Abstract
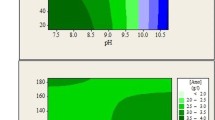
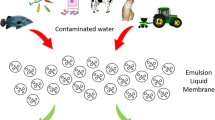
In this work, the removal of the worldwide non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ibuprofen (IBP) and ketoprofen (KTP) by emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) was carried out. An ELM system is made up of hexane as diluent, Span 80 as the surfactant and sodium carbonate as the inner aqueous solution. Effect of experimental conditions that affect the extraction of IBP such as surfactant concentration, emulsification time, sulfuric acid concentration in external phase, acid type in external phase, internal phase concentration, type of internal phase, stirring speed, volume ratio of internal phase to membrane phase, treatment ratio, IBP initial concentration, diluent type and salt was investigated. The obtained results showed that by appropriate selection of the operational parameters, it was possible to extract nearly all of IBP molecules from the feed solution even in the presence of high concentration of salt. Under optimum operating conditions, the efficiencies of IBP removal from distilled water (99.3 %), natural mineral water (97.3 %) and sea water (94.0 %) were comparable, which shows that the ELM treatment process represents a very interesting advanced separation process for the removal of IBP from complex matrices such as natural and sea waters. Under the optimized experimental conditions, approximately 97.4 % KTP was removed in less than 20 min of contact time.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso E, Villar P, Santos A, Aparicio I (2006) Fractionation of heavy metals in sludge from anaerobic wastewater stabilization ponds in southern Spain. Waste Manage 26:1270–1276
Andreozzi R, Canterino M, Marotta R (2006) Fe(III) homogeneous photocatalysis for the removal of 1,2-dichlorobenzene in aqueous solution by means UV lamp and solar light. Water Res 40:3785–3792
Balasubramanian A, Venkatesan S (2012) Removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane containing ionic liquid [BMIM]+[PF6]− in tributyl phosphate. Desalination 289:27–34
Bundgaard H, Nielsen NM (1988) Glycolamide esters as a novel biolabile prodrug type for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory carboxylic acid drugs. Int J Pharm 43:101–110
Chiha M, Samar MH, Hamdaoui O (2006) Extraction of chromium(VI) from sulphuric acid aqueous solutions by a liquid surfactant membrane (LSM). Desalination 194:69–80
Choina J, Kosslick H, Fischer C, Flechsig G-U, Frunza L, Schulz A (2013) Photocatalytic decomposition of pharmaceutical ibuprofen pollutions in water over titania catalyst. Appl Catal B-Environ 129:589–598
Dâas A, Hamdaoui O (2010a) Extraction of anionic dye from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. J Hazard Mater 178:973–981
Dâas A, Hamdaoui O (2010b) Extraction of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membrane. J Membr Sci 348:360–368
Djenouhat M, Hamdaoui O, Chiha M, Samar MH (2008a) Ultrasonication-assisted preparation of water-in-oil emulsions and application to the removal of cationic dyes from water by emulsion liquid membrane: Part 1. Membrane stability. Sep Purif Technol 62:636–641
Djenouhat M, Hamdaoui O, Chiha M, Samar MH (2008b) Ultrasonication-assisted preparation of water-in-oil emulsions and application to the removal of cationic dyes from water by emulsion liquid membrane: Part 2. Permeation and stripping. Sep Purif Technol 63:231–238
Fent K, Weston A, Caminada D (2006) Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat Toxicol 76:122–159
Illés E, Takacs E, Dombi A, Gajda-Schrantz K, Gonter K, Wojnarovits L (2012) Radiation induced degradation of ketoprofen in dilute aqueous solution. Radiat Phys Chem 81:1479–1483
Juang R-S, Lin K-H (2004) Ultrasound-assisted production of W/O emulsions in liquid surfactant membrane processes. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 238:43–49
Kulkarni PS, Mahajani VV (2012) Application of liquid emulsion membrane (LEM) process for enrichment of molybdenum from aqueous solutions. J Membr Sci 201:123–135
Madhavan J, Grieser F, Ashokkumar M (2010) Combined advanced oxidation processes for the synergistic degradation of ibuprofen in aqueous environments. J Hazard Mater 178:202–208
Marco-Urrea E, Pérez-Trujillo M, Cruz-Morató C, Caminal G, Vicent T (2010) White-rot fungus-mediated degradation of the analgesic ketoprofen and identification of intermediates by HPLC–DAD–MS and NMR. Chemosphere 78:474–481
Méndez-Arriaga F, Torres-Palma RA, Pétrier C, Esplugas S, Gimenezd J, Pulgarin C (2008) Ultrasonic treatment of water contaminated with ibuprofen. Water Res 42:4243–4248
Méndez-Arriaga F, Esplugas S, Giménez J (2010) Degradation of the emerging contaminant ibuprofen in water by photo-Fenton. Water Res 44:589–595
Metcalfe CD, Miao XS, Koenig BG, Struger J (2003) Distribution of acidic and neutral drugs in surface waters near sewage treatment plants in the lower Great Lakes, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2881–2889
Miege C, Choubert JM, Ribeiro L, Eusebe M, Coquery M (2007) Removal efficiency of pharmaceuticals and personal care products with varying wastewater treatment processes and operating conditions – conception of a database and first results. In: Köhl A (ed) Proceedings of fifth IWA specialized conference on assessment and control of micropollutants/hazardous substances in water. Micropol & Ecohazard. DECHEMA e.V, Frankfurt/Main, pp 220–225
Mozia S, Morawski AW (2012) The performance of a hybrid photocatalysis–MD system for the treatment of tap water contaminated with ibuprofen. Catal Today 193:213–220
Ng YS, Jayakumar NS, Hashim MA (2010) Performance evaluation of organic emulsion liquid membrane on phenol removal. J Hazard Mater 184:255–260
Peng W, Jiao H, Shi H, Xu C (2012) The application of emulsion liquid membrane process and heat-induced demulsification for removal of pyridine from aqueous solutions. Desalination 286:372–378
Sabry R, Hafez A, Khedr M, El-Hassanin A (2007) Removal of lead by an emulsion liquid membrane: Part I. Desalination 212:165–175
Santos JL, Aparicio I, Alonso E (2007) Occurrence and risk assessment of pharmaceutically active compounds in wastewater treatment plants. A case study: Seville city (Spain). Environ Int 33:596–601
Takagi T, Ramachandran C, Bermejo M, Yamashita S, Yu LX, Amidon GL (2006) A provisional biopharmaceutical classification of the top 200 oral drug products in the United States, Great Britain, Spain, and Japan. Mol Pharm 3:631–643
Tixier C, Singer HP, Oellers S, Müller SR (2003) Occurrence and fate of carbamazepine, clofibric acid, diclofenac, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, and naproxen in surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 37:1061–1068
Williams NS, Ray MB, Gomaa HG (2012) Removal of ibuprofen and 4-isobutylacetophenone by non-dispersive solvent extraction using a hollow fibre membrane contactor. Sep Purif Technol 88:61–69
Williams NS, Gomaa HG, Ray MB (2013) Effect of solvent immobilization on membrane separation of ibuprofen metabolite: a green and organic solvent analysis. Sep Purif Technol 115:57–65
Yalkowski SH, He Y, Jain P (2010) Handbook of aqueous solubility data, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Yan J, Pal R (2004) Effects of aqueous-phase acidity and salinity on isotonic swelling of W/O/W emulsion liquid membranes under agitation conditions. J Membr Sci 244:193–203
Yang L, Zhang Z, Guo Y, Gao X, Takeuchi H (2005) Uranium(VI) extraction by liquid surfactant membrane with N-alkylcaprolactams as a carrier. Sep Purif Technol 47:88–94
Zheng BG, Zheng Z, Zhang JB, Luo XZ, Wang JQ, Liu Q, Wang LH (2011) Degradation of the emerging contaminant ibuprofen in aqueous solution by gamma irradiation. Desalination 276:379–385
Acknowledgments
The financial support by the General Directorate for Scientific Research and Technological Development (PNR project no. 4/D/25) and the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research of Algeria (projects No. J0101120090018 and J0101120120098) is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dâas, A., Hamdaoui, O. Removal of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ibuprofen and ketoprofen from water by emulsion liquid membrane. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 2154–2164 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2140-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2140-9