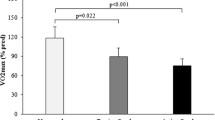
Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of an active lifestyle on the respiratory function in healthy smokers (n=14) and non–smokers (n=14) aged 29–41 years. Respiratory function was measured using a spirometric test yielding the following parameters: FVC (forced vital capacity), VC/IVC (slow vital capacity and ventilatory profile), MVV (maximum voluntary ventilation), FEV1 (volume expired after 1 s). The subjects’ lifestyles were assessed by questionnaire, and answers concerning level of physical activity were translated into a physical activity score using a modification of the Borg scale. Nonsmoking subjects were closer to the theoretical index of FEV1 provided by the spirometer than smoking subjects. Since FEV1 was markedly associated with body weight (r=0.64, p=0.003), analysis of covariance was used to assess the effect of physical activity on FEV1 using body weight as covariate. We found that physical activity was significantly associated with respiratory function (p<0.05), thus indicating that the pulmonary function of individuals who practice sports is better than those who do not. These results support the clinical use of physical training to counteract the harmful effects of smoking on respiratory function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alberti, G., Oliveri, E., Caumo, A. et al. Effect of the practice of constant physical exercise on respiratory parameters in smoking and non–smoking subjects. Sport Sci Health 1, 91–95 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-2005-004-0016-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-2005-004-0016-1