Abstract
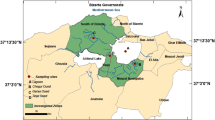
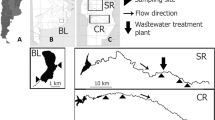
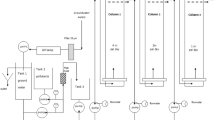
Polar organic chemical integrative samplers (POCISs) for the monitoring of polar pesticides in groundwater were tested on two sites in order to evaluate their applicability by comparison with the spot-sampling approach. This preliminary study shows that, as in surface water, POCIS is a useful tool, especially for the screening of substances at low concentration levels that are not detected by laboratory analysis of spot samples. For quantitative results, a rough estimation is obtained. The challenge is now to define the required water-flow conditions for a relevant quantification of pesticides in groundwater and to establish more representative sampling rates for groundwater.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- POCIS:
-
Polar organic chemical integrative sampler
- TWA:
-
Time-weighted average
- GWD:
-
Groundwater Directive
- SPE:
-
Solid-phase extraction
- UPLC:
-
Ultraperformance liquid chromatography
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
References
Allan IJ, Vrana B, Greenwood R, Mills GA, Roig B, Gonzalez C (2006) A “toolbox” for biological and chemical monitoring requirements for the European Union’s Water Framework Directive. Talanta 69:302–322
Alvarez DA, Petty JD, Huckins JN, Jones-Lepp TL, Getting DT, Goddard JP, Manahan SE (2004) Development of a passive, in situ, integrative sampler for hydrophilic organic contaminants in aquatic environments. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1640–1648
Alvarez DA, Huckins JN, Petty JD, Jones-Lepp T, Stuer-Lauridsen F, Getting DT, Goddard JP, Gravell (2007) Tool for monitoring hydrophilic contaminants in water: polar organic chemical integrative sampler (POCIS). In: Greenwood R, Mills GA, Vrana B (eds) Comprehensive analytical chemistry. Passive sampling techniques in environmental monitoring. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 171–197
Baran N, Lepiller M, Mouvet C (2008) Agricultural diffuse pollution in a chalk aquifer (Trois Fontaines, France): influence of pesticide properties and hydrodynamic constraints. J Hydrol 358:56–69
Bidwell JR, Becker C, Hensley S, Stark R, Meyer MT (2010) Occurrence of organic wastewater and other contaminants in cave streams in northeastern Oklahoma and northwestern Arkansas. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:286–298
Booij K, Hofmans HE, Fischer CV, Van Weerlee EM (2003) Temperature-dependent uptake rates of nonpolar organic compounds by semipermeable membrane devices and low-density polyethylene membranes. Environ Sci Technol 37:361–366
Bopp S, Weiß H, Schirmer K (2005) Time-integrated monitoring of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in groundwater using the ceramic dosimeter passive sampling device. J Chromatogr A 1072:137–147
Choquette AF, Kroening SE (2009) Water quality and evaluation of pesticides in lakes in the Ridge Citrus Region of Central Florida. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2008–5178, pp. 1–55
Dougherty JA, Swarzenski PW, Dinicola RS, Reinhard M (2010) Occurrence of herbicides and pharmaceutical and personal care products in surface water and groundwater around Liberty Bay, Puget Sound, Washington. J Environ Qual 39:1173–1180
European Parliament and the Council of the European Union (2006) Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 December 2006 on the protection of groundwater against pollution and deterioration (2006/118/EC). Off. J. Eur. Communities: Legis., L 372
Greenwood R, Mills G, Vrana B (eds) (2007) Passive sampling techniques in environmental monitoring. Comprehensive analytical chemistry monitoring. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hernando MD, Martínez-Bueno MJ, Fernández-Alba AR (2005) Seawater quality control of microcontaminants in fish farm cage systems: application of passive sampling devices. Bol Inst Esp Oceanogr 21:37–46
Huckins JN, Petty JD, Lebo JA, Almeida FV, Booij K, Alvarez DA, Cranor WL, Clark RC, Mogensen BB (2002) Development of the permeability/performance reference compound approach for in situ calibration of semipermeable membrane devices. Environ Sci Technol 36:85–91
Huckins JN, Petty JD, Orazio CE, Lebo JA, Clark RC, Gibson VL, Gala WR, Echols KR (1999) Determination of uptake kinetics (sampling rates) by lipid-containing semipermeable membrane devices (SPMDs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water. Environ Sci Technol 33:3918–3923
ISO 5725 standard (1994) Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results—part 1: general principles and definitions 17p; part 2: basic method for determination and reproducibility of standard measurement method 42p; part 3: intermediate measures of the precision of a standard measurement method 25p
ISO/TR 13530 standard (1997) Water quality—guide to analytical quality control for water analysis
ISO/CEI 17025 (2005) General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories
Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council (ITRC) (2007) DSP-5. Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council, Diffusion/Passive Sampler Team, Washington, pp 1–121
Kingston JK, Greenwood R, Mills GA, Morrison GM, Persson LB (2000) Development of a novel passive sampling system for the time-averaged measurement of a range of organic pollutants in aquatic environments. J Environ Monit 2:487–495
Kot-Wasik A, Zabiegala B, Urbanowicz M, Dominiak E, Wasik A, Namiesnik J (2007) Advances in passive sampling in environmental studies. Anal Chim Acta 602:141–143
Macleod SL, McClure EL, Wong CS (2007) Laboratory calibration and field deployment of the polar organic chemical integrative sampler for pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater and surface water. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:2517–2529
Martin H, Patterson BM, Davis GB, Grathwohl P (2003) Field trial of contaminant groundwater monitoring: comparing time-integrating ceramic dosimeters and conventional water sampling. Environ Sci Technol 37:1360–1364
Martinez Bueno MJ, Hernando MD, Aguera A, Fernandez-Alba AR (2009) Application of passive sampling devices for screening of micro-pollutants in marine aquaculture using LC-MS/MS. Talanta 77:1518–1527
Mazzella N, Lissalde S, Moreira S, Delmas F, Mazellier P, Huckins JN (2010) Evaluation of the use of performance reference compounds in an Oasis-HLB adsorbent based passive sampler for improving water concentration estimates of polar herbicides in freshwater. Environ Sci Technol 44:1713–1719
Mazzella N, Dubernet J, Delmas F (2007) Determination of kinetic and equilibrium regimes in the operation of polar organic chemical integrative samplers: application to the passive sampling of the polar herbicides in aquatic environments. J Chromatogr A 1154:42–51
McDonald JP, Smith RM (2009) Concentration profiles in screened wells under static and pumped conditions. Ground Water Monit Remediat 29:78–86
MDBC (1997) Technical Report No. 3. Groundwater Working Group. http://www2.mdbc.gov.au/__data/page/127/GroundwaterqualityguideliesReport.pdf. Accessed 21 July 2012
Mills GA, Greenwood R, Vrana B, Allan IJ, Ocelka T (2011) Measurement of environmental pollutants using passive sampling devices—a commentary on the current state of the art. J Environ Monit 13:2979–2982
Morvan X, Mouvet C, Baran N, Gutierrez A (2006) Pesticides in the groundwater of a spring draining a sandy aquifer: temporal variability of concentrations and fluxes. J Contam Hydrol 87:176–190
NFT 90–210 Standard (2009) Water quality—protocol for the initial method performance assessment in a laboratory. 43 p
Parker LV (1994) The effects of ground water sampling devices on water quality: a literature review. Ground Water Monit Remediat 14:130–141
Petty JD, Orazio CE, Huckins JN, Gale RW, Lebo JA, Meadows JC, Echols KR, Cranor WL (2000) Considerations involved with the use of semipermeable membrane devices for monitoring environmental contaminants. J Chromatogr A 879:83–95
Powell RM, Puls RW (1993) Passive sampling of groundwater monitoring wells without purging: multilevel well chemistry and tracer disappearance. J Contam Hydrol 12:51–77
Puls RW, Barcelona MJ. (1996) Low-flow (minimal drawdown) ground-water sampling procedures. http://permanent.access.gpo.gov/lps722/lwflw2a.pdf. Accessed 10 July 2012.
Robin MJL, Gillham RW (1987) Field evaluation of well purging procedures. Ground Water Monit Remediat 7:85–93
Sara O'Brien SD, Chiswell B, Mueller JF (2009) A novel method for the in situ calibration of flow effects on a phosphate passive sampler. J Environ Monit 11:212–219
Söderström H, Lindberg RH, Fick J (2009) Strategies for monitoring the emerging polar organic contaminants in water with emphasis on integrative passive sampling. J Chromatogr A 1216:623–630
Stuer-Lauridsen F (2005) Review of passive accumulation devices for monitoring organic micropollutants in the aquatic environment. Environ Pollut 136:503–524
Sundaram B, Feitz A, Caritat P, Plazinska A, Brodie R, Coram J, Ransley T (2009) Groundwater sampling and analysis—a field guide. Geoscience Australia, Record. http://www.ga.gov.au/image_cache/GA15501.pdf. Accessed 21 Jan 2013
Vrana B, Paschke H, Paschke A, Popp P, Schuurmann G (2005a) Performance of semipermeable membrane devices for sampling of organic contaminants in groundwater. J Environ Monit 7:500–508
Vrana B, Allan IJ, Greenwood R, Mills GA, Dominiak E, Svensson K, Knutsson J, Morrison G (2005b) Passive sampling techniques for monitoring pollutants in water. Trends Anal Chem 24:845–868
XPT 90–220 Standard (2003) Water quality—protocol for the estimation of the uncertainty associated to an analysis result for physico-chemical analysis method. 74p
Yeskis D, Zavala B (2002) Ground-water sampling guidelines for superfund and RCRA project managers. http://www.epa.gov/superfund/remedytech/tsp/download/gw_sampling_guide.pdf. Accessed 21 July 2012
Zabiegala B, Kot-Wasik A, Urbanowicz M, Namiesnik J (2010) Passive sampling as a tool for obtaining reliable analytical information in environmental quality monitoring. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:273–296
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support from ONEMA (AQUAREF) and the Scientific Division of BRGM. We also thank the BRGM technicians who carried out the field sampling and analysis. We also thank Marinus KLUIJVER for the English corrections of this publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berho, C., Togola, A., Coureau, C. et al. Applicability of polar organic compound integrative samplers for monitoring pesticides in groundwater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 5220–5228 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1508-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1508-1