Abstract
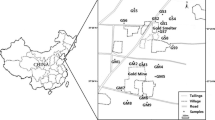
The horizontal and vertical distribution patterns and contamination status of ten trace metal/metalloids (Ag, Bi, Co, Cr, Ge, In, Ni, Sb, Sn, Tl) in soils around one of the largest Chinese Pb–Zn smelter in Zhuzhou City, Central China, were revealed. Different soil samples were collected from 11 areas, including ten agricultural areas and one city park area, with a total of 83 surface soil samples and six soil cores obtained. Trace metal/metalloids were determined by inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry after digestion by an acid mixture of HF and HNO3. The results showed that Ag, Bi, In, Sb, Sn, and Tl contents decreased both with the distance to the Pb–Zn smelter as well as the soil depth, hinting that these elements were mainly originated from the Pb–Zn smelting operations and were introduced into soils through atmospheric deposition. Soil Ge was influenced by the smelter at a less extent, while the distributions of Co, Cr, and Ni were roughly even among most sampling sites and soil depths, suggesting that they were primarily derived from natural sources. The contamination status, as revealed by the geo-accumulation index (I geo), indicated that In and Ag were the most enriched elements, followed by Sb, Bi, and Sn. In general, Cr, Tl, Co, Ni, and Ge were of an uncontaminated status.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barcan V, Kovnatsky E (1998) Soil surface geochemical anomaly around the copper–nickel metallurgical smelter. Water Air Soil Pollut 103(1–4):197–218
Bi X, Feng X, Yang Y, Qiu G, Li G, Li F, Liu T, Fu Z, Jin Z (2006) Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang Country, western Guizhou, China. Environ Int 32(7):883–890
Chen G, Zeng G, Du C, Huang D, Tang L, Wang L, Shen G (2010) Transfer of heavy metals from compost to red soil and groundwater under simulated rainfall conditions. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):211–216
Cheng S (2003) Heavy metal pollution in China: origin, pattern and control. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10(3):192–198
Cui C, Liu Z (1988) Chemical speciation and distribution of arsenic in water, suspended solids and sediment of Xiangjiang River, China. Sci Total Environ 77(1):69–82
China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association (2011) The year book of nonferrous metals industry of China. Beijing, China
da Silva EF, Ávila PF, Salgueiro AR, Candeias C, Pereira HG (2013) Quantitative-spatial assessment of soil contamination in S. Francisco de Assis due to mining activity of the Panasqueira mine (Portugal). Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7534–7549
Douay F, Pruvot C, Roussel H, Ciesielski H, Fourrier H, Proix N, Waterlot C (2008) Contamination of urban soils in an area of northern France polluted by dust emissions of two smelters. Water Air Soil Pollut 188:247–260
Du P, Xue N, Liu L, Li F (2008) Distribution of Cd, Pb, Zn and Cu and their chemical speciations in soils from a peri-smelter area in northeast China. Environ Geol 55:205–213
Dudka S, Piotrowska M, Terelak H (1996) Transfer of cadmium, lead, and zinc from industrially contaminated soil to crop plants: a field study. Environ Pollut 94(2):181–188
Factory Records of Zhuzhou Smelter: 1953–1980 (1983) Hunan Zhuzhou Printing House, China
Factory Records of Zhuzhou Smelter: second volume (1995) Hunan Press, China
Guo ZH, Zhu YG (2004) Contamination and available contents of heavy metals in soils in the typical mining and smelting circumjacent districts. Ecol Environ 13(4):553–555
Hu Y, Liu X, Bai J, Shih K, Zeng EY, Cheng H (2013) Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6150–6159
Jiang JM (2004) Status and sustainable development of lead and zinc smelting industry in China. Chin J Nonferrous Met 14(S1):52–62
Jiang JM (2006) Current status and recent technical progress of zinc smelting in China. China Nonferrous Metall 10(5):19–23
Karadaş C, Kara D (2011) In vitro gastro-intestinal method for the assessment of heavy metal bioavailability in contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(4):620–628
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 152(3):686–692
Lei M, Zeng M, Zheng YM, Liao MH, Zhu Y (2008) Heavy metals pollution and potential ecological risk in paddy soils around mine areas and smelting areas in Hunan Province. Acta Sci Circumst 6:1212–1220
Li Y, Wang Y, Gou X, Su Y, Wang G (2006) Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables around non-ferrous metals mining and smelting sites, Baiyin, China. J Environ Sci 6:1124–1134
Li Z, Feng X, Li G, Bi X, Sun G, Zhu J, Qin H, Wang J (2011) Mercury and other metal and metalloid soil contamination near a Pb/Zn smelter in east Hunan Province, China. Appl Geochem 26(2):160–166
Li Z, Feng X, Li G, Bi X, Zhu J, Qin H, Dai Z, Liu J, Li Q, Sun G (2013) Distributions, sources and pollution status of 17 trace metal/metalloids in the street dust of a heavily industrialized city of Central China. Environ Pollut 182:408–416
Liu H, Probst A, Liao B (2005) Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci Total Environ 339:153–166
Loska K, Wiechuła D, Korus I (2004) Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ Int 30:159–165
Meadows M, Watmough SA (2012) An assessment of long-term risks of metals in Sudbury: a critical loads approach. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(7):4343–4354
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J 2:108–118
Nahmani J, Lavelle P (2002) Effects of heavy metal pollution on soil macrofauna in a grassland of northern France. Eur J Soil Biol 38(3–4):297–300
Nriagu JO, Pacyna JM (1988) Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature 333:134–139
Peng DH, Wu P, Cao ZX, Yang SZ, Xie HH (2011) Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of heavy metal pollution of water-sediments in stream of zinc smelting area, Hezhang of Guizhou, China. J Agro-Environ Sci 30(5):979–985
Poggio L, Vrščj B, Schulin R, Hepperle W, Marsan FA (2009) Metals pollution and human bioaccessibility of topsoils in Grugliasco (Italy). Environ Pollut 157:680–689
Qi L, Grégoire DC (2000) Determination of trace elements in twenty six Chinese geochemistry reference materials by inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry. Geostand Geoanal Res 24:51–63
Reimann C, Garrett G (2005) Geochemical background—concept and reality. Sci Total Environ 350(1–3):12–27
Šajn R, Aliu M, Stafilov T, Alijagić J (2013) Heavy metal contamination of topsoil around a lead and zinc smelter in Kosovska Mitrovica/Mitrovicë, Kosovo/Kosovë. J Geochem Explor 134:1–16
SEPA (State Environmental Protection Administration) (1990) Elemental background values of soils in China. Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing
SEPA (State Environmental Protection Administration) (1995) Environmental quality standard for soils (GB 15618-1995). Beijing, China
Shang J, Long A, Li B, Jiang J (1996) The corresponding analysis of heavy-metal pollution of soil in Zhuzhou City. Chinese Geogr Sci 6(2):177–184
Stafilov T, Šajn R, Pančevski Z, Boev B, Frontasyeva MV, Strelkova LP (2010) Heavy metal contamination of topsoils around a lead and zinc smelter in the Republic of Macedonia. J Hazard Mater 175(1–3):896–914
Sterckeman T, Douay F, Proix N, Fourrier H (2000) Vertical distribution of Cd, Pb and Zn in soils near smelters in the north of France. Environ Pollut 107(3):377–389
Sterckeman T, Douay F, Proix N, Fourrier H, Perdrix E (2002) Assessment of the contamination of cultivated soils by eighteen trace elements around smelters in the north of France. Water Air Soil Pollut 135:173–194
van Alphen M (1999) Atmospheric heavy metal deposition plumes adjacent to a primary lead–zinc smelter. Sci Total Environ 236(1–3):119–134
Verner JF, Ramsey MH, Helios-Rybicka E, Jêdrzejczyk B (1996) Heavy metal contamination of soils around a Pb–Zn smelter in Bukowno, Poland. Appl Geochem 11(1–2):11–16
Wang H, Arne OS (2003) Heavy metal pollution in air-water-soil-plant system of Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 147:79–107
Wang L, Guo Z, Xiao X, Chen T, Liao X, Song J, Wu B (2008) Heavy metal pollution of soils and vegetables in the midstream and downstream of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan Province. J Geogr Sci 18:353–362
Wang S, Feng X, Qiu G, Fu X, Wei Z (2007) Characteristics of mercury exchange flux between soil and air in the heavily air-polluted area, eastern Guizhou, China. Atmos Environ 41(27):5584–5594
Wang X, He M, Xie J, Xi J, Lu X (2010) Heavy metal pollution of the world largest antimony mine-affected agricultural soils in Hunan Province (China). J Soils Sediments 10:827–837
Wei C, Wang C, Yang L (2009) Characterizing spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in the soils from mining–smelting activities in Shuikoushan, Hunan Province, China. J Environ Sci 21:1230–1236
Wu QR, Wang SX, Zhang L, Song JX, Yang H, Meng Y (2012) Update of mercury emissions from China’s primary zinc, lead and copper smelters, 2000–2010. Atmos Chem Phys 12:11153–11163
Yang Y, Liu C, Xu L, Wu P, Zhang G (2004) Effects of heavy metal contamination on microbial biomass and community structure in soils. Chin J Geochem 23(4):319–328
Ye L, Cook NJ, Ciobanu CL, Liu YP, Zhang Q, Liu TG, Gao W, Yang Y, Danyushevskiy L (2011) Trace and minor elements in sphalerite from base metal deposits in South China: a LA-ICPMS study. Ore Geol Rev 39:188–217
Yin C, Sun Q, Zhao X (2012a) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in paddy soils from Daye mining area of Hubei Province, China. Adv Mater Res 599:434–440
Yin R, Feng X, Li Z, Zhang Q, Bi X, Li G, Liu J, Zhu J, Wang J (2012b) Metallogeny and environmental impact of Hg in Zn deposits in China. Appl Geochem 27(1):151–160
Zhang X, Yang L, Li Y, Li H, Wang W, Ge Q (2011) Estimation of lead and zinc emissions from mineral exploitation based on characteristics of lead/zinc deposits in China. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 21(11):2513–2519
Zhang X, Yang L, Li Y, Li H, Wang W, Ye B (2012) Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ Monit Assess 184(4):2261–2273
Zheng N, Liu J, Wang Q, Liang Z (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, northeast of China. Sci Total Environ 408(4):726–733
Zheng N, Wang Q, Liang Z, Zheng D (2008) Characterization of heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, northeast China. Environ Pollut 154(1):135–142
Zheng N, Wang Q, Zheng D (2007) Health risk of Hg, Pb, Cd, Zn, and Cu to the inhabitants around Huludao Zinc Plant in China via consumption of vegetables. Sci Total Environ 383(1–3):81–89
Zhou H, Zeng M, Zhou X, Liao BH, Liu J, Lei M, Zhong QY, Zeng H (2013) Assessment of heavy metal contamination and bioaccumulation in soybean plants from mining and smelting areas of southern Hunan Province, China. Environ Toxicol Chem 32(12):2719–2727
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Dr. Atindra Sapkota for the English language editing of our manuscript. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21077103, 41273003, 41003007) and the Government of Norway (“Sino-Norwegian Cooperation Project on Capacity Building for Reducing Mercury Pollution in China”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 302 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Feng, X., Bi, X. et al. Probing the distribution and contamination levels of 10 trace metal/metalloids in soils near a Pb/Zn smelter in Middle China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 4149–4162 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2407-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2407-1