Abstract
Background, aim, and scope
We recently developed a new isolation method for diesel exhaust particles (DEP), involving successive extraction with H2O, sodium bicarbonate, and sodium hydroxide, in which the sodium hydroxide extract was found to consist of phenolic components. Analysis of the extract revealed that vasodilative-active nitrophenols are in DEP in significantly higher concentrations than those estimated by an earlier method involving a combination of solvent extraction and repeated chromatography. These findings indicated that our new procedure offers a simple, efficient, and reliable method for the isolation and identification of bioactive substances in DEP. This encouraged us to extend our work toward investigating new vasodilatory substances in the sodium bicarbonate extract.
Materials and methods
DEP were collected from the exhaust of a 4JB1-type engine (ISUZU Automobile Co., Tokyo, Japan). GC-MS analysis was performed with a GCMS-QP2010 instrument (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan).
Results
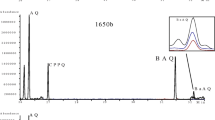
DEP dissolved in 1-butanol was successively extracted with water, sodium bicarbonate, and then aqueous sodium hydroxide. The sodium bicarbonate extract was neutralized and the resulting mixture of acidic components was subjected to reverse-phase (RP) column chromatography followed by RP-HPLC with fractions assayed for vasodilative activity. This led to the identification of terephthalic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, isophthalic acid, phthalic acid, 3-hydroxy-4-nitrobenzoic acid, 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenol, and 1,4,5-naphthalene tricarboxylic acid as components of DEP.
Discussion
The sodium bicarbonate extract was rich in aromatic carboxylic acid components. Repeated reverse-phase chromatography resulted in the successful isolation of several acidic substances including the new vasodilative materials, 4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzoic acid, and 3-hydroxy-4-nitrobenzoic acid.
Conclusions
Our new fractionation method for DEP has made possible the isolation of new vasodilative compounds from the sodium bicarbonate extract.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airborne Particles Expert Group (1999) Source apportionment of airborne particulate matter in the United Kingdom. United Kingdom Department of Environment, Transport and Regions, The Welsh Office, the Scottish Office and the Department of Environment (Northern Ireland) 9–37
Bayona JM, Markides KE, Lee M (1988) Characterization of polar polycyclic aromatic compounds in a heavy-duty diesel exhaust particulate by capillary column gas chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 22:1440–1447
Draper WM (1986) Quantitation of nitro- and dinitropolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in diesel exhaust particulate matter. Chemosphere 15:437–447
Erdinger L, Durr M, Hopker KA (2005) Correlations between mutagenic activity of organic extracts of airborne particulate matter, NO x , and sulphur dioxide in southern Germany—results of a two-year study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12:10–20
Heeb NV, Schmid P, Kohler M, Gujer E, Zennegg M, Wenger D, Wichser A, Ulrich A, Gfeller U, Honegger P, Zeyer K, Emmenegger L, Petermann J-L, Czerwinski J, Mosimann T, Kasper M, Mayer A (2008) Secondary effects of catalytic diesel particulate filters: conversion of PAHs versus formation of nitro-PAHs. Environ Sci Technol 42:3773–3779
Ichinose T, Yajima Y, Nagashima M, Takenoshita S, Nagamachi Y, Sagai M (1997) Lung carcinogenesis and formation of 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine in mice by diesel exhaust particles. Carcinogenesis 18:185–192
Japan Environmental Agency (1998) The research on the total amount of emission and automobile exhaust source unit-the NOX according to object automobile in the usual transit. pp 200–203
McClellan RO (1987) Health effects of exposure to diesel exhaust particles. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 27:279–300
Mestres R (2005) Green chemistry—views and strategies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 12:128–132
Miyabara Y, Ichinose T, Takano H, Lim HB, Sagai M (1998) Effects of diesel exhaust on allergic airway inflammation in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 102:805–812
Mori Y, Kamata K, Toda N, Hayashi H, Seki K, Taneda S, Yoshino S, Sakushima A, Sakata M, Suzuki AK (2003a) Isolation of nitrophenols from diesel exhaust particles (DEP) as vasodilatation compounds. Biol Pharm Bull 26:394–395
Mori Y, Taneda S, Kamata K, Sakushima A, Hayashi H, Suzuki AK, Sakata M, Yoshino S, Sagai M, Seki K (2003c) Identification of phenanthrene and related compounds in diesel exhaust particles by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Environ Sci 10:187–192
Mori Y, Taneda S, Kamata K, Sakushima A, Hayashi H, Suzuki AK, Sakata M, Yoshino S, Sagai M, Seki K (2003d) Identification of alkyldibenzothiophenes in diesel exhaust particles by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Environ Sci 10:157–164
Mori Y, Taneda S, Sakushima A, Hayashi H, Kamata K, Suzuki AK, Sakata M, Yoshino S, Sagai M, Seki K (2003b) Isolation and characterization of hydroxyphthalate derivatives in diesel exhaust particles. Environ Sci 10:51–54
Morville S, Scheyer A, Mirabel P, Millet M (2006) Spatial and geographical variations of urban, suburban and rural atmospheric concentrations of phenols and nitrophenols. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:83–89
Muranaka M, Suzuki S, Koizumi K, Takafuji S, Miyamoto T, Ikemori R, Tokiwa H (1986) Adjuvant activity of diesel-exhaust particulates for the production of IgE antibody in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 77:616–623
Noya Y, Mikami Y, Taneda S, Mori Y, Suzuki A, Ohkura K, Yamaki K, Yoshino S, Seki K-I (2008) Improvement of a facile and efficient separation method for chemicals in diesel exhaust particles: analysis of the contents of nitrophenols. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:318–321
Ona LF, Melinda A, Alberto P, Prudente JA, Sigua GC (2006) Levels of lead in urban soils from selected cities in a central region of the Philippines. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:177–183
Petroleum Energy Center Japan (1999) Workshop report with the European experts. PEC-1998TA37:112–115
Sagai M, Furuyama A, Ichinose T (1996) Biological effects of diesel exhaust particles (DEP). III. Pathogenesis of asthma like symptoms in mice. Free Radical Biol Med 21:199–209
Schuetzle D (1983) Sampling of vehicle emissions for chemical analysis and biological testing. Environ Health Persp 47:65–80
Schuetzle D, Lewtas J (1986) Bioassay-directed chemical analysis in environmental research. Anal Chem 58:1060A–1075A
Seidel B, Alm M, Peters R, Kordell W, Schaffer A (2006) Safety evaluation for a biodiesel process using prion-contaminated animal fat as a source. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:125–130
Takafuji S, Suzuki S, Koizumi K, Tadokoro K, Miyamoto T, Ikemori R, Muranaka M (1987) Diesel-exhaust particulates inoculated by the intranasal route have an adjuvant activity for IgE production in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 79:639–645
Taneda S, Kamata K, Hayashi H, Toda N, Seki K, Sakushima A, Yoshino S, Yamaki K, Sakata M, Mori Y, Suzuki AK (2004a) Investigation of vasodilatory substances in diesel exhaust particles (DEP) Isolation and identification of nitrophenol derivatives. J Health Sci 50:133–141
Taneda S, Mori Y, Akiy S, Kamata K, Hayashi H, Seki K, Sakata M, Yoshino S, Yamaki K, Sagai M, Suzuki AK (2004b) Separation and characterization of alkyltrimethylbenzene derivatives in diesel exhaust particles (DEP). Environ Sci 11:171–178
Tsukue N, Toda N, Sagai M, Watanabe G, Taya K, Tsubone H, Suzuki AK (2002) Diesel exhaust particulate extract (DEPE)-induced abnormal parturition associated with increased myometrial contractility in C57BL mice. Environ Sci 9:355–367
Tsukue N, Toda N, Tsubone H, Sagai M, Jin WZ, Watanabe G, Taya K, Birumachi J, Suzuki AK (2001) Diesel exhaust (DE) affects the regulation of testicular function in male Fischer 344 rats. J Toxicol Environ Health A 63:115–126
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1999) Analysis of the impacts of control program on motor vehicle toxics emissions and exposure in urban areas and nationwide EPA420-R-99-029:120
Watanabe N, Oonuki Y (1999) Inhalation of diesel engine exhaust affects spermatogenesis in growing male rats. Environ Health Persp 107:539–544
Yoshida S, Sagai M, Oshio S, Umeda T, Ihara T, Sugamata M, Sugawara I, Takeda K (1999) Exposure to diesel exhaust affects the male reproductive system of mice. Int J Androl 22:307–315
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Basic Research C-17510052). KS gratefully acknowledges Dr. Nagara Tamaki (Hokkaido University) and Dr. Raymond Jeremy Hugh Davies (Emeritus professor, Queens University Belfast) for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seki, Ki., Noya, Y., Mikami, Y. et al. Isolation and identification of new vasodilative substances in diesel exhaust particles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17, 717–723 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0207-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0207-4