Abstract
Background
Cell phones emit radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation (RF-EMR) that negatively affects the hematological blood profile. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate whether exercise training can exert any protective impacts on hematological parameters in male Wistar rats.
Methods
Twenty-four male Wistar rats (10 weeks old) were randomly assigned to e exposure to RF-EMR (RF-EMR) group, exercise group RF-EMR plus exercise (RF-EMR + Exercise) group, and control group. The rats in the exposure to RF-EMR groups (RF-EMR and RF-EMR + exercise) were exposed to RF-EMR 3 h/day for 28 days. The rats in the exercise groups (exercise and RF-EMR + exercise) were administered to moderate exercise training 6 days a week for 28 days. After 28 days, animals were sacrificed 24 h following the completion of the experiment, and hematological parameters, including complete blood count, were assessed.
Results
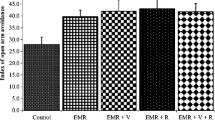
Exposure to RF-EMR induced a significant decrease in RBC, HGB, HCT, MCV, MCH, and MCHC, and an increase in PLT and WBC in compared with the control group (p < 0.05). However, most of the hematological parameters of the RF-EMR + exercise group were similar to the control group (except for PLT) that showed the inhibitory effect of exercise training against the harmful effects of cell phone radiation.
Conclusions
28 day moderate exercise training is beneficial to attenuate the harmful effects of RF-EMR emitted from the cell phone.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamada AJ, Singh A, Agarwal A (2011) Cell phones and their impact on male fertility: fact or fiction. Open Reprod Sci J 5(4):125–137
Tohidi FZ, Fardid R, Arian Rad S, Tohidi M, Bahrayni Toosi MH, Kianosh T (2016) The effect of cellphone radiation on hematological blood cell factors in BALB/C mice. Iran J Med Physi 13(1):58–64
Aziz IA, El-Khozondar HJ, Shabat M, Elwasife K, Mohamed-Osman A (2010) Effect of electromagnetic field on body weight and blood indices in albino rats and the therapeutic action of vitamin C or E. Rom J Biophys 20(3):235–244
Otitoloju A, Osunkalu V, Akogun M, Obe I, Adewale O, OR A, (2011) Stimulation of haemopoetic activity in bone marrow and deformation of red blood cells in albino mice, Mus musculus exposed to radiations from GSM base stations. Sierra Leone J Biomed Res 2(2):127–134
Corra U, Piepoli MF, Carre F, Heuschmann P, Hoffmann U, Verschuren M et al (2010) Secondary prevention through cardiac rehabilitation: physical activity counselling and exercise training: key components of the position paper from the Cardiac Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation. Eur Heart J 31(16):1967–1974
Lippi G, Salvagno GL, Danese E, Tarperi C, Guidi GC, Schena F (2014) Variation of red blood cell distribution width and mean platelet volume after moderate endurance exercise. Adv Hematol 2014:192173
Bobeuf F, Labonté M, Khalil A, Dionne IJ (2009) Effect of resistance training on hematological blood markers in older men and women: a pilot study. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res 2009:156820
Sandor B, Nagy A, Toth A, Rabai M, Mezey B, Csatho A et al (2014) Effects of moderate aerobic exercise training on hemorheological and laboratory parameters in ischemic heart disease patients. PLoS One 9(10):e110751
Oyewopo A, Olaniyi S, Oyewopo C, Jimoh A (2017) Radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation from cell phone causes defective testicular function in male Wistar rats. Andrologia 49:e12772
Salim S, Sarraj N, Taneja M, Saha K, Tejada-Simon MV, Chugh G (2010) Moderate treadmill exercise prevents oxidative stress-induced anxiety-like behavior in rats. Behav Brain Res 208(2):545–552
Nemzek JA, Bolgos GL, Williams BA, Remick DG (2001) Differences in normal values for murine white blood cell counts and other hematological parameters based on sampling site. Inflamm Res 50(10):523–527
Ragan HA, Buschbom RL, Pipes MJ, Phillips RD, Kaune WT (1983) Hematologic and serum chemistry studies in rats exposed to 60-Hz electric fields. Bioelectromagnetics 4(1):79–90
El-Bediwi AB, Saad M, El-kott AF, Eid E (2013) Influence of electromagnetic radiation produced by mobile phone on some biophysical blood properties in rats. Cell Biochem Biophys 65(3):297–300
Osbakken M, Griffith J, Taczanowsky P (1986) A gross morphologic, histologic, hematologic, and blood chemistry study of adult and neonatal mice chronically exposed to high magnetic fields. Magn Reson Med 3(4):502–517
Szygula Z (1990) Erythrocytic system under the influence of physical exercise and training. Sports Med 10(3):181–197
Pasricha SR, Low M, Thompson J, Farrell A, De-Regil LM (2014) Iron supplementation benefits physical performance in women of reproductive age: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr 144(6):906–914
Wardyn GG, Rennard SI, Brusnahan SK, McGuire TR, Carlson ML, Smith LM et al (2008) Effects of exercise on hematological parameters, circulating side population cells, and cytokines. Exp Hematol 36(2):216–223
Fujitsuka S, Koike Y, Isozaki A, Nomura Y (2005) Effect of 12 weeks of strenuous physical training on hematological changes. Mil Med 170(7):590–594
Yeh SH, Chuang H, Lin LW, Hsiao CY, Eng HL (2006) Regular tai chi chuan exercise enhances functional mobility and CD4CD25 regulatory T cells. Br J Sports Med 40(3):239–243
Mohanty J, Nagababu E (2014) Rifkind JMJFip. Red blood cell oxidative stress impairs oxygen delivery and induces red blood cell aging 5:84
Waggiallah H, Alzohairy M (2011) The effect of oxidative stress on human red cells glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase level, and prevalence of anemia among diabetics. N. Am J Med Sci 3(7):344
Gomez-Cabrera M-C, Domenech E, Viña J (2008) Moderate exercise is an antioxidant: upregulation of antioxidant genes by training. Free Radic Biol Med 44(2):126–131
Broberg CS, Bax BE, Okonko DO, Rampling MW, Bayne S, Harries C et al (2006) Blood viscosity and its relationship to iron deficiency, symptoms, and exercise capacity in adults with cyanotic congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 48(2):356–365
Haines AP, Howarth D, North WR, Goldenberg E, Stirling Y, Meade TW et al (1983) Haemostatic variables and the outcome of myocardial infarction. Thromb Haemost 50(4):800–803
Danesh J, Collins R, Peto R, Lowe GD (2000) Haematocrit, viscosity, erythrocyte sedimentation rate: meta-analyses of prospective studies of coronary heart disease. Eur Heart J 21(7):515–520
Furuncuoglu Y, Tulgar S, Dogan AN, Cakar S, Tulgar YK, Cakiroglu B (2016) How obesity affects the neutrophil/lymphocyte and platelet/lymphocyte ratio, systemic immune-inflammatory index and platelet indices: a retrospective study. Eur Review Med Pharmacol Sci 20(7):1300–1306
Funding
No funding was awarded to support this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted (Animal Care and Ethics Committee of Sport Sciences Research Institute of Iran, IR.SSRI.REC.1397.376).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbari, H.A., Gaeini, A.A. & Choobineh, S. Moderate exercise training reduced the harmful effects of electromagnetic radiation emitted from a cell phone on hematological parameters in male Wistar rats. Sport Sci Health 16, 267–272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-019-00600-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-019-00600-x