Abstract
Purposes
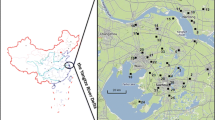
Very few data for polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) were available in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), one of the most developed and urbanized region in China. In this study, Chongming Island, located at the estuary of the Yangtze River, was selected as background area to investigate the occurrence, sources, and inventory of PBDEs.
Methods
Forty-two PBDE congeners were determined in surface soils from farmland, woodland, grassland, tideland, and road collected in Chongming Island.
Results
The mean concentrations of Σ26PBDE (not including BDE-209) and BDE-209 in soils were 0.76 and 12 ng/g dry weight, respectively. BDE-209 contributed more than 90% of the total of 27 frequently detected BDE congeners, followed by BDE-99 and BDE-47. Weak correlations were found between total organic carbon content and PBDE congeners concentrations in surface soils. PBDE levels varied with land use. Farmland and woodland soils contained higher Σ26PBDE concentrations. BDE-209 levels were the highest in road soils. The mass inventories of PBDEs in soils of Chongming Island were estimated at 3.1 and 310 kg for Σ26PBDEs and BDE-209, respectively.
Conclusions
The PBDE levels in Chongming Island were similar to those in European background soils, suggesting minimum influence of pollutants from the YRD via air, and wastewater inputs or few PBDE products were used herein. From the standpoint of eco-inland, more studies are needed to explore the reasons of PBDE difference by land use and to assess people intake PBDEs via agriculture products consumption in this region.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai ZW, Jiang GB (2006) Determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soil from e-waste recycling site. Talanta 70:88–90
Chen SJ, Gao XJ, Mai BX, Chen ZM, Luo XJ, Sheng GY, Fu JM, Zeng EY (2006a) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Delta: levels, distribution and potential hydrodynamic influence. Environ Pollut 144:951–957
Chen SJ, Luo XJ, Mai BX, Sheng GY, Fu JM, Zeng EY (2006b) Distribution and mass inventories of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the northern South China Sea. Environ Sci Technol 40:709–714
Chen LG, Huang YM, Peng XC, Xu ZC, Zhang SK, Ren MZ, Ye ZX, Wang XH (2009) PBDEs in sediments of the Beijiang River, China: levels, distribution, and influence of total organic carbon. Chemosphere 76:226–231
de Wit CA, Alaee M, Muir DCG (2006) Levels and trends of brominated flame retardants in the Arctic. Chemosphere 64:209–233
Eljarrat E, Marsh G, Labandeira A, Barceló D (2008) Effect of sewage sludges contaminated with polybrominated diphenylethers on agricultural soils. Chemosphere 71:1079–1086
Gerecke AC, Hartmann PC, Heeb NV, Kohler HPE, Giger W, Schmid P, Zennegg M, Kohler M (2005) Anaerobic degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether. Environ Sci Technol 39:1078–1083
Gouin T, Harner T (2003) Modelling the environmental fate of the polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Environ Int 29:717–724
Guan YF, Wang JZ, Ni HG, Luo XJ, Mai BX, Zeng EY (2007) Riverine inputs of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the Pearl River Delta (China) to the coastal ocean. Environ Sci Technol 41:6007–6013
Hale RC, La Guardia MJ, Harvey E, Mainor TM (2002) Potential role of fire retardant-treated polyurethane foam as a source of brominated diphenyl ethers to the US environment. Chemosphere 46:729–735
Hale RC, Kim SL, Harvey E, La Guardia MJ, Mainor TM, Bush EO, Jacobs EM (2008) Antarctic research bases: local sources of polybrominated diphenlyl ether (PBDE) flame retardants. Environ Sci Technol 42:1452–1457
Harrad S, Hunter S (2006) Concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in air and soil on a rural–urban transect across a major UK conurbation. Environ Sci Technol 40:4548–4553
Hassanin A, Breivik K, Meijer SN, Steinnes E, Thomas GO, Jones KC (2004) PBDEs in European background soils: levels and factors controlling their distribution. Environ Sci Technol 38:738–745
Hites RA (2004) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and in people: a meta-analysis of concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 38:945–956
Jin J, Wang Y, Liu W, Tang X (2008) Level and distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soil from Laizhou Bay. Acta Sci Circum 28:1463–1468 (in Chinese)
Kajiwara N, Noma Y, Takigami H (2008) Photolysis studies of technical decabromodiphenyl ether (DecaBDE) and ethane (DeBDethane) in plastics under natural sunlight. Environ Sci Technol 42:4404–4409
La Guardia MJ, Hale RC, Harvey E (2006) Detailed polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) congener composition of the widely used penta-, octa-, and deca-PBDE technical flame-retardant mixtures. Environ Sci Technol 40:6247–6254
Law RJ, Allchin CR, de Boer J, Covaci A, Herzke D, Lepom P, Morris S, Tronczynski J, de Wit CA (2006) Levels and trends of brominated flame retardants in the European environment. Chemosphere 64:187–208
Leung AOW, Luksemburg WJ, Wong AS, Wong MH (2007) Spatial distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in soil and combusted residue at Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling site in southeast China. Environ Sci Technol 41:2730–2737
Li K, Fu S, Yang Z, Xu X (2008) Composition, distribution and characterization of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the soil in Taiyuan, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:588–593
Lohmann R, Northcott GL, Jones KC (2000) Assessing the contribution of diffuse domestic burning as a source of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, and PAHs to the UK atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol 34:2892–2899
Luo Y, Luo XJ, Lin Z, Chen SJ, Liu J, Mai BX, Yang ZY (2009) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in road and farmland soils from an e-waste recycling region in southern China: concentrations, source profiles, and potential dispersion and deposition. Sci Total Environ 407:1105–1113
Mai BX, Chen SJ, Luo XJ, Chen LG, Yang QS, Sheng GY, Peng PG, Fu JM, Zeng EY (2005) Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Pearl River Delta and adjacent South China Sea. Environ Sci Technol 39:3521–3527
Matscheko N, Tysklind M, de Wit C, Bergek S, Andersson R, Sellström U (2002) Application of sewage sludge to arable land-soil concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls, and their accumulation in earthworms. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:2515–2525
Mattina MI, Eitzer BD, Iannucci-Berger W, Lee WY, White JC (2004) Plant uptake and translocation of highly weathered, soil-bound technical chlordane residues: data from field and rhizotron studies. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2756–2762
Meijer SN, Ockenden WA, Sweetman A, Breivik K, Grimalt JO, Jones KC (2003) Global distribution and budget of PCBs and HCB in background surface soils: implications or sources and environmental processes. Environ Sci Technol 37:667–672
Meng XZ, Zeng EY, Yu LP, Mai BX, Luo XJ, Ran Y (2007) Persistent halogenated hydrocarbons in consumer fish of China: regional and global implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 41:1821–1827
Meng XZ, Yu L, Guo Y, Mai BX, Zeng EY (2008) Congener-specific distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish of China: implication for input sources. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:67–72
Mueller KE, Mueller-Spitz SR, Henry HF, Vonderheide AP, Soman RS, Kinkle BK, Shann JR (2006) Fate of pentabrominated diphenyl ethers in soil: abiotic sorption, plant uptake, and the impact of interspecific plant interactions. Environ Sci Technol 40:6662–6667
Nam JJ, Gustafsson O, Kurt-Karakus P, Breivik K, Steinnes E, Jones KC (2008) Relationships between organic matter, black carbon and persistent organic pollutants in European background soils: implications for sources and environmental fate. Environ Pollut 156:809–817
Sellström U, De Wit CA, Lundgren N, Tysklind M (2005) Effect of sewage-sludge application on concentrations of higher-brominated diphenyl ethers in soils and earthworms. Environ Sci Technol 39:9064–9070
Shanghai Municipal Housing Land and Resource Administratic Bureau (2009) Agriculture developing framework of Chongming County, Shanghai. Shanghai Municipal Housing Land and Resource Administratic Bureau, Shanghai, China
Shen M, Yu YJ, Zheng GJ, Yu HX, Lam PKS, Feng JF, Wei ZB (2006) Polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface sediments from the Yangtze River Delta. Mar Pollut Bull 52:1299–1304
Singer AC, Smith D, Jury WA, Hathuc K, Crowley DE (2003) Impact of the plant rhizosphere and augmentation on remediation of polychlorinated biphenyl contaminated soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1998–2004
Söderström G, Sellström U, De Wit CA, Tysklind M (2004) Photolytic debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209). Environ Sci Technol 38:127–132
UNEP (2009) Governments unite to step-up reduction on global DDT reliance and add nine new chemicals under international treaty. United Nations Environment Programme, Geneva
Vonderheide AP, Mueller-Spitz SR, Meija J, Welsh GL, Mueller KE, Kinkle BK, Shann JR, Caruso JA (2006) Rapid breakdown of brominated flame retardants by soil microorganisms. J Anal At Spectrom 21:1232–1239
Wang DL, Cai ZW, Jiang GB, Leung A, Wong MH, Wong WK (2005) Determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soil and sediment from an electronic waste recycling facility. Chemosphere 60:810–816
Wang P, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Wang T, Li X, Li Y, Ding L, Jiang G (2009) Altitude dependence of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in surface soil from Tibetan Plateau, China. Chemosphere 76:1498–1504
Wania F, McLachlan MS (2001) Estimating the influence of forests on the overall fate of semivolatile organic compounds using a multimedia fate model. Environ Sci Technol 35: 582–590
Xian QM, Ramu K, Isobe T, Sudaryanto A, Liu XH, Gao ZS, Takahashi S, Yu HX, Tanabe S (2008) Levels and body distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in freshwater fishes from the Yangtze River, China. Chemosphere 71:268–276
Yogui GT, Sericano JL (2009) Polybrominated diphenyl ether flame retardants in the US marine environment: a review. Environ Int 35:655–666
Yun SH, Addink R, McCabe JM, Ostaszewski A, Mackenzie-Taylor D, Taylor AB, Kannan K (2008) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polybrominated biphenyls in sediment and floodplain soils of the Saginaw River watershed, Michigan, USA. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55:1–10
Zou MY, Ran Y, Gong J, Maw BX, Zeng EY (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in watershed soils of the Pearl River Delta, China: occurrence, inventory, and fate. Environ Sci Technol 41:8262–8267
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40901251), the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology, China (No. 09ZR1433700), the Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse, China (No. PCRRY09001), and International S&T Cooperation Projects from Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2009DFA90740).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ake Bergman
Elementary supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 264 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, YP., Meng, XZ., Yang, C. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in background surface soils from the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), China: occurrence, sources, and inventory. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17, 948–956 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0295-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0295-1