Abstract
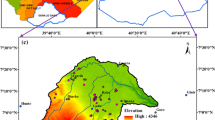
In densely populated countries like China, clean water is one of the most challenging issues of prospective politics and environmental planning. Water pollution and eutrophication by excessive input of nitrogen and phosphorous from nonpoint sources is mostly linked to soil erosion from agricultural land. In order to prevent such water pollution by diffuse matter fluxes, knowledge about the extent of soil loss and the spatial distribution of hot spots of soil erosion is essential. In remote areas such as the mountainous regions of the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze River, rainfall data are scarce. Since rainfall erosivity is one of the key factors in soil erosion modeling, e.g., expressed as R factor in the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation model, a methodology is needed to spatially determine rainfall erosivity. Our study aims at the approximation and spatial regionalization of rainfall erosivity from sparse data in the large (3,200 km2) and strongly mountainous catchment of the Xiangxi River, a first order tributary to the Yangtze River close to the Three Gorges Dam. As data on rainfall were only obtainable in daily records for one climate station in the central part of the catchment and five stations in its surrounding area, we approximated rainfall erosivity as R factors using regression analysis combined with elevation bands derived from a digital elevation model. The mean annual R factor (R a) amounts for approximately 5,222 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 a−1. With increasing altitudes, R a rises up to maximum 7,547 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 a−1 at an altitude of 3,078 m a.s.l. At the outlet of the Xiangxi catchment erosivity is at minimum with approximate R a = 1,986 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 a−1. The comparison of our results with R factors from high-resolution measurements at comparable study sites close to the Xiangxi catchment shows good consistance and allows us to calculate grid-based R a as input for a spatially high-resolution and area-specific assessment of soil erosion risk.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar E, Auer I, Brunet M, Peterson TC, Wieringa J (2003) WCDMP No. 53, WMD/TD No. 1186: Guidelines on climate metadata and homogenization. World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, pp. 51. http://www.wmo.ch/pages/prog/wcp/wcdmp/wcdmp_series/documents/WCDMP-53.pdf
Alexandersson H (1986) A homogeneity test applied to precipitation data. J Climatol 6:661–675
Alipour ZT, Mahdian MH, Pazira E, Hakimkhani S, Saeedi M (2012) The determination of the best rainfall erosivity index for Namak Lake Basin and evaluation of spatial variations. J Basic Appl Sci Res 2:484–494
Arnoldus HMJ (1977) Methodology used to determine the maximum potential average annual soil loss due to sheet and rill erosion in Morocco. FAO Soils Bulletin 34:39–51
Ateshian KH (1974) Estimation of rainfall erosion index. J Irrig Drain Eng, ASCE, IR-3, 293–307
Auerswald K (1998) Bodenerosion durch Wasser. In: Richter G (ed) Bodenerosion; Analyse und Bilanz eines Umweltproblems. Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft, Stuttgart, pp 33–42
Bagarello V, D’Asaro F (1994) Estimating single storm erosion index. T ASAE 37:785–791
Batjes NH (1996) Global assessment of land vulnerability to water erosion on a ½° by ½° grid. Land Degrad Dev 7:353–365
Bergmann A, Bi Y, Chen L, Floehr T, Henkelmann B, Holbach A, Hollert H, Hu W, Kranzioch I, Klumpp E, Küppers S, Norra S, Ottermanns R, Pfister G, Roß-Nickoll M, Schäffer A, Schleicher N, Schmidt B, Scholz-Strake B, Schramm KW, Subklew G, Tiehm A, Temoka C, Wang J, Westrich B, Wilken RD, Wolf A, Xiang X, Yuan Y (2012) The Yangtze-Hydro Project: a Chinese–German environmental program. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1341–1344
Bieger K, Hörmann G, Fohrer N (2012) Simulation of streamflow and sediment with the Soil Water Assessment Tool in a data scarce catchment in the Three Gorges Region. China J Environ Qual. doi:10.2134/jeq2011.0383
Bolinne A, Lauant A, Rosseau P, Pauwels JM, Gabriels D, Aeltermann J (1980) Provisional rain erosivity map of Belgium. In: DeBoodt M, Gabriels D (eds) Assessment of erosion. Wiley, Chichester, pp 111–120
Brown LC, Foster GR (1987) Storm erosivity using idealized intensity distributions. Trans ASEA 30:379–386
Buishand TA (1982) Some methods for testing the homogeneity of rainfall records. J Hydrol 58:11–27
Cai GG, Wang H, Curtin D, Zhu Y (2005) Evaluation of the EUROSEM model with single event data on Steeplands in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena 59:19–33
Chorley RJ (1978) The hillslope hydrological cycle. In: Kirkby MJ (ed) Hillslope hydrology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 1–42
Cornelis WM, Oltenfreiter G, Gabriels D, Hartmann R (2004) Splash-saltation of sand due to wind-driven rain: vertical deposition flux and sediment transport rate. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:532–540
Da Silva AM (2004) Rainfall erosivity map for Brazil. Catena 57:251–259
De Lima JLMP, Tavares P, Singh VP, De Lima MIP (2009) Investigating the importance of rainstorm direction on overland flow and soil loss in a laboratory circular soil-flume. Geoderma 152:9–15
Dettling W (1989) Eine mathematische Betrachtung des R-Faktors. Z Geomorphol 33:373–377
Diodato N, Bellocchi G (2009) Assessing and modelling changes in rainfall erosivity at different climate scales. Earth Surf Proc Land 34:969–980
DVWK (1990) Grundlagen der Verdunstungsermittlung und Erosivität von Niederschlägen. Deutscher Verband für Wasserwirtschaft und Kulturbau (eds) Parey, Hamburg
Elsenbeer H, Cassel DK, Tinner W (1993) A daily rainfall erosivity model for Western Amazonia. J Soil Water Conserv 48:439–444
Erpul G, Gabriels D, Norton LD (2005) Sand detachment by wind-driven raindrops. Earth Surf Proc Land 30:241–250
Ferro V, Porto P, Yu B (1999) A comparative study of rainfall erosivity estimation for southern Italy and southeastern Australia. Hydrolog Sci J 44:3–24
Foster GR, McCool DK, Renard KG, Moldenhauer WC (1981) Conversion of the universal soil loss equation to SI metric units. J Soil Water Conserv 36:355–359
Fournier F (1960) Climat et erosion; la relation entre l’erosion du sol par l’eau et les precipitations atmosperiques. Presses universitaires de Frances, Paris, p 201
Fu BJ, Zhao WW, Chen LD, Zhang QJ, Lü YH, Gulinck H, Poesen J (2005) Assessment of soil erosion at large watershed scale using RUSLE and GIS: a case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad Dev 16:73–85
Gasman PW, Reyes MR, Green CH, Arnold JG (2007) The Soil and Water Assessment Tool: historical development, applications, and future research directions. Trans ASABE 50:1211–1250
Geißler C, Kühn P, Böhnke M, Bruelheide H, Shi X, Scholten T (2012) Measuring splash erosion under vegetation using sand-filled splash cups. Catena 91:85–93
Ghahramani A, Yoshiharu I, Mudd SM (2011) Field experiments constraining the probability distribution of particle travel distances during natural rainstorms on different slope gradients. Earth Surf Proc Land 37:473–485
Goovaerts P (1999) Using elevation to aid the geostatistical mapping of rainfall erosivity. Catena 34:227–242
Hao F, Chang Y, Ning D (2004) Assessment of China’s economic loss resulting from the degradation of agricultural land in the end of 20th century. J Environ Sci 16:199–203
He L, King L, Jiang T (2003) On the land use in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. J Geogr Sci 13:416–422
Hudson N (1995) Soil conservation, 3rd edn. Batsford, London, p 210
Jarvis A, Reuter HI, Nelson A, Guevara E (2008) Hole-filled seamless SRTM data V4, International Centre for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT). http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org
Jones A, Panagos P, Barcelo S, Bouraoui F, Bosco C, Dewitte O, Gardi C, Erhard M, Hervás J, Hiederer R, Jeffery S, Lükewille A, Marmo L, Montanarella L, Olazábal C, Petersen JE, Penizek V, Strassburger T, Tóth G, Van Den Eeckhaut M, Van Liedekerke M, Verheijen F, Viestova E, Yigini Y (2012) The state of soil in Europe—a contribution of the JRC to the EEA Environment State and Outlook Report – SOER 2010. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union, 76 pp, doi:10.2788/77361 (online)
Kavian A, Fathollah Nejad Y, Habibnejad M, Soleimani K (2011) Modeling seasonal rainfall erosivity on a regional scale: a case study from Northeastern Iran. Int J Environ Res 5:939–950
Lal R (1976)Soil erosion problems on an alfisol in western Nigeria and their control. Communications and Information Office, IITA Monograph no. 1, Ibadan, Nigeria, pp. 208, available from http://library.wur.nl/isric
Lal R (1990) Soil erosion in the Tropics: principles and management. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 580
Liu Y, Luo Z (2005) A study on estimation of the amount of soil erosion in small watershed based on GIS: a case study in the Three Gorge Area of China. IGARSS IEEE 3:1859–1863
Lo A, El-Swaify SA, Dangler EW, Shinshirl L (1985) Effectiveness of EI30 as an erosivity index in Hawaii. In: El-Swaify SA, Moldenhauer WC, Lo A (eds) Soil erosion and conservation. Soil Conserv. Soc. Am, Ankeny, pp 384–392
Lu X, Higgitt D (2000) Estimating erosion rates on sloping agricultural land in the Yangtze Three Gorges, China, from caesium- 137 measurements. Catena 39:33–51
Mannaerts CM, Gabriels D (2000) Rainfall erosivity in Cape Verde. Soil Till Res 55:207–212
Men M, Yu Z, Xu H (2008) Study on the spatial pattern of rainfall erosivity based on geostatistics in Hebei Province. China Front Agric China 2:281–289
Meng QH, Fu BJ, Yang LZ (2001) Effects on land use on soil erosion and nutrient loss in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. China Soil Use Manage 17:288–291
Meusberger K, Steel A, Panagos P, Montanarella L, Alewell C (2012) Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall erosivity factor for Switzerland. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16:167–177
Mikhailova EA, Bryant RB, Schwager SJ, Smith SD (1997) Predicting rainfall erosivity in Honduras. Soil Sci Soc Am J 61:273–279
Mölg T, Chiang JCH, Gohm A, Cullen NJ (2009) Temporal precipitation variability versus altitude on a tropical high mountain: Observations and mesoscale atmospheric modelling. Q J R Meteorol Soc 135:1439–1455
Montgomery DR (2007) Dirt: The erosion of civilizations. University of California Press, London, p 285
Morgan RPC, Nearing MA (eds) (2011) Handbook of erosion modelling, 1st edn. Blackwell, Chichester, p. 416
Nearing MA, Jetten V, Baffaut C, Cerdan O, Couturier A, Hernandez M, Le Bissonnais Y, Nichols MH, Nunes JP, Renschler CS, Souchère V, Van Oost K (2005) Modeling response of soil erosion and runoff to changes in precipitation and cover. Catena 61:131–154
Oduro-Afriyie K (1996) Rainfall erosivity map for Ghana. Geoderma 74:161–166
Onchev NG (1985) Universal index for calculating rainfall erosivity. In: El-Swaify SA, Moldenhauer WC, Lo A (eds) Soil erosion and conservation. Soil Conserv. Soc. Am, Ankeny, pp 424–431
Pimentel D (2006) Soil erosion: a food and environmental threat. Environ Dev Sustain 8:119–137
Renard KG, Freimund JR (1994) Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the revised USLE. J Hydrol 157:287–306
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder, DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). USDA Agriculture Handbook No.703, pp. 384
Richardson CW, Foster GR, Wright DA (1983) Estimation of erosion index from daily rainfall amount. T ASAE 26:153–156
Rogler H, Schwertmann U (1981) Erosivität der Niederschläge und Isoerodentkarte Bayerns. Z. Kult.tech. Flurbereinig 22:99–112
Roose EJ (1976) Use of the universal soil loss equation to predict erosion in West Africa. Soil Conserv. Soc. Am, Ankeny, Iowa, pp 60–74
Salako FK (1995) Rainfall temporal variability and erosivity in subhumid and humid zones of southern Nigeria. Land Degrad Dev 17:541–555
de Santos Loureiro N, de Azevedo Coutinho M (2001) A new procedure to estimate the RUSLE EI30 index based on monthly rainfall data and applied to the Algarve region. Portugal J Hydrol 250:12–18
Scholten T, Geißler C, Goc J, Kühn P, Wiegand C (2011) A new splash cup to measure the kinetic energy of rainfall. J Plant Nutr Soil Sc 174:596–601
Schönbrodt S, Saumer P, Behrens T, Seeber C, Scholten T (2010) Assessing the USLE crop and management factor C for soil erosion modeling in a large mountainous watershed in Central China. JES 21:835–845
Seeber C, Hartmann H, Xiang W, King L (2010) Land use change and causes in the Xiangxi Catchment, Three Gorges Area, derived from multispectral data. JES 21:846–855
Seuffert O (1998) Zukunftsperspektiven der Bodenerosionsforschung. In: Richter G (ed) Bodenerosion; Analyse und Bilanz eines Umweltproblems. Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft, Stuttgart, pp 152–168
Shamshad A, Azhari MN, Isa MH, Wan Hussin WMA, Parida BP (2008) Development of an appropriate procedure for estimation of RUSLE EI30 index and preparation of erosivity maps for Pulau Penang in Peninsular Malaysia. Catena 72:423–432
Shi ZH, Cai CF, Ding SW, Wang TW, Chow TL (2004) Soil conservation planning at the small watershed level using RUSLE with GIS. A case study in the Three Gorges Area of China. Catena 55:33–48
Shi ZH, Ai L, Fang NF, Zhu HD (2012) Modeling the impacts of integrated small watershed management on soil erosion and sediment delivery: a case study in the Three Gorges Area. China J Hydrol 438–439:156–167
Smithen AA, Schulze RE (1982) The spatial distribution in Southern Africa of rainfall erosivity for use in the universal soil loss equation. Water SA 8:74–78
Stocking, M.A., Elwell, H.A., 1976. Rainfall erosivity over Rhodesia. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr., New Series 1, 231–245
Subklew G, Ulrich J, Fürst L, Höltkemeier A (2010) Environmental Impacts of the Yangtze Three Gorges Project—an overview of the Chinese–German Research Cooperation. JES 21:817–823
Sukhanovski YP, Ollesch G, Khan KY, Meißner R (2002) A new index for rainfall erosivity on a physical basis. J Plant Nutr Soil Sc 165:51–57
Sun G, McNulty SG, Moore J, Bunch C, Ni J (2002) Potential impacts of climate change on rainfall erosivity and water availability in China in the next 100 years. Proceedings of the 12th Intern. Soil. Conserv. Conference, Beijing, China. http://efetac4.sref.info
Toy TJ, Foster GR (1998) Guidelines for the use of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) version 1.06 on mined land, construction sites, reclaimed land. Office of Surface Mining, Reclamation, and Enforcement, p. 149. http://www.greenfix.com/Channel%20Web/pdfs/RUSLE%20Guidelines.pdf
Van der Knijff JM, Jones RJA, Montanarella L (1999) Soil erosion risk management in Italy. European Commission, European Soil Bureau, p. 52
Wang G, Gertner G, Singh V, Shinkareva S, Parysow P, Anderson A (2002) Spatial and temporal prediction and uncertainty of soil loss using revised universal soil loss equation: a case study in rainfall and runoff erosivity for soil loss. Ecol Model 153:143–155
Weilguni V (2006) Regionalisierung des Niederschlags. Wiener Mitteilungen Band 197, Methoden der hydrologischen Regionalisierung, 71–92
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1958) Rainfall energy and its relationship to soil loss. Trans Am Geophys Union 39:285–291
Wischmeier WH (1959) A rainfall erosion index for a universal soil-loss equation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 23:246–249
Wischmeier WH (1962) Rainfall erosion potential. J Agr Eng Res 43:212–225
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1965) Predicting rainfall-erosion losses from cropland east of the Rocky Mountains - Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation. Agriculture Handbook No. 282, USDA, Washington, p. 47. http://naldc.nal.usda.gov/download/CAT87208342/PDF
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses—a guide to conservation planning. Agriculture Handbook No. 537, USDA, Washington, p. 58, available from http://naldc.nal.usda.gov/download/CAT79706928/PDF
Wu YJ, King L, Jiang T (2006) Climatic vertical graduation and its use in the Xiangxi River Catchment. In: Cai Q, Fohrer N (eds) Sino-German Workshop on Environmental Impacts of Large-scale Hydraulic Engineer. Programme and Abstracts, March 2006, Xingshan, pp 104–108
Wu C, Zhou Z, Xiao W, Wang P, Teng M, Huang Z (2011) Estimation of soil erosion in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of China using RUSLE, remote sensing and GIS. J. Food. Agri Environ 9:728–734
Xie Y, Liu B, Nearing MA (2002) Practical tresholds for separating erosive and non-erosive storms. Trans ASAE 45:1843–1847
Xu Y, Peng J, Shao X (2009) Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: a case study of the Maotiao River watershed, Guizhou Province. China Environ Geol 56:1643–1652
Yu B, Rosewell CJ (1998) RECS: A program to calculate the R-factor for the USLE/RUSLE using BOM/ AWS Pluviograph data. ENS Working Paper No. 8/98, pp. 15
Zhang WB, Fu JS (2003) Rainfall erosivity estimation under different rainfall amount. Resources Science 25:35–41 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhou P (2008) Landscape-scale erosion modeling and ecological restoration for a mountainous watershed in Sichuan, China. Univ Helsinki Tropic Forest Rep 35:95
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted within the framework of the Sino-German joint research project YANGTZE GEO. The funding by the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF, grant no. 03G 0669) is highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Michael Matthies
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schönbrodt-Stitt, S., Bosch, A., Behrens, T. et al. Approximation and spatial regionalization of rainfall erosivity based on sparse data in a mountainous catchment of the Yangtze River in Central China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 6917–6933 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1441-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1441-8