Abstract
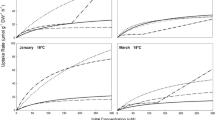
Aquaculture effluents are rich in nitrogen compounds that may enhance local primary productivity, leading to the development of algae blooms. The goal of this study was to assess the potential use of naturally occurring green macroalgae (Ulva and Enteromorpha) as bioremediators for nitrogen-rich effluents from a fish aquaculture plant, by evaluating their respective uptake dynamics under controlled conditions. Ulva and Enteromorpha were incubated separately in aquaculture effluent from a local pilot station. Algae tissue and water samples were collected periodically along 4 h. For each sample, nitrate, nitrite, and ammonia concentrations were quantified in the effluent, while internal algae reserve pools and nitrate reductase activity (NRA) were determined within the algae tissues. Both macroalgae absorbed all dissolved inorganic nitrogen compounds in less than 1 h, favoring ammonia over nitrate. Ulva stored nitrate temporarily as an internal reserve and only used it after ammonia availability decreased, whereas Enteromorpha stored and metabolized ammonia and nitrate simultaneously. These distinct dynamics of ammonia and nitrate uptake supported an increase in NRA during the experiment. This study supports the hypothesis that Ulva or Enteromorpha can be used as bioremediators in aquaculture effluents to mitigate excess of dissolved inorganic nitrogen.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu MH, Pereira R, Buschmann AH, Sousa-Pinto I, Yarish C (2011) Nitrogen uptake responses of Gracilaria vermiculophylla (Ohmi) Papenfuss under combined and single addition of nitrate and ammonium. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 407:190–199. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2011.06.034
Aníbal J, Rocha C, Sprung M (2007) Mudflat surface morphology as a structuring agent of algae and associated macroepifauna communities: a case study in Ria Formosa. J Sea Res 57:36–46. doi:10.1016/j.seares.2006.07.002
Barsanti L, Gualtieri P (2006) Algae: anatomy, biochemistry, and biotechnology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Berges JA (1997) Miniview: algal nitrate reductases. Eur J Phycol 32:3–8. doi:10.1080/09541449710001719315
Bird KT, Habig C, DeBusk T (1982) Nitrogen allocation and storage patterns in Gracilaria tikvahiae (Rhodophyta). J Phycol 18:344–348. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.1982.tb03194.x
Cabello-Pasini A, Macías-Carranza V, Abdala R, Korbee N, Figueroa FL (2010) Effect of nitrate concentration and UVR on photosynthesis, respiration, nitrate reductase activity, and phenolic compounds in Ulva rigida (Chlorophyta). J Appl Phycol 23:363–369. doi:10.1007/s10811-010-9548-0
Cardinale BJ (2011) Biodiversity improves water quality through niche partitioning. Nature 472:86–89. doi:10.1038/nature09904
Cohen RA, Fong P (2005) Experimental evidence supports the use of δ15N content of the opportunistic green macroalga Enteromorpha intestinalis (Chlorophyta) to determine nitrogen sources to estuaries. J Phycol 41:287–293. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.04022.x
Chow F, de Oliveira MC, Pedersén M (2004) In vitro assay and light regulation of nitrate reductase in red alga Gracilaria chilensis. J Plant Physiol 161:769–776. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2004.01.002
Corzo A, Niell FX (1991) Determination of nitrate reductase activity in Ulva rigida C Agardh by the in situ method. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 146:181–191. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(91)90024-Q
Corzo A, Niell FX (1994) Nitrate-reductase activity and in vivo nitrate-reduction rate in Ulva rigida illuminated by blue light. Mar Biol 120:17–23
Cruz-Suárez LE, León A, Peña-Rodríguez A, Rodríguez-Peña G, Moll B, Ricque-Marie D (2010) Shrimp/Ulva co-culture: a sustainable alternative to diminish the need for artificial feed and improve shrimp quality. Aquaculture 301:64–68. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.01.021
EEA (2010) The European environment: state and outlook 2010—marine and coastal environment. European Environment Agency, Copenhagen
Fei X (2004) Solving the coastal eutrophication problem by large scale seaweed cultivation. Hydrobiologia 512:145–151. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000020320.68331.ce
Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M, Kremling K (1983) Methods of seawater analysis. Chemie, Weinheim
Hayden HS, Blomster J, Maggs CA, Silva PC, Stanhope MJ, Waaland JR (2003) Linnaeus was right all along: Ulva and Enteromorpha are not distinct genera. Eur J Phycol 38:277–294. doi:10.1080/1364253031000136321
He P, Xu S, Zhang H, Wen S, Dai Y, Lin S, Yarish C (2008) Bioremediation efficiency in the removal of dissolved inorganic nutrients by the red seaweed, Porphyra yezoensis, cultivated in the open sea. Water Res 42:1281–1289. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.09.023
Hernández I, Tovar A, Vergara JJ (2002) Biofiltering efficiency in removal of dissolved nutrients by three species of estuarine macroalgae cultivated with sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) waste waters 2. Ammonium J App Phycol 14:375–384
Hong HS, Wang YJ, Wang DZ (2011) Response of phytoplankton to nitrogen addition in the Taiwan strait upwelling region: nitrate reductase and glutamine synthetase activities. Cont Shelf Res 31:S57–S66. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2011.01.018
Huo Y, Wu H, Chai Z, Xu S, Han F, Dong L, He P (2012) Bioremediation efficiency of Gracilaria verrucosa for an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system with Pseudosciaena crocea in Xiangshan harbor, China. Aquaculture 326–329:99–105. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.11.002
Hurd CL, Berges JA, Osborne J, Harrison PJ (1995) An in vitro nitrate reductase assay for marine macroalgae: optimization and characterization of the enzyme for Fucus gardneri (phaeophyta). J Phycol 31:835–843. doi:10.1111/j.0022-3646.1995.00835.x
Jiménez del Río M, Ramazanov Z, García-Reina G (1996) Ulva rigida (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) tank culture as biofilters for dissolved inorganic nitrogen from fishpond effluents. Hydrobiologia 326(327):61–66. doi:10.1007/BF00047787
Jones AB, Dennison WC, Preston NP (2001) Integrated treatment of shrimp effluent by sedimentation, oyster filtration and macroalgal absorption: a laboratory scale study. Aquaculture 193:155–178. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00486-5
Kang YH, Park SR, Chung IK (2011) Biofiltration efficiency and biochemical composition of three seaweed species cultivated in a fish-seaweed integrated culture. Algae 26:97–108. doi:10.4490/algae.2011.26.1.097
Kim JK, Kraemer GP, Neefus CD, Chung IK, Yarish C (2007) Effects of temperature and ammonium on growth, pigment production and nitrogen uptake by four species of Porphyra (Bangiales, Rhodophyta) native to the New England coast. J Appl Phycol 19:431–440. doi:10.1007/s10811-006-9150-7
Lartigue J, Sherman TD (2002) Field assays for measuring nitrate reductase activity in Enteromorpha sp. J Phycol 38:971–982. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2002.t01-2-01193.x
Lartigue J, Sherman TD (2005) Response of Enteromorpha sp. (Chlorophyceae) to a nitrate pulse: nitrate uptake, inorganic nitrogen storage and nitrate reductase activity. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 292:147–157. doi:10.3354/meps292147
Liu J, Wang Z, Lin W (2010) De-eutrophication of effluent wastewater from fish aquaculture by using marine green alga Ulva pertusa. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 28:201–208. doi:10.1007/s00343-010-9245-5
Lobban CS, Harrison PJ (1997) Seaweed ecology and physiology. Cambridge University Press, New York
Luo MB, Liu F, Xu ZL (2012) Growth and nutrient uptake capacity of two co-occurring species, Ulva prolifera and Ulva linza. Aquat Bot 100:18–24. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2012.03.006
Marinho-Soriano E, Nunes SO, Carneiro MAA, Pereira DC (2009a) Nutrients’ removal from aquaculture wastewater using the macroalgae Gracilaria birdiae. Biomass Bioenergy 33:327–331. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2008.07.002
Marinho-Soriano E, Panucci RA, Carneiro MAA, Pereira DC (2009b) Evaluation of Gracilaria caudata J. Agardh for bioremediation of nutrients from shrimp farming wastewater. Bioresour Technol 100:6192–6198
Marinho-Soriano E, Azevedo CAA, Trigueiro TG, Pereira DC, Carneiro MAA, Camara MR (2011) Bioremediation of aquaculture wastewater using macroalgae and Artemia. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65:253–257. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.06.102
Naldi M, Wheeler PA (2002) 15N measurements of ammonium and nitrate uptake by Ulva fenestrata (Chlorophyta) and Gracilaria pacifica (Rhodophyta): comparison of net nutrient disappearance, release of ammonium and nitrate, and 15N accumulation in algal tissue. J Phycol 38:135–144. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2002.01070.x
de Paula Silva PH, McBride S, de Nys R, Paul NA (2008) Integrating filamentous “green tide” algae into tropical pond-based aquaculture. Aquaculture 284:74–80. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.07.035
Pregnall AM, Smith RD, Alberte RS (1987) Glutamine synthetase activity and free amino acid pools of eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) roots. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 106:211–228. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(87)90094-3
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Ritz C, Streibig JC (2008) Nonlinear regression with R. Springer, New York
Skriptsova AV, Miroshnikova NV (2011) Laboratory experiment to determine the potential of two macroalgae from the Russian Far-East as biofilters for integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA). Bioresour Technol 102:3149–3154. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.093
Teichberg M, Heffner LR, Fox S, Valiela I (2007) Nitrate reductase and glutamine synthetase activity, internal N pools, and growth of Ulva lactuca: responses to long and short-term N supply. Mar Biol 151:1249–1259. doi:10.1007/s00227-006-0561-4
Thomas TE, Harrison PJ (1985) Effect of nitrogen supply on nitrogen uptake, accumulation and assimilation in Porphyra perforata (Rhodophyta). Mar Biol 85:269–278. doi:10.1007/BF00393247
Thompson SM, Valiela I (1999) Effect of nitrogen loading on enzyme activity of macroalgae in estuaries in Waquoit Bay. Bot Mar 42:519–529
Troell M, Halling C, Nilsson A, Buschmann AH, Kautsky N, Kautsky L (1997) Integrated marine cultivation of Gracilaria chilensis (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta) and salmon cages for reduced environmental impact and increased economic output. Aquaculture 156:45–61. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(97)00080-X
Xu D, Gao Z, Zhang X, Qi Z, Meng C, Zhuang Z, Ye N (2011) Evaluation of the potential role of the macroalga Laminaria japonica for alleviating coastal eutrophication. Bioresour Technol 102:9912–9918. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.035
Yokoyama H, Ishihi Y (2010) Bioindicator and biofilter function of Ulva spp. (Chlorophyta) for dissolved inorganic nitrogen discharged from a coastal fish farm—potential role in integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Aquaculture 310:74–83. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.10.018
Young EB, Berges JA, Dring MJ (2009) Physiological responses of intertidal marine brown algae to nitrogen deprivation and resupply of nitrate and ammonium. Physiol Plant 135:400–411. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2008.01199.x
Acknowledgments
The research leading to these results was primarily funded by the project NITROLINKS–NITROgen loading into the Ria Formosa through Coastal Groundwater Discharge (CGD)—pathways, turnover and LINKS between land and sea in the Coastal Zone (PTDC/MAR/70247/2006) financed by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT). This research was also partially supported by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through the COMPETE-Operational Competitiveness Programme and national funds through Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT), under the projects “PEst-OE/MAR/UI0350/2011 (CIMA)” and “PEst-C/MAR/LA0015/2011 (CCMAR)”. We also like to thank Dr. Pedro Pousão from EPPO–IPMA for the aquaculture effluents used in the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aníbal, J., Madeira, H.T., Carvalho, L.F. et al. Macroalgae mitigation potential for fish aquaculture effluents: an approach coupling nitrogen uptake and metabolic pathways using Ulva rigida and Enteromorpha clathrata . Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 13324–13334 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2427-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2427-x