Abstract
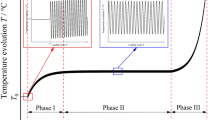
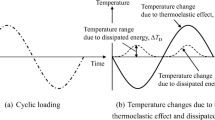
This paper presents an experimental device developed to detect and estimate dissipated energy during very high cycle fatigue tests (VHCF) at high loading frequency (20 kHz) and low stress (i.e. far below the yield stress). Intrinsic dissipation is computed using local expressions of the heat diffusion equation and thermal data fields provided by an infrared focal plane array camera. The results obtained from tests performed on pure copper specimens show that dissipated energy exists whatever the attainable stress range and show that the dissipated energy rate is not constant throughout the test. Both findings are respectively incompatible with the concepts of fatigue limit based on elastic shakedown or on stabilized cyclic state associated with the mechanical hysteresis loop (viscoplastic shakedown).













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathias C (1999) There is no infinite fatigue life in metallic materials. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 22(7):559–565
Pyttel B, Schwerdt D, Berger C (2011) Very high cycle fatigue—Is there a fatigue limit? Int J Fatigue 33(1):49–58
Bathias C, Drouillac L, Le François P (2001) How and why the fatigue S-N curve does not approach a horizontal asymptote. Int J Fatigue 23(1):143–151
Stanzl-Tschegg S (2013) Very high cycle fatigue measuring techniques. Int J Fatigue. doi:10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2012.11.016
Ebara R (2006) The present situation and future problems in ultrasonic fatigue testing - Mainly reviewed on environmental effects and materials’ screening. Int J Fatigue 28(11):1465–1470
Laird HM (1995) Frequency effects on cyclic plastic strain of polycrystalline copper under variable loading. Mater Sci Eng A 194(2):137–145
Morrissey RJ, Golden PJ (2007) Fatigue strength of a single crystal in the gigacycle regime. Int J Fatigue 29(9–11):2079–2084
Morrissey RJ, McDowell DL, Nicholas T (1999) Frequency and stress ratio effects in high cycle fatigue of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Fatigue 21(7):679–685
Fatemi A, Yang L (1998) Cumulative fatigue damage and life prediction theories: a survey of the state of the art for homogeneous materials. Int J Fatigue 20(1):9–34
Ozaltun H, Shen M-H, George T, Cross C (2011) An energy based fatigue life prediction framework for in-service structural components. Exp Mech 51(5):707–718
Kim J, Jeong H-Y (2010) A study on the hysteresis, surface temperature change and fatigue life of SM490A, SM490A-weld and FC250 metal materials. Int J Fatigue 32(7):1159–1166
Li H, Nishimura A, Nagasaka T, Muroga T (2007) Fatigue life and cyclic softening behavior of JLF-1 steel. Fusion Eng Des 82(15–24):2595–2600
Amiri M, Khonsari M (2010) Rapid determination of fatigue failure based on temperature evolution: fully reversed bending load. Int J Fatigue 32(2):382–389
Doudard C, Calloch S, Cugy P, Galtier A, Hild F (2005) A probabilistic two-scale model for high cycle fatigue life predictions. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 28:279–288
Ezanno A, Doudard C, Calloch S, Millot T, Heuzé J-L (2010) Fast characterization of high-cycle fatigue properties of a cast copper-aluminum alloy by self-heating measurements under cyclic loadings. Procedia Eng 2(1):967–976
Krapez J-C, Pacou D (2002) Thermography detection of early thermal effects during fatigue tests of steel and aluminum samples. Am Inst Phys Conf Proc 615(1):1545–1552
La Rosa G, Risitano A (2000) Thermographic methodology for rapid determination of the fatigue limit of materials and mechanical components. Int J Fatigue 22(1):65–73
Le Saux V, Marco Y, Calloch S, Doudard C, Charrier P (2010) An energetic criterion for the fatigue of rubbers: an approach based on a heat build-up protocol and μ-tomography measurements. Procedia Eng 2(1):949–958
Poncelet M, Doudard C, Calloch S, Weber B, Hild F (2010) Probabilistic multiscale models and measurements of self-heating under multiaxial high cycle fatigue. J Mech Phys Solids 58:578–593
Luong MP (1998) Fatigue limit evaluation of metals using an infrared thermographic technique. Mech Mater 28(1–4):155–163
Luong MP (1995) Infrared thermographic scanning of fatigue in metals. Nucl Eng Des 158(2–3):363–376
Galtier A, Bouaziz O, Lambert A (2002) Influence de la microstructure des aciers sur leur propriétés. Méc Ind 3(5):457–462
Mason W (1950) Piezoelectric crystals and their application to ultrasonics. Van Nostrand, New York
Bathias C (2006) Piezoelectric fatigue testing machines and devices. Int J Fatigue 28(11):1438–1445
Bathias C, Paris P, Dekker M (eds) (2004) Gigacycle fatigue in mechanical practice. CRC Press, Boca Ranton
Papadopoulos IV, Panoskaltsis VP (1996) Invariant formulation of a gradient dependant multiaxial high-cycle fatigue criterion. Eng Fract Mech 55(4):513–528
Stanzl-Tschegg S, Mughrabi H, Schoenbauer B (2007) Life time and cyclic slip of copper in the VHCF regime. Int J Fatigue 29(9–11):2050–2059
Phung NL (2012) Fatigue sous très faibles amplitudes de contrainte : Analyse des mécanismes précurseurs de l’amorçage de fissure dans le cuivre polycristallin. PhD Thesis, ENSAM Paris
Honorat V, Moreau S, Muracciole J, Wattrisse B, Chrysochoos A (2005) Calorimetric analysis of polymer behaviour using a pixel calibration of an IRFPA camera. Quant InfraRed Thermography J 2:153–171
Germain P, Nguyen QS, Suquet P (1983) Continuum Thermomechanics. J Appl Mech Trans ASME 50(4B):1010–1020
Berthel B, Chrysochoos A, Wattrisse B, Galtier A (2008) Infrared image processing for the calorimetric analysis of fatigue phenomena. Exp Mech 48:79–90
Boulanger T, Chrysochoos A, Mabru C, Galtier A (2004) Calorimetric analysis of dissipative and thermoelastic effects associated with the fatigue behavior of steels. Int J Fatigue 26(3):221–229
Chrysochoos A, Louche H (2000) An infrared image processing to analyse the calorific effects accompanying strain localisation. Int J Eng Sci 38(16):1759–1788
Mareau C, Favier V, Weber B, Galtier A (2009) Influence of the free surface and the mean stress on the heat dissipation in steels under cyclic loading. Int J Fatigue 31(8–9):1407–1412
Doudard C, Calloch S, Hild F, Roux S (2010) Identification of heat source fields from infra-red thermography: determination of ‘self-heating’ in a dual-phase steel by using a dog bone sample. Mech Mater 42:55–62
Wang C, Blanche A, Wagner D, Chrysochoos A, Bathias C (2014) Dissipative and microstructural effects associated with fatigue crack initiation on an Armco iron. Int J Fatigue 58:152–157
Chrysochoos A, Huon V, Jourdan F, Muracciole J-M, Peyroux R, Wattrisse B (2010) Use of full-field digital image correlation and infrared thermography measurements for the thermomechanical analysis of material behaviour. Strain 46(1):117–130
Connesson N, Maquin F, Pierron F (2011) Dissipated energy measurements as a marker of microstructural evolution: 316L and DP600. Acta Mater 59(10):4100–4115
Berthel B, Wattrisse B, Chrysochoos A, Galtier A (2007) Thermographic analysis of fatigue dissipation properties of steel sheets. Strain 43(3):273–279
Morabito A, Chrysochoos A, Dattoma V, Galietti U (2007) Analysis of heat sources accompanying the fatigue of 2024 T3 aluminium alloys. Int J Fatigue 29(5):977–984
Mareau C, Favier V, Weber B, Galtier A, Berveiller M (2012) Micromechanical modeling of the interactions between the microstructure and the dissipative deformation mechanisms in steels under cyclic loading. Int J Plast 32–33:106–120
Munier R (2012) Etude de la fatigue des aciers laminés à partir de l’auto-échauffement sous sollicitation cyclique: Essais, observations, modélisation et influence d’une pré-déformation plastique. PhD thesis, Université de Bretagne Occidentale
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Agence Nationale de la Recherche France ANR-09-BLAN-0025-01 for its financial support in the framework of the ANR project DISFAT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanche, A., Chrysochoos, A., Ranc, N. et al. Dissipation Assessments During Dynamic Very High Cycle Fatigue Tests. Exp Mech 55, 699–709 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-014-9857-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-014-9857-3