Abstract
Purpose and aim
Removal of an anionic azo dye Brilliant Yellow has been carried out from its aqueous solutions by using hen feathers as potential adsorbent.
Materials and methods
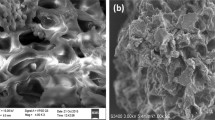
Hen feathers procured from local poultry were cut, washed, and activated. Detailed chemical and physical analysis of hen feathers and its characterization through scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and infrared measurements have been made. Procured dye has been adsorbed over under batch measurements and adsorption process is monitored using UV spectrophotometer.
Results
Optimum parameters for the adsorption of Brilliant Yellow over hen feathers have been determined by studying the effect of pH, temperature, concentration of dye, and amount of adsorbent. On the basis of Langmuir adsorption, isotherms feasibility of the ongoing adsorption has been ascertained and thermodynamic parameters have been calculated. Attempts have also been made to verify Freundlich, Tempkin, and Dubinin–Radushkevich adsorption isotherm models. It is found that during adsorption, uniform distribution of binding energy takes place due to interaction of the dye molecules and the ongoing adsorption process is chemisorptions. The kinetic measurements indicate dominance of pseudo-second-order process during the adsorption. The mathematical treatment on the kinetic data reveals the rate-determining step to be governed through particle diffusion at 8 × 10−5 M and involvement of film diffusion mechanism at higher concentration at temperatures at all the temperatures.
Conclusions
The developed process is highly efficient and it can be firmly concluded that hen feather exhibits excellent adsorption capacity towards hazardous azo dye Brilliant Yellow.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acemioglu B (2004) Removal of Fe(II) ions from aqueous solution by calabrian pine bark wastes. Bioresour Technol 93:99–102
Aitcheson SJ, Arnett J, Murray KR, Zhang J (2000) Removal of aquaculture therapeutants by carbon adsorption 1. Equilibrium adsorption behaviour of single components. Aquaculture 183:269–284
Alaerts GJ, Jitjaturunt V, Kelderman P (1989) Use of coconut shell-based activated carbon for chromium (VI) removal. Water Sci Technol 21:1701–1704
Ali I, Gupta VK (2006) Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat Protoc 1(6):2661–2667
Allen SJ, McKay G, Khader KYH (1989) Intraparticle diffusion of a basic dye during adsorption onto sphagnum peat. Environ Pollut 56:39–50
Al-Qodah Z (2000) Adsorption of dyes using shale oil ash. Water Res 34:4295–4303
Arenas LT, Gay DSF, Moro CC, Dias SLP, Azambuja DS, Costa TMH, Benvenutti EV, Gushikem Y (2008) Brilliant Yellow dye immobilized on silica and silica/titania based hybrid xerogels containing bridged positively charged 1,4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane: preparation, characterization and electrochemical properties study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 112:273–283
Basar CA (2006) Applicability of the various adsorption models of three dyes adsorption on to activated carbon prepared waste apricot. J Hazard Mater 135:232–241
Bingol D, Tekin N, Alkan M (2010) Brilliant Yellow dye adsorption onto sepiolite using a full factorial design. Appl Clay Sci 50:315–321
Boyd GE, Adamson AW, Meyers LS (1947) The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solution by organic zeolites II. Kinetics. J Am Chem Soc 69:2836–2848
Brown MA, DeVitro SC (1993) Predicting azo dye toxicity. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 23(3):249–324
Chang JS, Chou C, Lin YC, Lin PJ, Ho JY, Hu TL (2001) Kinetic characteristics of azo-dye decolorization by Pseudomonas luteola. Water Res 35:2841–2850
Chern JM, Wu CY (2001) Desorption of dye from activated carbon beds: effects of temperature, pH, and alcohol. Water Res 35:4159–4165
Crank J (1956) The mathematics of diffusion. Clarenden Press, Oxford
Egawa Y, Hayashida R, Anzai J (2006) Multilayered assemblies composed of Brilliant Yellow and poly(allylamine) for an optical pH sensor. Anal Sci 22(8):1117–1119
Eiras C, Zucolotto V, Oliveira ON, Goncalves D (2003) Electrochemical synthesis of polypyrrole-azo dyes composite films. Synth Met 161:135–136
El-Geundi MS (1991) Color removal from textile effluents by adsorption techniques. Water Res 25:271–273
Gay SF, Fernandes THM, Amavisca CV, Cordoso NF, Benvenutti EV, Costa TMH, Lima EC (2010) Silica grafted with a silsesquioxane containing the positively charged 1,4-diazoniabicyclo [2.2.2] Octane group used as adsorbent for anionic dye removal. Desalination 258:128–135
Gupta VK, Ali I (1998) Removal of lead from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste material. Sep Sci Technol 33(9):1331–1343
Gupta VK, Ali I (2001) Removal of DDD and DDE from wastewater using bagasse fly ash, a sugar industry waste. Water Res 35:33–40
Gupta VK, Ali I (2003) Adsorbents for water treatment: development of low cost alternatives to carbon. In: Somasundaram P (ed) Encyclopedia of surface and colloid science. Marcel Dekker, pp 1–34
Gupta VK, Ali I (2008) Removal of endosulfan and methoxychlor from water on carbon slurry. Environ Sci Technol 42(3):766–770
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008a) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium(II) biosorption by nonliving algal biomass Oedogonium sp. from aqueous phase. J Hazard Mater 153(1–2):759–766
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008b) Sorption and desorption studies of chromium(VI) from nonviable cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum biomass. J Hazard Mater 154(1–3):347–354
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008c) Biosorption of lead(II) from aqueous solutions by non-living algal biomass Oedogonium sp. and Nostoc sp.—a comparative study. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 64(2):170–178
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2009) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by raw and acid-treated green alga Oedogonium hatei from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 163(1):396–402
Gupta VK, Shrivastava SK, Mohan D (1997a) Equilibrium uptake, sorption dynamics, process optimization, and column operations for the removal and recovery of malachite green from wastewater using activated carbon and activated slag. Ind Eng Chem Res 36:2207–2218
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Dwivedi MK, Mohan D (1997b) Process development for the removal of zinc and cadmium from wastewater using slag—a blast furnace waste material. Sep Sci Technol 32(17):2883–2912
Gupta VK, Mangla R, Agarwal S (2002a) Pb(II) selective potentiometric sensor based on 4-tert-butylcalix[4]arene in PVC matrix. Electroanalysis 14(15–16):1127–1132
Gupta VK, Jain CK, Ali I, Chandra S, Agarwal S (2002b) Removal of lindane and malathion from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste. Water Res 36:2483–2490
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Gajbe V, Mittal J (2006) Removal and recovery of the hazardous azo dye acid orange 7 through adsorption over waste materials: Bottom ash and de-oiled soya. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(4):1446–1453
Gupta VK, Jain R, Mittal A, Mathur M, Sikarwar S (2007a) Photochemical degradation of the hazardous dye Safranin-T using TiO2 catalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci 309(2):464–469
Gupta VK, Jain R, Mittal A, Mathur M, Sikarwar S (2007b) Adsorption of Safranin-T from wastewater using waste materials—activated carbon and activated rice husks. J Colloid Interface Sci 303(1):80–86
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saini VK (2007c) Adsorption studies on the removal of Vertigo Blue 49 and Orange DNA13 from aqueous solutions using carbon slurry developed from a waste material. J Colloid Interface Sci 315(1):87–93
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007d) Removal of Reactofix golden yellow 3 RFN from aqueous solution using wheat husk—an agricultural waste. J Hazard Mater 142(1–2):443–448
Gupta VK, Khayat M, Al SAK, Pal MK (2009) Nano level detection of Cd(II) using poly(vinyl chloride) based membranes of Schiff bases. Anal Chim Acta 634(1):36–43
Ho YS, Mckay G (1998) A two stage batch sorption optimized design for dye removal to minimize contact time. Trans Inst Chem Eng 76:313–318
Jain AK, Gupta VK, Singh LP (1995a) Neutral carrier and organic resin based membranes as sensors for uranyl ions. Anal Proc Incl Anal Commun 32(7):263–266
Jain AK, Gupta VK, Sahoo BB, Singh LP (1995b) Copper(II)-selective electrodes based on macrocyclic compounds. Anal Proc Incl Anal Commun 32(3):99–101
Jain AK, Gupta VK, Khurana U, Singh LP (1997) A new membrane sensor for UO + 22 Ions Based on 2-hydroxyacetophenoneoxime-thiourea-trioxane resin. Electroanalysis 9(11):857–860
Kavitha D, Namasivayam C (2007) Recycling coir pith, an agricultural solid waste, for the removal of Procion Orange from wastewater. Dyes Pigments 74:237–248
Kislislioglu A, Bilgin B (2003) Thermodynamic and kinetic investigations of uranium adsorption on amberlite IR-118 H resin. Appl Radiat Isot 58:155–160
Kuleyin A (2007) Removal of phenol and 4-chlorophenol by surfactant-modified natural zeolite. J Hazard Mater 144:307–315
Lambert SD, Graham NJD (1989) Adsorption methods for treating organically coloured upland waters. Environ Technol Lett 10:785–798
Mascini M (1995) Enzyme-based optical-fibre biosensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem B29:121–125
Memon SQ, Memon N, Solangi AR, Memon J (2008) Sawdust: a green and economical sorbent for thallium removal. Chem Eng J 140:235–240
Mittal A, Gupta VK (2010) Adsorptive removal and recovery of hazardous azo dye eriochrome black T. Toxicol Environ Chem 92(10):1813–1823
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Gupta VK (2009a) Adsorptive removal of hazardous anionic dye “Congo red” from wastewater using waste materials and recovery by desorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 340(1):16–26
Mittal A, Kaur D, Malviya A, Mittal J, Gupta VK (2009b) Adsorption studies on the removal of colouring agent phenol red from wastewater using waste materials as adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 337(2):345–354
Mittal A, Kaur D, Mittal J (2009c) Batch and bulk removal of a triarymethane dye—fast green FCF, from wastewater by adsorption over waste materials. J Hazard Mater 163:568–577
Mittal A, Jain R, Mittal J, Shrivastava M (2010a) Adsorptive removal of hazardous dye Quinoline Yellow from waste water using coconut-husk as potential adsorbent. Fresenius Environ Bull 19(6):1–9
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Gupta VK (2010b) Removal and recovery of Chrysoidine Y from aqueous solutions by waste materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 344:497–507
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Kaur D, Gupta VK (2010c) Adsorption of hazardous dye crystal violet from wastewater by waste materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 343:463–473
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Kaur D, Gupta VK (2010d) Decoloration treatment of a hazardous triaryl methane dye, light green SF (yellowish) by waste material adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 342(2):518–527
Reddy N, Yang Y (2007) Structure and properties of chicken feather barbs as natural protein fibers. J Polym Environ 15:81–87
Reichenberg D (1953) Properties of ion exchange resins in relation to their structure. III. Kinetics of exchange. J Am Chem Soc 75:589–597
Sari A, Tuzen M (2008) Biosorption of cadmium (II) from aqueous solution by red algae (Ceramium Virgatum): equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Hazard Mater 157:448–454
Shen ZM, Wu D, Yang J, Yuan T, Wang WH, Jia JP (2006) Methods to improve electrochemical treatment effect of dye wastewater. J Hazard Mater 131:90–97
Shrivastava VC, Mall ID, Mishra IM (2006) Characterization of mesoporous rice husk ash (RHA) and adsorption kinetics of metal ions from aqueous solutions onto RHA. J Hazard Mater 134:257–267
Slejko FL (1985) Adsorption technology: a step-by-step approach to process evaluation and application. Marcel Dekker, New York
Srivastava SK, Gupta VK, Dwivedi MK, Jain S (1995) Caesium PVC-crown (dibenzo-24-crown-8) based membrane sensor. Anal Proc Incl Anal Commun 32(1):21–23
Suffet IH, McGuire MJ (1980) Activated carbon adsorption of organics from aqueous phase. Vols. 1 and 2. An Arbor Science, Michigan
Tan NCG, Prenafeta-Boldu FX, Opsteeg JL, Lettinga G, Field JA (1999) Biodegradation of azo dyes in cocultures of anaerobic granular sludge with aerobic aromatic amine degrading enrichment cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:865–871
Taras M (1948) Photometric determination of magnesium in water with Brilliant Yellow. Anal Chem 20:1156–1158
Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (1985) 5th ed. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinhein
Weber WJ (1972) Physicochemical processes for water quality control. Wiley, New York
Won SW, Wu G, Ma H, Liu Q, Yan Y, Cui L, Yu YS (2006) Performance and mechanism in adsorption of Reactive Red 4 by solid waste from coke wastewater treatment plant. Waste Manag Resour 24:299–300
Acknowledgment
One of the authors, VT, thanks MANIT for providing financial assistance to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vinod Kumar Gupta
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittal, A., Thakur, V. & Gajbe, V. Evaluation of adsorption characteristics of an anionic azo dye Brilliant Yellow onto hen feathers in aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19, 2438–2447 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0756-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0756-9