Abstract
Background
Apoptosis is one of the indications of programmed cell death (PCD) and is known as a physiological event in multicellular organisms. This study was designed to determine the effect of aerobic training alongside vitamin D supplementation on lung cell apoptosis in male rats exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
Methods
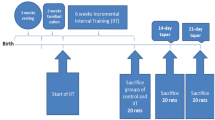
48 male rats were assigned into six groups: H2O2, (H); H2O2 + D3, (HD); H2O2 + training, (HE); H2O2 + D3 + E, (HDE); dimethyl sulfoxide, (DMSO) and control intact. 1 mmol/kg of H2O2 was injected three times per week. The exercising rats performed the program on a rodent’s treadmill for 8 weeks, 5 days a week. The HD and HDE groups received a daily dose of 0.5 µg for 8 weeks. The lung tissue was exposed and stored at − 80. Then, the RT-PCR method was employed to examine the gene expressions of BAX, BCL2, Caspase-3 and Bcl-2/Bax ratios.
Results
Results indicated that training, as well as a combination of training and vitamin D had a significant effect on BAX, BCL2 and Bel2/Bax ratio in case of H2O2 toxicity. The training and vitamin D groups both had no significant effect on Caspase-3 gene expression.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this research, it can be concluded that regular aerobic training alongside consumption of D3 might result in significant alteration of the genes involved in apoptosis caused by H2O2 presence in lung tissues.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fedirko V, Bostick RM, Flanders WD, Long Q, Shaukat A, Rutherford RE, Daniel CR, Cohen V, Dash C (2009) Effects of vitamin D and calcium supplementation on markers of apoptosis in normal colon mucosa: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Cancer Prev Res 2(3):213–23
Savill J, Hogg N, Ren Y, Haslett C (1992) Thrombospondin cooperates with CD36 and the vitronectin receptor in macrophage recognition of neutrophils undergoing apoptosis. J Clin Investig 90:1513–1522
Lu Q, Harrington EO, Rounds S (2005) Apoptosis and lung injury. Keio J Med 54:184–189
Magi B, Bargagli E, Bini L, Rottoli P (2006) Proteome analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage in lung diseases. Proteomics 6:6354–6369
De Torre C, Ying SX, Munson PJ, Meduri GU, Suffredini AF (2006) Proteomic analysis of inflammatory biomarkers in bronchoalveolar lavage. Proteomics 6:3949–3957
Bargagli E, Olivieri C, Bennett D, Prasse A, Muller-Quernheim J, Rottoli P (2009) Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diffuse lung diseases: a review. Respir Med 103:1245–1256
Ye Q, Dalavanga Y, Poulakis N, Sixt SU, Guzman J, Costabel U (2008) Decreased expression of heme oxygenase-1 by alveolar macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J 31(5):1030–6
Sato T, Takeno M, Honma K, Yamauchi H, Saito Y, Sasaki T, Morikubo H, Nagashima Y, Takagi S, Yamanaka K (2006) Heme oxygenase-1, a potential biomarker of chronic silicosis, attenuates silica-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174:906–914
Hatao H, Oh-ishi S, Itoh M, Leeuwenburgh C, Ohno H, Ookawara T, Kishi K, Yagyu H, Nakamura H, Matsuoka T (2006) Effects of acute exercise on lung antioxidant enzymes in young and old rats. Mech Ageing Dev 127:384–390
Aldini G, Yeum K-J, Niki E, Russell RM. Biomarkers for antioxidant defense and oxidative damage: principles and practical applications. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Gönenç A, Tokgöz D, Aslan S, Torun M (2005) Oxidative stress in relation to lipid profiles in different stages of breast cancer. Indian J Biochem Biophys 42(3):190–4
Franco R, Sánchez-Olea R, Reyes-Reyes EM, Panayiotidis MI (2009) Environmental toxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis: menage a trois. Mutat Res 674:3–22
Uhal B (2008) The role of apoptosis in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev 17:138–144
Weinmann M, Jendrossek V, Handrick R, Güner D, Goecke B, Belka C (2004) Molecular ordering of hypoxia-induced apoptosis: critical involvement of the mitochondrial death pathway in a FADD/caspase-8 independent manner. Oncogene 23:3757
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Krüger K, Mooren FC (2014) Exercise-induced leukocyte apoptosis. Exerc Immunol Rev 20:117–134
Youle RJ, Strasser A (2008) The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:47
Wei MC, Zong W-X, Cheng EH-Y, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ (2001) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292:727–730
Polidoro L, Properzi G, Marampon F, Gravina G, Festuccia C, Di Cesare E, Scarsella L, Ciccarelli C, Zani B, Ferri C (2013) Vitamin D protects human endothelial cells from H2O2 oxidant injury through the Mek/Erk-Sirt1 axis activation. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 6:221–231
Tashkin DP, Celli B, Senn S, Burkhart D, Kesten S, Menjoge S, Decramer M (2008) A 4-year trial of tiotropium in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 359:1543–1554
Kuepper T, Morrison A, Gieseler U, Schoeffl V (2009) Sport climbing with pre-existing cardio-pulmonary medical conditions. Int J Sports Med 30:395–402
Powers S, Nelson WB, Larson-Meyer E (2011) Antioxidant and vitamin D supplements for athletes: sense or nonsense? J Sports Sci 29(Suppl 1):S47–S55
Quadrilatero J, Alway SE, Dupont-Versteegden EE (2011) Skeletal muscle apoptotic response to physical activity: potential mechanisms for protection. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 36:608–617
Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, Nieman DC, Swain DP (2011) American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1334–1359
Li SF, Liu HX, Zhang YB, Yan YC, Li YP (2010) The protective effects of alpha-ketoacids against oxidative stress on rat spermatozoa in vitro. Asian J Androl 12:247–256
Makino A, Skelton MM, Zou AP, Cowley AW Jr (2003) Increased renal medullary H2O2 leads to hypertension. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979) 42:25–30
Husain K, Hazelrigg SR (2002) Oxidative injury due to chronic nitric oxide synthase inhibition in rat: effect of regular exercise on the heart. Biochimica et biophysica Acta 1587:75–82
Halder SK, Sharan C, Al-Hendy A (2012) 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 treatment shrinks uterine leiomyoma tumors in the Eker rat model. Biol Reprod 86:116
Plant DR, Gregorevic P, Warmington SA, Williams DA, Lynch GS (2003) Endurance training adaptations modulate the redox-force relationship of rat isolated slow-twitch skeletal muscles. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:77–81
Wong ML, Medrano JF (2005) Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation. Biotechniques 39:75
Weiner P, Berar-Yanay N, Davidovich A, Magadle R, Weiner M (2000) Specific inspiratory muscle training in patients with mild asthma with high consumption of inhaled beta(2)-agonists. Chest 117:722–727
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24:R453–R462
Wattenberg B, Lithgow T (2001) Targeting of C-terminal (tail)-anchored proteins: understanding how cytoplasmic activities are anchored to intracellular membranes. Traffic (Copenhagen Denmark); 2:66–71
McArdle WD, Katch FI, Katch VL. Exercise physiology: nutrition, energy, and human performance. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Fernandes T, Magalhães FdC, ECd C, Oliveira EMd (2012) Aerobic exercise training inhibits skeletal muscular apoptotic signaling mediated by VEGF-VEGR2 in spontaneously hypertesive rats. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte 18:412–418
Phaneuf S, Leeuwenburgh C (2001) Apoptosis and exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:393–396
Siu PM, Bryner RW, Martyn JK, Alway SE (2004) Apoptotic adaptations from exercise training in skeletal and cardiac muscles. FASEB J 18:1150–1152
Allon N, Amir A, Manisterski E, Rabinovitz I, Dachir S, Kadar T (2009) Inhalation exposure to sulfur mustard in the guinea pig model: clinical, biochemical and histopathological characterization of respiratory injuries. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 241:154–162
Islam T, Gauderman WJ, Berhane K, McConnell R, Avol E, Peters JM, Gilliland FD (2007) Relationship between air pollution, lung function and asthma in adolescents. Thorax 62:957–963
Bagci E, Vodovotz Y, Billiar T, Ermentrout G, Bahar I (2006) Bistability in apoptosis: roles of Bax, Bcl-2, and mitochondrial permeability transition pores. Biophys J 90:1546–1559
Skommer J, Wlodkowic D, Deptala A (2007) Larger than life: mitochondria and the Bcl-2 family. Leuk Res 31:277–286
Hildeman DA, Mitchell T, Aronow B, Wojciechowski S, Kappler J, Marrack P (2003) Control of Bcl-2 expression by reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:15035–15040
Ahmad D, Bakairy AK, Katheri AM, Tamimi W (2015) MDM2 (RS769412) G> a polymorphism in cigarette smokers: a clue for the susceptibility to smoking and lung cancer risk. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16:4057–4060
Packer N, Pervaiz N, Hoffman-Goetz L (2010) Does exercise protect from cognitive decline by altering brain cytokine and apoptotic protein levels? A systematic review of the literature. Exerc Immunol Rev 16:138–162
Fisher G, Schwartz DD, Quindry JC, Barberio MD, Foster EB, Jones KW, Pascoe DD (2010) Lymphocyte enzymatic antioxidant responses to oxidative stress following high-intensity interval exercise. Am J Physiol-Heart Circul Physiol 110:730–737
Pope CA, Burnett RT, Thun MJ, Calle EE, Krewski D, Ito K, Thurston GD (2002) Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 287:1132–1141
Hoffman-Goetz L, Pervaiz N, Guan J (2009) Voluntary exercise training in mice increases the expression of antioxidant enzymes and decreases the expression of TNF-α in intestinal lymphocytes. Brain Behav Immun 23:498–506
Quadrilatero J, Bombardier E, Norris SM, Talanian JL, Palmer MS, Logan HM, Tupling AR, Heigenhauser GJ, Spriet LL (2009) Prolonged moderate-intensity aerobic exercise does not alter apoptotic signaling and DNA fragmentation in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 298:E534–E547
Adams JM, Cory S (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322–1326
Salakou S, Kardamakis D, Tsamandas AC, Zolota V, Apostolakis E, Tzelepi V, Papathanasopoulos P, Bonikos DS, Papapetropoulos T, Petsas T (2007) Increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio up-regulates caspase-3 and increases apoptosis in the thymus of patients with myasthenia gravis. In vivo 21:123–132
Jacobson MD, Raff MC (1995) Programmed cell death and Bcl-2 protection in very low oxygen. Nature 374:814
Zadeh-Vakili A, Tehrani FR, Daneshpour MS, Zarkesh M, Saadat N, Azizi F (2013) Genetic polymorphism of vitamin D receptor gene affects the phenotype of PCOS. Gene 515:193–196
Zhu S, Li M, Figueroa BE, Liu A, Stavrovskaya IG, Pasinelli P, Beal MF, Brown RH, Kristal BS, Ferrante RJ (2004) Prophylactic creatine administration mediates neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia in mice. J Neurosci 24:5909–5912
Deminice R, Rosa FT, Franco GS, Jordao AA, de Freitas EC (2013) Effects of creatine supplementation on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers after repeated-sprint exercise in humans. Nutrition 29:1127–1132
Marfe G, Manzi V, Tafani M, Pucci B, Gambacurta A, Russo M, Sinibaldi Salimei P (2012) The modulation of sirtuins and apoptotic proteins in rats after exhaustive exercise. Open J Mol Integr Physiol 2:65–74
Umegaki K, Higuchi M, Inoue K, Esashi T (1998) Influence of one bout of intensive running on lymphocyte micronucleus frequencies in endurance-trained and untrained men. Int J Sports Med 19:581–585
Thompson D, Williams C, McGregor SJ, Nicholas CW, McArdle F, Jackson MJ, Powell JR (2001) Prolonged vitamin C supplementation and recovery from demanding exercise. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 11:466–481
Gomez-Cabrera M-C, Domenech E, Romagnoli M, Arduini A, Borras C, Pallardo FV, Sastre J, Vina J (2008) Oral administration of vitamin C decreases muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and hampers training-induced adaptations in endurance performance. Am J Clin Nutr 87:142–149
Wadley GD, McConell GK (2010) High-dose antioxidant vitamin C supplementation does not prevent acute exercise-induced increases in markers of skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in rats. J Appl Physiol 108:1719–1726
Simon-Schnass I, Pabst H (1988) Influence of vitamin E on physical performance. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 58:49–54
Gomes E, Allgrove J, Florida-James G, Stone V (2011) Effect of vitamin supplementation on lung injury and running performance in a hot, humid, and ozone-polluted environment. Scand J Med Sci Sports 21:e452–e460
Sumida S, Tanaka K, Kitao H, Nakadomo F (1989) Exercise-induced lipid peroxidation and leakage of enzymes before and after vitamin E supplementation. Int J Biochem 21:835–838
Buzina R, Suboticanec K (1985) Vitamin C and physical working capacity. Int J Vitam Nutr Res Suppl 27:157–166
Close GL, Ashton T, Cable T, Doran D, Holloway C, McArdle F, MacLaren DP (2006) Ascorbic acid supplementation does not attenuate post-exercise muscle soreness following muscle-damaging exercise but may delay the recovery process. Br J Nutr 95:976–981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramezani, S., Peeri, M., Azarbayjani, M.A. et al. Administration of vitamin D and aerobic training: recovery of lung apoptosis markers in male rats exposed to hydrogen peroxide. Sport Sci Health 15, 569–576 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-019-00546-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-019-00546-0