, Stieglitz L, Hell K, Huang H, Segers P (2001) Dioxins from thermal and metallurgical processes recent studies for the iron and steel industry. Chemosphere 42:729–735
Chiu JC, Shen YH, Li HW, Lin LF, Wang LC, Chang-Chien GP (2011) Emissions of polychlorinated pibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from an electric arc furnace, secondary aluminum smelter, crematory and Joss Paper incinerators. Aerosol Air Qual Res 11:13–20
Fisher R, Anderson DR, Pearson SL, Quinn P (1997) Characterisation of releases of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from integrated iron and steelworks in the United Kingdom. Organohalogen Compd 31:261–267
Grochowalski A, Lassen C, Holtzer M, Sadowski M, Hudyma T (2006) Determination of PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBs and HCB emissions from the metallurgical sector in Poland. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 14:326–332
Hu J, Zheng M, Nie Z, Liu W, Liu G, Zhang B, Xiao K (2013a) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran and polychlorinated biphenyl emissions from different smelting stages in secondary copper metallurgy. Chemosphere 90:89–94
Hu J, Zheng M, Liu W, Li C, Nie Z, Liu G, Zhang B, Xiao K, Gao L (2013b) Characterization of polychlorinated naphthalenes in stack gas emissions from waste incinerators. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2905–2911
Jackson K, Aries E, Fisher R, Anderson DR, Parris A (2012) Assessment of exposure to PCDD/F, PCB, and PAH at a basic oxygen steelmaking (BOS) and an iron ore sintering plant in the UK. Ann Occup Hyg 56:37–48
Jager J (1993) PCDD/F and PCB emission from steel producing, processing and reclamation plants with varying input. Toxicol Environ Chem 40:201–211
Liu G, Zheng M, Liu W, Wang C, Zhang B, Gao L, Su G, Xiao K, Lv P (2009) Atmospheric emission of PCDD Fs, PCBs, hexachlorobenzene, and pentachlorobenzene from the coking industry. Environ Sci Technol 43:9196–9201
Liu G, Zheng M, Lv P, Liu W, Wang C, Zhang B, Xiao K (2010) Estimation and characterization of polychlorinated naphthalene emission from coking industries. Environ Sci Technol 44:8156–8161
Liu G, Zheng M, Du B, Nie Z, Zhang B, Hu J, Xiao K (2012a) Identification and characterization of the atmospheric emission of polychlorinated naphthalenes from electric arc furnaces. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 19:3645–3650
Liu G, Zheng M, Du B, Nie Z, Zhang B, Liu W, Li C, Hu J (2012b) Atmospheric emission of polychlorinated naphthalenes from iron ore sintering processes. Chemosphere 89:467–472
Lohmann R, Jones KC (1998) Dioxins and furans in air and deposition. A review of levels, behaviour and processes. Sci Total Environ 219:53–81
Nie Z, Zheng M, Liu W, Zhang B, Liu G, Su G, Lv P, Xiao K (2011) Estimation and characterization of PCDD/Fs, dl-PCBs, PCNs, HxCBz and PeCBz emissions from magnesium metallurgy facilities in China. Chemosphere 85:1707–1712
Nie Z, Liu G, Liu W, Zhang B, Zheng M (2012a) Characterization and quantification of unintentional POP emissions from primary and secondary copper metallurgical processes in China. Atmos Environ 57:109–115
Nie Z, Zheng M, Liu G, Liu W, Lv P, Zhang B, Su G, Gao L, Xiao K (2012b) A preliminary investigation of unintentional POP emissions from thermal wire reclamation at industrial scrap metal recycling parks in China. J Hazard Mater 215–216:259–265
NIP of China (2007) National Implementation Plan for the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants. http://www.pops.int/documents/implementation/nips/submissions/China NIP En.pdf>
Noma Y, Yamamoto T, Sakai SI (2004) Congener-specific composition of polychlorinated naphthalenes, coplanar PCBs, dibenzo-p-dioxins, and dibenzofurans in the Halowax Series. Environ Sci Technol 38:1675–1680
Sofilic T, Jendricko J, Kovacevic Z, Cosic M (2012) Measurement of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran. Arch Metall Mater 57:811–821
Tian B, Huang J, Wang B, Deng S, Yu G (2012) Emission characterization of unintentionally produced persistent organic pollutants from iron ore sintering process in China. Chemosphere 89:409–415
UNEP (2012) Toolkit for identification and quantification of releases of dioxins, furans and other unintentional POPs (under Article 5 of the Stockholm Convention). http://toolkit.pops.int/Publish/Downloads/UNEP-POPS-TOOLKIT-2012-En.pdf
Yu Y, Zheng M, Li X, He X (2012) Operating condition influences on PCDD/Fs emissions from sinter pot tests with hot flue gas recycling. J Environ Sci 24:875–881
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21037003, 21321004, and 21007084), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013 M540151), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences(YSW2013B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Constantini Samara
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Zheng, M., Liu, W. et al. Estimation and characterization of unintentionally produced persistent organic pollutant emission from converter steelmaking processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 7361–7368 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2652-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2652-y