Abstract
Purpose
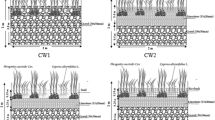
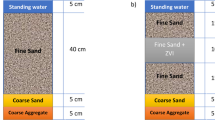
The performances of filter systems that use earthworms and plants, combined with earthworm eco-filter (EE) systems in treating synthetic domestic sewage (SDS) with different C/N ratios, were investigated for a 9-month period.
Methods
The effects of the combination of filters, earthworms, plants, as well as the combination of earthworms and plants on SDS nutrient removal efficiency were separately investigated to select the optimum system for treating SDS. The results of the current study could be used to determine how treatment performance responds to different C/N ratios and to explain and predict the performance of an operating EE system.
Results
EE systems with earthworms and plants (EP groups) consistently performed better than the other types of systems (CK, E, and P; that is, without earthworms and without plants, with earthworms and without plants, and without earthworms and with plants, respectively) under all C/N ratios. The highest removal efficiencies of chemical oxygen demand, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and total organic carbon were achieved under C/N ratios of 6:1, 6:1, 6:1, and 9:1, respectively. The optimum nutrient removal efficiency was achieved at C/N = 6, and the contribution order for nutrient removal was EP > P > E > CK.
Conclusions
Influent C/N ratios, the time of year, and the synergetic effects of earthworm behavior and microorganisms significantly affected nutrient removal efficiencies. Considering the removal of all nutrients, EE systems with plants and earthworms achieved optimum removal effects in July when the influent C/N ratio was controlled at 6. Appropriate control of carbon and nitrogen source concentrations permitted the achievement of optimal nutrient removal effects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiarawatchai N, Nuengjamnong C (2009) The use of earthworms in lab-scale constructed wetlands to treat swine wastewater. Thai J Vet Med 39:157–162
de-Bashan LE, Bashan Y (2004) Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997–2003). Water Res 38:4222–4246
Fang CX, Guo FH, Luo XZ, Chen JY, Zheng Z (2011) Performance of a three-stage tower earthworm ecofilter for simultaneous removal of carbon and nutrients from domestic wastewater. Fresen Environ Bull 20:235–243
Fang CX, Zheng Z, Luo XZ, Guo FH (2010) Effect of hydraulic load on domestic wastewater treatment and removal mechanism of phosphorus in earthworm ecofilter. Fresen Environ Bull 19:1099–1108
Ghani A, Dexter M, Perrott KW (2003) Hot-water extractable carbon in soils: a sensitive measurement for determining impacts of fertilization, grazing and cultivation. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1231–1243
Henze CM, Harremoes P (1978) Nitrification and denitrification in wastewater treatment. In: Mitchell R (ed) Water pollution microbiology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 391–414
Hughes RJ, Nair J, Ho G (2009) The risk of sodium toxicity from bed accumulation to key species in the vermifiltration wastewater treatment process. Bioresour Technol 100:3815–3819
Li YS, Xiao YQ, Qiu JP, Dai YQ, Robin P (2009) Continuous village sewage treatment by vermifiltration and activated sludge process. Water Sci Technol 60:3001–3010
Loehr TC, Lee YC, Liang JB, Tan D (1988) Stabilization of liquid municipal sludge using earthworms. In: Edwards CA, Neuhauser EF (eds) Earthworms in waste and environmental management, 1st edn. SPB, Academic, The Hague, pp 95–110
Luth RP, Germain P, Lecomte M, Landrain B, Li YS, Cluzeau D (2011) Earthworm effects on gaseous emissions during vermifiltration of pig fresh slurry. Bioresour Technol 102:3679–3686
Munch EV, Lant P, Keller J (1996) Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in bench-scale sequencing batch reactors. Water Res 30:277–284
OECD (1996) Guidelines for testing of chemicals simulation test—aerobic sewage treatment. Technical report. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Paris
Pant HK, Reddy KR, Lemon E (2001) Phosphorus retention capacity of root bed media of sub-surface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 17:345–355
Renman A, Renman G, Gustafsson JP, Hylander L (2009) Metal removal by bed filter materials used in domestic wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater 166:734–739
Sen B, Chandra TS (2009) Do earthworms affect dynamics of functional response and genetic structure of microbial community in a lab-scale composting system. Bioresour Technol 100:804–811
Sinha RK, Bharambe B, Chaudhari U (2008) Sewage treatment by vermifiltration with synchronous treatment of sludge by earthworms: a low-cost sustainable technology over conventional systems with potential for decentralization. Environmentalist 28:409–420
SPSS (2003) Analytical software. SPSS, Chicago
Taylor M, Clarke WP, Greenfield PF (2003) The treatment of domestic wastewater using small-scale vermicompost filter beds. Ecol Eng 21:197–203
Tomar P, Suthar S (2011) Urban wastewater treatment using vermi-biofiltration system. Desalination 282:95–103
Wang LM, Guo FH, Zheng Z, Luo XZ, Zhang JB (2011a) Enhancement of rural domestic sewage treatment performance and assessment of microbial community diversity and structure using tower vermifiltration. Bioresour Technol 102:9462–9470
Wang LM, Zheng Z, Luo XZ, Zhang JB (2011b) Performance and mechanisms of a microbial-earthworm ecofilter for removing organic matter and nitrogen from synthetic domestic wastewater. J Hazard Mater 195:245–253
Wang S, Yang J, Lou SJ, Yang J (2010) Wastewater treatment performance of a vermifilter enhancement by a converter slag–coal cinder filter. Ecol Eng 36:489–494
Wang XJ, Zhang W, Huang YN, Li SJ (2004) Modeling and simulation of point–non-point source effluent trading in Taihu Lake area: perspective of non-point sources control in China. Sci Total Environ 325:39–50
Wen B, Liu Y, Hu XY, Shan XQ (2006) Effect of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) on the fractionation and bioavailability of rare earth elements in nine Chinese soils. Chemosphere 63:1179–1186
Xia SQ, Li JY, Wang RC (2008) Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure dynamics response to carbon nitrogen ratio in a compact suspended carrier biofilm reactor. Ecol Eng 32:256–262
Xing MY, Li XW, Yang J (2010) Treatment performance of small-scale vermifilter for domestic wastewater and its relationship to earthworm growth, reproduction and enzymatic activity. Afr J Biotechnol 9:7513–7520
Ye FX, Li Y (2009) Enhancement of nitrogen removal in towery hybrid constructed wetland to treat domestic wastewater for small rural communities. Ecol Eng 35:1043–1050
Zhao LM, Wang YY, Yang J, Xing MY, Li XW, Yi DH, Deng DH (2010) Earthworm–microorganism interactions: a strategy to stabilize domestic wastewater sludge. Water Res 44:2572–2582
Zhao YJ, Zhang H, Chao X, Nie E, Li JH, He J, Zheng Z (2011) Efficiency of two-stage combinations of subsurface vertical down-flow and up-flow constructed wetland systems for treating variation in influent C/N ratios of domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 37:1546–1554
Zou JL, Dai Y, Sun TH, Li YH, Li GB, Li QY (2009) Effect of amended soil and hydraulic load on enhanced biological nitrogen removal in lab-scale SWIS. J Hazard Mater 163:816–822
Acknowledgments
We thank colleagues and students from Fudan University for maintaining the EE systems during the study period. We are very grateful to Naomi Cappuccino, Department of Biology, Carleton University, Canada, for comments on the draft and grammar of the manuscript. This study was financially supported by the National Water Special Project of China (no. 2008ZX07101-001-04) and National Science Funds of China (grant nos. 51102136/E021301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, YJ., Yan, C., Li, YL. et al. Effect of C/N ratios on the performance of earthworm eco-filter for treatment of synthetics domestic sewage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19, 4049–4059 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0871-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0871-7