Abstract
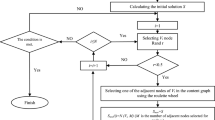
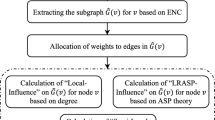
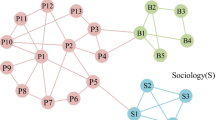
In this paper, we address the problem of community detection in social networks. We present two maximum cost spanning tree-based community detection methods, namely P-SPAT and K-SPAT, for social networks. Communities are defined as dense subgraphs present in social networks. However, detecting communities in a social network can still be a challenging task, in terms of computational overheads and accuracy of the detected communities. Therefore, finding communities from a social network is considered to be an interesting problem. Again, due to practical applications of community detection techniques, it is a key area of research in social network analysis and is also well studied. Experimental results show that these methods can detect highly accurate communities faster than the state-of-the-art community detection techniques.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palla G, Derenyi I, Farkas I, Vicsek T (2005) Uncovering the overlapping community structure of complex networks in nature and society. Nature 435(7043):814–818
Radicchi F, Castellano C, Cecconi F, Loreto V, Parisi D (2004) Defining and identifying communities in networks. PNAS 101(9):2658–2663
Girvan M, Newman MEJ (2002) Community structure in social and biological networks. PNAS 99(12):7821–7826
Blondel VD, Guillaume JL, Lambiotte R, Mech ELJS (2008) Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J Stat Mech 70(6):P10008
Clauset A, Newman MEJ, Moore C (2004) Finding community structure in very large networks. Phys Rev E 70:066111
Basuchowdhuri P, Anand S, Srivastava DR, Mishra K, Saha SK (2014) Detection of communities in social networks using spanning tree. In: Kundu MK, Mohapatra DP, Konar A, Chakraborty A (eds) Advanced computing, networking and informatics-vol 2, vol 28. Springer International Publishing, pp 589–597
Leskovec J, Kleinberg J, Faloutsos C (2005) Graphs over time: densification laws, shrinking diameters and possible explanations. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery in Data Mining, KDD ’05, pp 177–187
Kim D-H, Jeong H (2004) Scale-free spanning trees of complex networks. In: Journal of the Korean Physical Society, pp 624–627, Daejeon, Mar 2004
Chiang Z, Liu M, Lam H, Poor V (2013) Why steiner-tree type algorithms work for community detection. In: 16th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS) Scottsdale, AZ, USA
Newman MEJ (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Nat Acad Sci 103(23):8577–8582
Lancichinetti A, Fortunato S (2009) Community detection algorithms: a comparative analysis. Phys Rev E 80:056117
Dunn G, Everitt B (1982) An introduction to mathematical taxonomy. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Paul W (1971) Holland and Samuel Leinhardt. Transitivity in structural models of small groups. Small Group Res 2(2):107–124
Prim RC (1957) Shortest connection networks and some generalizations. Bell Syst Tech J 36(6):1389–1401
Cormen TH, Leiserson CE, Rivest RL, Stein C (2009) Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd edn. MIT Press, Cambridge
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M (2009) Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In: International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media (ICWSM), pp 361–362
Zachary Wayne (1977) An information flow model for conflict and fission in small groups. J Anthropol Res 33:452–473
Lusseau D, Newman MEJ (2004) Identifying the role that animals play in their social networks. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B: Biol Sci 271:S477–S481
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basuchowdhuri, P., Roy, R., Anand, S. et al. Spanning tree-based fast community detection methods in social networks. Innovations Syst Softw Eng 11, 177–186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11334-015-0246-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11334-015-0246-6