Abstract
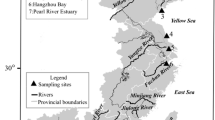
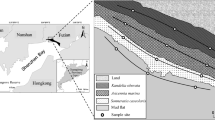
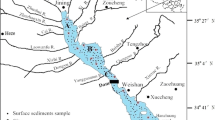
The aims of this paper were to survey the total Hg levels and distribution character in intertidal sediment in continental coast of Shanghai, and identify the environment factors that might influence the sediment Hg concentrations, and to assess the pollution degree and potential ecological risk of Hg in sediment. Eighty-eight surface sediment samples and 18 sediment cores were collected for Hg contamination analysis. Physicochemical properties including Eh, particle size, content of total organic carbon (TOC), and acid volatile sulfide (AVS) were also measured. Index of geo-accumulation (I geo) and potential ecological risk index were used respectively to assess the pollution levels and the ecological risk of sediment Hg. The average of total Hg concentrations in surface sediments was 107.4 ± 90.9 ng/g with the range from 0 to 465.9 ng/g. Higher Hg concentrations were generally found in surface sediments near sewage outfalls and the mouth of rivers. Total Hg concentrations were significantly correlated with TOC (p < 0.05) both in surface (r = 0.24) and core (r = 0.29) sediments, but not with the other environment factors (Eh, AVS, and particle size). Geo-accumulation index indicated that Hg contamination in intertidal sediments was generally at none to moderate degree, while potential ecological risk index demonstrated that the risk caused by Hg were at moderate to considerable level. Intertidal sediment in continental coast of Shanghai has generally been contaminated by Hg, and it might pose moderate to considerable risk to the local ecosystem. The Hg contamination is related more to the coastal pollution sources and complicated hydrodynamic and sedimentary conditions than the other environment factors studied.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahim G, Parker R (2008) Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ Monit Assess 136:227–238
An Q, Wu Y, Wang J, Li Z (2009) Heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Yangtze river estuary, China. Environ Earth Sci 59:363–370
AQSIQ (General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China) (2002) The People’s Republic of China National Standards GB 18668-2002—Marine Sediment Quality (in Chinese)
Bowles KC, Ernste MJ, Kramer JR (2003) Trace sulfide determination in oxic freshwaters. Anal Chim Acta 477:113–124
Canário J, Vale C, Caetano M (2005) Distribution of monomethlymercury and mercury in surface sediments of the Tagus estuary (Portugal). Mar Pollut Bull 50:1142–1145
Canário J, Branco V, Vale C (2007) Seasonal variation of monomethylmercury concentrations in surface sediments of the Tagus estuary (Portugal). Environ Pollut 148:380–383
Chen Z, Xu S, Liu L, Yu J, Yu L (2000) Spatial distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in tidal flat sediments of Shanghai coastal zone. Acta Geogr Sin 55:641–651 (in Chinese)
Chen C, Kao C, Chen C, Dong C (2007) Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere 66:1431–1440
Covelli S, Acquavita A, Piani R, Predonzani S, De Vittor C (2009) Recent contamination of mercury in an estuarine environment (Marano lagoon, Northern Adriatic, Italy). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 82:273–284
Covelli S, Protopsalti I, Acquavita A, Sperle M, Bonardi M, Emili A (2012) Spatial variation, speciation and sedimentary records of mercury in the Guanabara Bay (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Cont Shelf Res 35:29–42
Delaune R, Gambrell R, Jugsujinda A, Devai I, Hou A (2008) Total Hg, methyl Hg and other toxic heavy metals in a northern Gulf of Mexico estuary: Louisiana Pontchartrain Basin. J Environ Sci Health A 43:1006–1015
Deng H, Zhang J, Wang D, Chen Z, Xu S (2010) Heavy metal pollution and assessment of the tidal flat sediments near the coastal sewage outfalls of shanghai, China. Environ Earth Sci 60:57–63
Ding Z, Liu J, Li L, Lin H, Wu H, Hu Z (2009) Distribution and speciation of mercury in surficial sediments from main mangrove wetlands in China. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1319–1325
Duran R, Ranchou-Peyruse M, Menuet V, Monperrus M, Bareille G, Goňi M, Salvado J, Amouroux D, Guyoneaud R, Donard O, Caumette P (2008) Mercury methylation by a microbial community from sediments of the Adour Estuary (Bay of Biscay, France). Environ Pollut 156:951–958
Fang T, Chen R (2010) Mercury contamination and accumulation in sediments of the East China Sea. J Environ Sci China 22:1164–1170
García E, Cruz-Motta J, Farina O, Bastidas C (2008) Anthropogenic influences on heavy metals across marine habitats in the western coast of Venezuela. Cont Shelf Res 28:2757–2766
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Kwokal Ž, Frančišković-Biliniski S, Bilinski H, Branica M (2002) A comparison of anthropogenic mercury pollution in Kaštela Bay (Croatia) with pristine estuaries in Öre (Sweden) and Krka (Croatia). Mar Pollut Bull 44:1152–1157
Lewis M, Chancy C (2008) A summary of total mercury concentrations in flora and fauna near common contaminant sources in the Gulf of Mexico. Chemosphere 70:2016–2024
Li P, Feng X, Qiu G, Shang L, Li Z (2009) Mercury pollution in Asia: a review of the contaminated sites. J Hazard Mater 168:591–601
Li Z, Feng X, He T, Yan H, Liang L (2005) Determination of total mercury in soil and sediment by aquaregia digestion in the water bath coupled with cold vapor atom fluorescence spectrometry. Bull Mineral Petrol and Geochem 24(2):140–143 (in Chinese)
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in the sediments of the Rhine River. Geoj 2(3):108–118
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, 2nd edn. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 539–577
Oh S, Kim M, Yi S, Zoh K (2010) Distribution of total mercury and methylmercury in surface sediments and fishes in Lake Shihwa, Korea. Sci Total Environ 408:1059–1068
Ouddane B, Mikac N, Cundy AB, Quillet L, Fischer JC (2008) A comparative study of mercury distribution and methylation in mudflats from two macrotidal estuaries: the Seine (France) and the Medway (United Kingdom). Appl Geochem 23:618–631
Rodríguez-Barroso M, Benhamou Y, Moumni B, Hatimi I, García-Morales J (2009) Evaluation of metal contamination in sediments from north of Morocco: geochemical and statistical approaches. Environ Monit Assess 159:169–181
Shi G, Chen Z, Bi C, Li Y, Teng J, Wang L, Xu S (2010a) Comprehensive assessment of toxic metals in urban and suburban street deposited sediments (SDSs) in the biggest metropolitan area of China. Environ Pollut 158:694–703
Shi J, Carman C, Zhang G, Jiang G, Li X (2010b) Mercury profiles in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area of South China. Environ Pollut 158:1974–1979
SMOB (Shanghai Municipal Oceanic Bureau) (2006) Bulletin of Marine Environmental Quality of Shanghai. http://sdinfo.coi.gov.cn/hygb/dfhygb/2006/shanghai/index.html. Accessed 1 July 2007 (in Chinese)
Song L, Zheng X, Zhou L, Zhang G, Ren S, Wang Y (2009) Cumulation characteristics and influencing factors of mercury in sediments from Chongming Wetland. Res Environ Sci 22(12):1426–1432 (in Chinese)
Yang M, Kostaschuk R, Chen Z (2004) Historical changes in heavy metals in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ Geol 46:857–864
Yu R, Yuan X, Zhao Y, Hu G, Tu X (2008) Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China. J Environ Sci China 20:664–669
Zhang W, Feng H, Chang J, Qu J, Xie H, Yu L (2009) Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze River intertidal zone: an assessment from different indexes. Environ Pollut 157:1533–1543
Zhu J (1991) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in tidal flat of Pudong District in Shanghai. J East China Norm Univ (Nat Sci): 79–85 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 40903049, 40971259, and 40973078), the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China and Ministry of Housing and Urban–Rural development of China (Grant No. 2009ZX07317-006), and the Science & Technology Department of Shanghai (Grant Nos. 10JC1404300 and 11230705800). The authors also would like to thank the reviewers and associate editor who aided in the development and improvement of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Céline Guéguen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, H., Wang, D., Chen, Z. et al. A comprehensive investigation and assessment of mercury in intertidal sediment in continental coast of Shanghai. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 6297–6305 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1665-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1665-2