Abstract
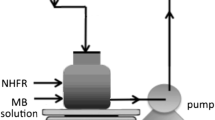
The present research deals with the development of a new heterogeneous photocatalysis and Fenton hybrid system for the removal of color from textile dyeing wastewater as Rhodamine B (RhB) solutions by using Fe2+/H2O2/Nb2O5 as a photocatalytic system. The application of this photocatalytic system for the decolorization of dye contaminants is not reported in the literature yet. Different parameters like dye concentration, Nb2O5/Fe2+ catalyst amount, pH, and H2O2 concentration have been studied. The optimum conditions for the decolorization of the dye were initial concentration of 10 mg L−1 of dye, pH 4, and Nb2O5/Fe2+ catalyst concentration of 0.5 g L−1/50 mg L−1. The optimum value of H2O2 concentration for the conditions used in this study was 700 mg L−1. Moreover, the efficiency of the Nb2O5/photo-Fenton hybrid process in comparison to photo-Fenton alone and a dark Fenton process as a control experiment to decolorize the RhB solution has been investigated. The combination of photo-Fenton and Nb2O5 catalysts has been proved to be the most effective for the treatment of such type of wastewaters. The results revealed that the RhB dye was decolorized in a higher percent (78 %) by the Nb2O5/photo-Fenton hybrid process (Fe2+/H2O2/Nb2O5/UV) than by the photo-Fenton process alone (37 %) and dark Fenton process (14 %) after 120 min of treatment. Moreover, the Nb2O5 catalyst as a heterogeneous part of the photocatalytic system was demonstrated to have good stability and reusability.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Messih MF, Ahmed MA, El-Sayed AS (2013) Photocatalytic decolorization of Rhodamine B dye using novel mesoporous SnO2–TiO2 nano mixed oxides prepared by sol–gel method. J Photochem Photobiol 260:1–8
Akpan UG, Hameed BH (2009) Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysts: a review. J Hazard Mater 170:520–529
Chen F, Xie YD, He JJ, Zhao JC (2001) Photo-Fenton degradation of dye in methanolic solution under both UV and visible irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A 138:139–146
Ge S, Jia H, Zhao H, Zheng Z, Zhang L (2010) First observation of visible light photocatalytic activity of carbon modified Nb2O5 nanostructures. J Mater Chem 20:3052–3058
Gomathi Devi L, Eraiah Rajashekhar K, Anantha Raju KS, Girish Kumar S (2011) Influence of various aromatic derivatives on the advanced photo Fenton degradation of Amaranth dye. Desalination 270:31–39
Hsueh CL, Huang YH, Wang CC, Chen CY (2005) Degradation of azo dyes using low iron concentration of Fenton and Fenton-like system. Chemosphere 58:1409–1414
Huai YJ, Hu XB, Lin ZJ, Deng ZH, Suo JH (2009) Preparation of nano-TiO2/activated carbon composite and its electrochemical characteristics in non-aqueous electrolyte. Mater Chem Phys 113:962–966
Hyodo T, Ohoka J, Shimizu Y, Egashira M (2006) Design of anodically oxidized Nb2O5 films as a diode-type H2 sensing material. Sens Actuators B 117:359–366
Kim HE, Lee JS, Lee HS, Lee CH (2012) Synergistic effects of TiO2 photocatalysis in combination with Fenton-like reactions on oxidation of organic compounds at circumneutral pH. Appl Catal B 115–116:219–224
Konstantinou IK, Albanis TA (2004) TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: a review. Appl Catal B Environ 49:1–14
Kumagai N, Tanno K, Nakajima T, Watanabe N (1983) Structural changes of Nb2O5 and V2O5 as rechargeable cathodes for lithium battery. Electrochim Acta 28:17–22
Leon y Leon CA, Solar JM, Calemma V, Radovic LR (1992) Evidence for the protonation of basal plane sites on carbon. Carbon 30:797–811
Li Y, Zhang FS (2010) Catalytic oxidation of Methyl Orange by an amorphous FeOOH catalyst developed from a high iron-containing fly ash. Chem Eng J 158:148–153
Lucas MS, Peres JA (2007) Degradation of Reactive Black 5 by Fenton/UV-C and ferrioxalate/H2O2/solar light processes. Dyes Pigm 74:622–629
Malato S, Balnco J, Richter C, Braun B, Maldonado MI (1998) Enhancement of the rate of solar photoactivity mineralization of organic pollutants by inorganic oxidizing species. Appl Catal B Environ 17:347–356
Merouani S, Hamdaoui O, Saoudi F, Chiha MS (2010) Sonochemical degradation of Rhodamine B in aqueous phase: effects of additives. Chem Eng J 158:550–557
Muruganandham M, Swaminathan M (2004) Solar photocatalytic degradation of a reactive azo dye in TiO2-suspension. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 81:439–457
Natarajan T, Thomas M, Natarajan K, Bajaj HC, Tayade RJ (2011) Study on UVLED/TiO2 process for degradation of Rhodamine B dye. Chem Eng J 169:126–134
Newcombe G, Hayes R, Drikas M (1993) Granular activated carbon: importance of surface properties in the adsorption of naturally occurring organics. Colloids Surf A 78:65–71
Pignatello JJ, Liu D, Huston P (1999) Evidence for an additional oxidant in the photoassisted Fenton reaction. Environ Sci Technol 33:1832–1839
Prado AGS, Costa LL (2009) Photocatalytic decouloration of malachite green dye by application of TiO2 nanotubes. J Hazard Mater 169:297–301
Prado AGS, Faria EA, SouzaDe JR, Torres JD (2005) Ammonium complex of niobium as a precursor for the hydrothermal preparation of cellulose acetate/Nb2O5 photocatalyst. J Mol Catal A 237:115–119
Qi S, Zuo R, Liu Y, Wang Y (2013) Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of electrospun niobium oxide nanofibers. Mater Res Bull 48:1213–1217
Ram MK, Andreescu S, Ding HM (2011) Nanotechnology for environmental decontamination. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 173–175
Rivera-Utrilla J, Bautista-Toledo I, Ferro-Garcia MA, Moreno-Castilla C (2001) Activated carbon surface modifications by adsorption of bacteria and their effect on aqueous lead adsorption. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 76:1209–1215
Schmitt M, Heusing S, Aegerter MA, Pawlicka A, Avellaneda C (1998) Electrochromic properties of Nb2O5 sol–gel coatings. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 54:9–17
Shimizu N, Ogino C, Dadjour MF, Murata T (2007) Sonocatalytic degradation of methylene blue with TiO2 pellets in water. Ultrason Sonochem 14:184–190
Sun JH, Wang YK, Sun RX, Dong SY (2009) Photodegradation of azo dye Congo Red from aqueous solution by the WO3–TiO2/activated carbon (AC) photocatalyst under the UV irradiation. Mater Chem Phys 115:303–308
Szymanowski H, Zabeida O, Klemberg-Sapieha JE, Martinu L (2005) Optical properties and microstructure of plasma deposited Ta2O5 and Nb2O5 films. J Vac Sci Tech-nol A 23:241–247
Tangestaninejad S, Moghadam M, Mirkhani V, Mohammadpoor-Baltork I, Salavati H (2008) Sonochemical and visible light induced photochemical and sonophotochemical degradation of dyes catalyzed by recoverable vanadium-containing polyphosphomolybdate immobilized on TiO2 nanoparticles. Ultrason Sonochem 15:815–822
Walling C (1975) Fentons reagent revisited. Acc Chem Res 8:125–131
Wang Q, Zhang M, Chen C, Ma W, Zhao J (2010) Photocatalytic aerobic oxidation of alcohols on TiO2: the acceleration effect of a bronsted acid. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:7976–7979
Weissman JG, Ko EI, Wynblatt P, Howex JM (1989) High-resolution electron microscopy and image simulation of TT-, T-, and H-niobia and model silica-supported niobium surface oxides. Chem Mater 1:187–193
Wolfrum EJ, Ollis DF (1994) Aquatic and surface photochemistry. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 451–465
Yu SR, Zhang XP, He ZM, Liu YH, Liu ZH (2004) Effects of Ce on the short-term biocompatibility of Ti–Fe–Mo–Mn–Nb–Zr alloy for dental materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:687–691
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemzadeh, F., Rahimi, R. & Gaffarinejad, A. Influence of operational key parameters on the photocatalytic decolorization of Rhodamine B dye using Fe2+/H2O2/Nb2O5/UV system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 5121–5131 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2456-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2456-5